Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2025; 31(26): 107044
Published online Jul 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i26.107044
Published online Jul 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i26.107044
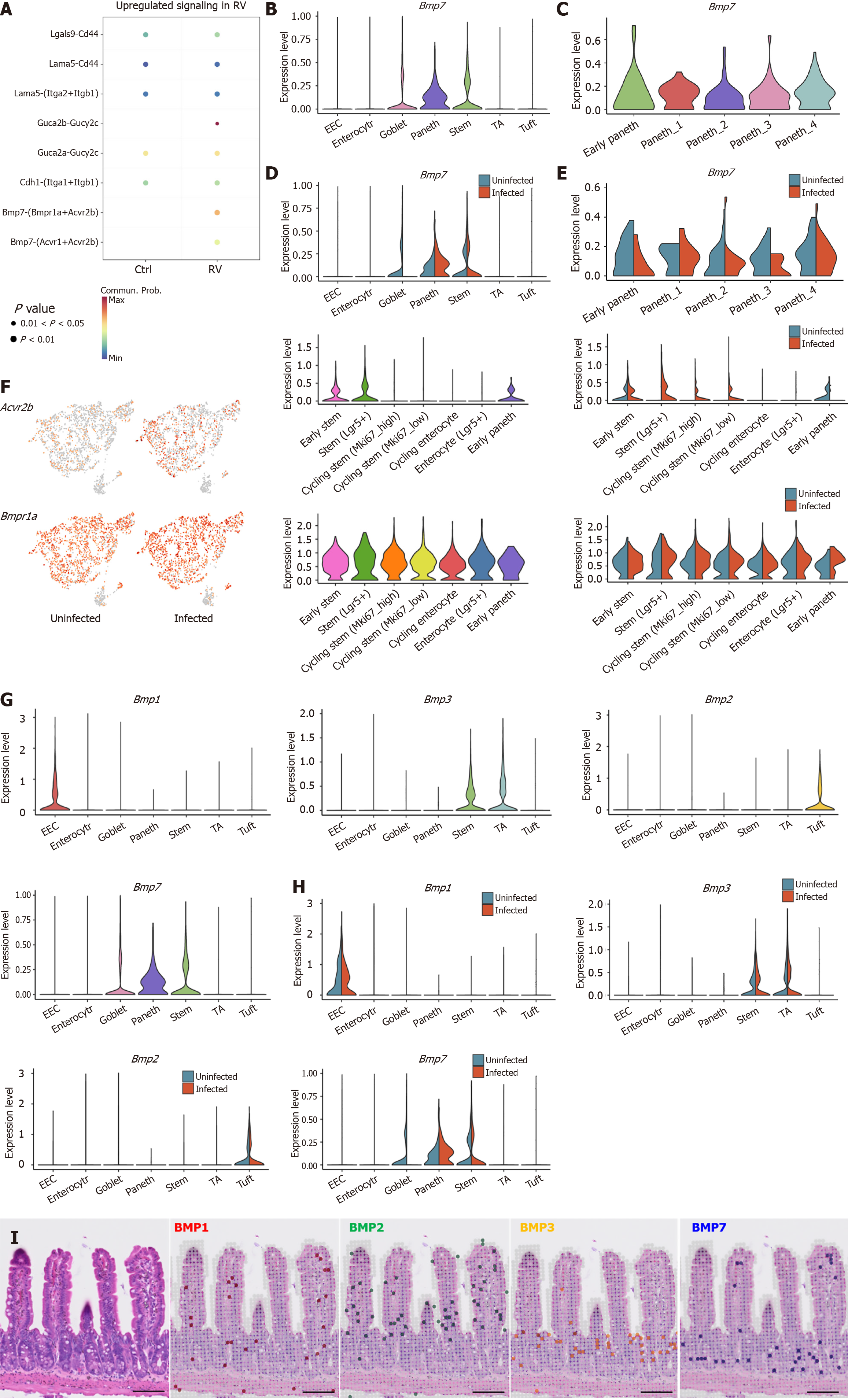
Figure 4 Paneth cells inhibit leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5+ intestinal stem cells proliferation by the bone morphogenic protein 7-activin A receptor type 2B/bone morphogenic protein receptor type 1A pathway.
A: CellChat analysis of Paneth-intestinal stem cells communication reveals upregulation of the bone morphogenic protein 7 (BMP7)-activin A receptor type 2B signaling pathway under rotavirus infection; B: Violin plot of the expression of Bmp7 in Paneth cells; C: Bmp7 expression of subclustered Paneth cells; D and E: Comparison of Bmp7 expression in uninfected and infected Paneth cells; F: Feature plots (left) and violin plots (right) of the expression of activin A receptor type 2B and BMP receptor type 1A pathway of uninfected and infected stem cells; G: The expression patterns of various BMP family members across intestinal epithelial cells subclusters; H: Comparison of BMP expression in uninfected and infected intestinal epithelial cells subclusters; I: Spatial transcriptomic analysis of BMP localization in intestinal epithelial tissue. RV: Rotavirus; BMP: Bone morphogenic protein; EEC: Enteroendocrine cell; TA: Transit-amplifying cells; Acvr2b: Activin A receptor type 2B; Bmpr1a: Bone morphogenic protein receptor type 1A.
- Citation: Bu XY, Tan HY, Wang AM, Wei MT, Pan S, Gao JZ, Li YH, Qian GX, Chen ZH, Ye C, Jia WD. Paneth cells inhibit intestinal stem cell proliferation through the bone morphogenic protein 7 pathway under rotavirus-mediated intestinal injury. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(26): 107044
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i26/107044.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i26.107044