Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2025; 31(27): 106166
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.106166
Published online Jul 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.106166
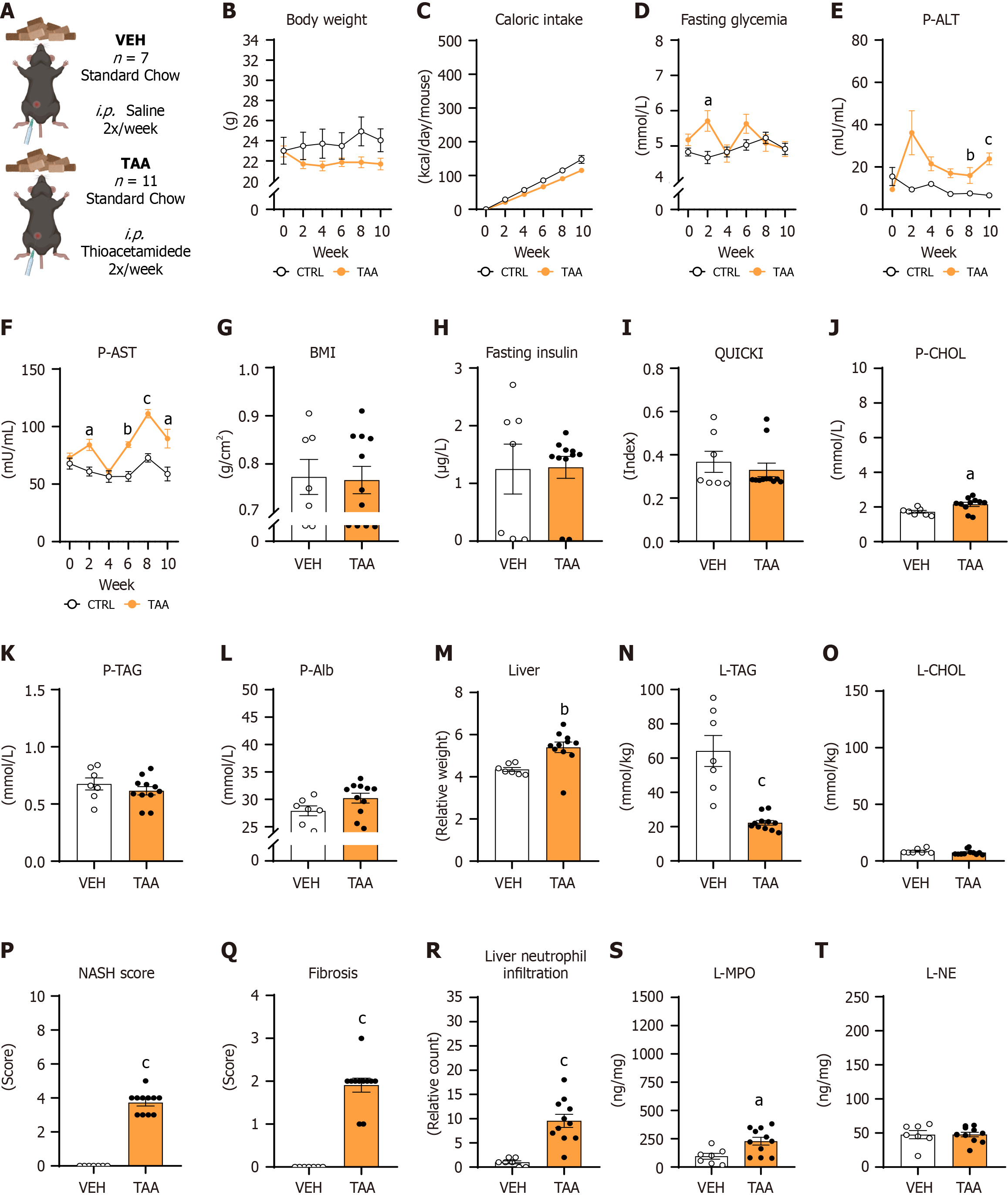
Figure 2 Liver damage-associated and metabolic parameters for the thioacetamide-induced model.
A: Experimental design; B: Dynamics of body weight; C: Dynamics of cumulative caloric intake; D: Dynamics of fasting glycemia; E: Dynamics of plasma alanine aminotransferase activity; F: Dynamics of plasma aspartate aminotransferase activity; G: Body mass index; H: Concentration of fasting insulin; I: Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index; J: Concentration of cholesterol; K: Concentrations of triacylglycerols; L: Concentrations of albumin; M: Relative liver weight; N: Concentrations of liver triacylglycerides; O: Concentrations of liver cholesterol; P: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis score; Q: Fibrotic score; R: Neutrophil infiltration into the liver; S: Concentration of myeloperoxidase in the liver; T: Concentration of neutrophil elastase in the liver. Data shown in G-T are after 10 weeks of the thioacetamide-induced model. Data are presented as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001; B-F: Repeated two-way analysis of variance and Bonferroni post-hoc test; G-T: Independent Student’s t-test. VEH: Control group of females (n = 7); TAA: Experimental liver fibrosis group of females (n = 11).
- Citation: Feješ A, Belvončíková P, Bečka E, Strečanský T, Pastorek M, Janko J, Filová B, Babál P, Šebeková K, Borbélyová V, Gardlík R. Myeloperoxidase, extracellular DNA and neutrophil extracellular trap formation in the animal models of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(27): 106166
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i27/106166.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i27.106166