Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2025; 31(26): 108662
Published online Jul 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i26.108662
Published online Jul 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i26.108662
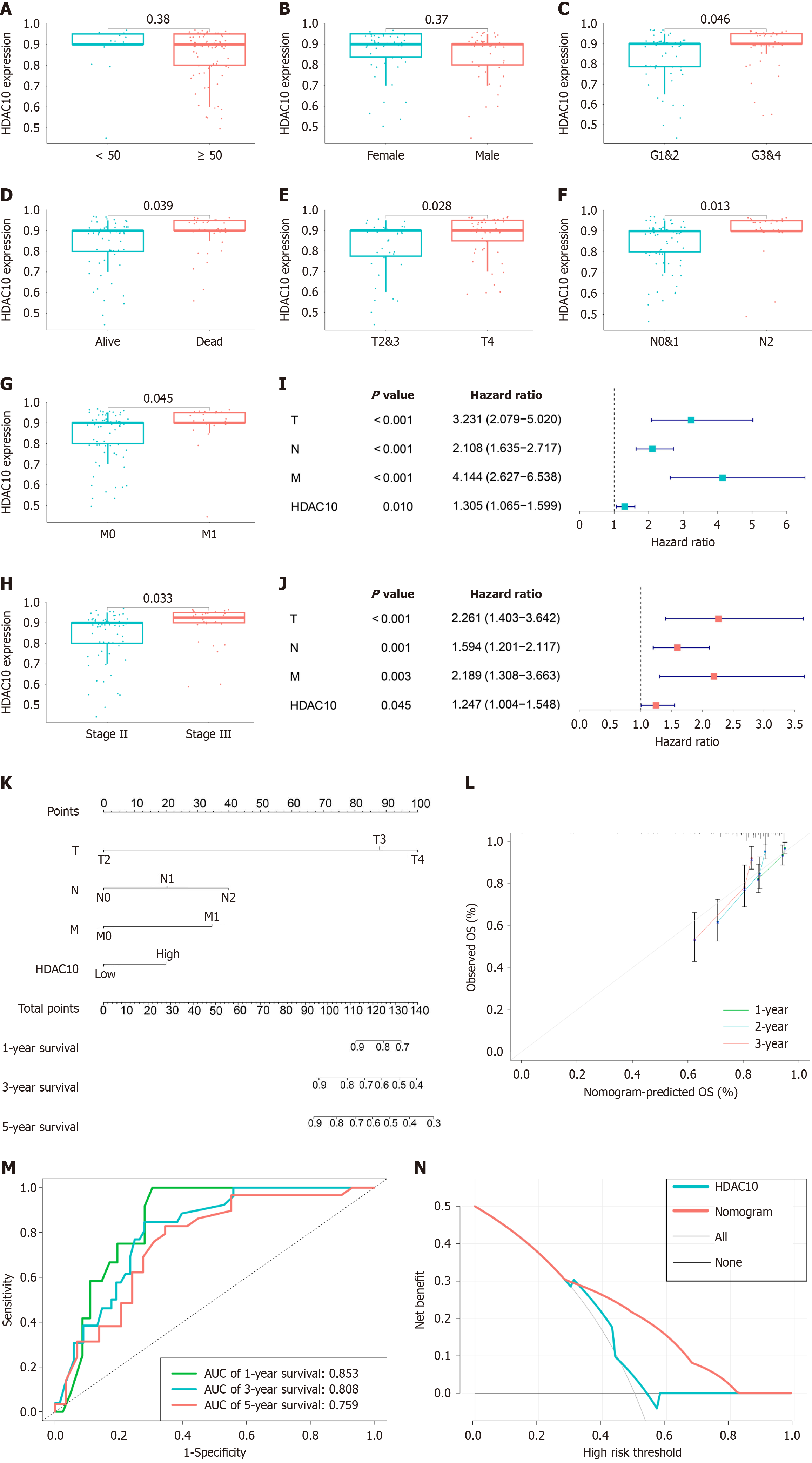
Figure 2 Histone deacetylases 10 was associated with clinicopathological characteristics and nomogram model construction.
A: Differential analysis for histone deacetylases 10 (HDAC10) expression in patients with different age; B: Gender; C: High HDAC10 expression in high grade; D: Status; E: High levels of HDAC10 in advanced T stage; F: High HDAC10 expression in advanced N stage; G: High HDAC10 expression in advanced M stage; H: High levels of HDAC10 in advanced pathologic stage; I and J: Univariate Cox and multivariate Cox regression analysis for clinical factors and HDAC10 expression with overall survival (OS). Hazard ratio > 1 represented risk factors for survival and hazard ratio < 1 represented protective factors; K: Nomogram for predicting the 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS from CRC tissue microarray; L: Calibration curves for predicting 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS; M: Receiver operating characteristic curve for predicting 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS; N: Decision curve analysis based on nomogram better determine survival than only HDAC10. OS: Overall survival; HDAC10: Histone deacetylases 10; AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Nie HH, Yang XY, Zhou JK, Gao GL, Ding L, Hong YT, Yu YL, Qiu PS, Zeng ZY, Lai J, Zheng T, Wang HZ, Zhao Q, Wang F. Histone deacetylases 10 as a prognostic biomarker correlates with tumor microenvironment and therapy response in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(26): 108662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i26/108662.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i26.108662