Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2025; 31(25): 107893
Published online Jul 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107893
Published online Jul 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107893
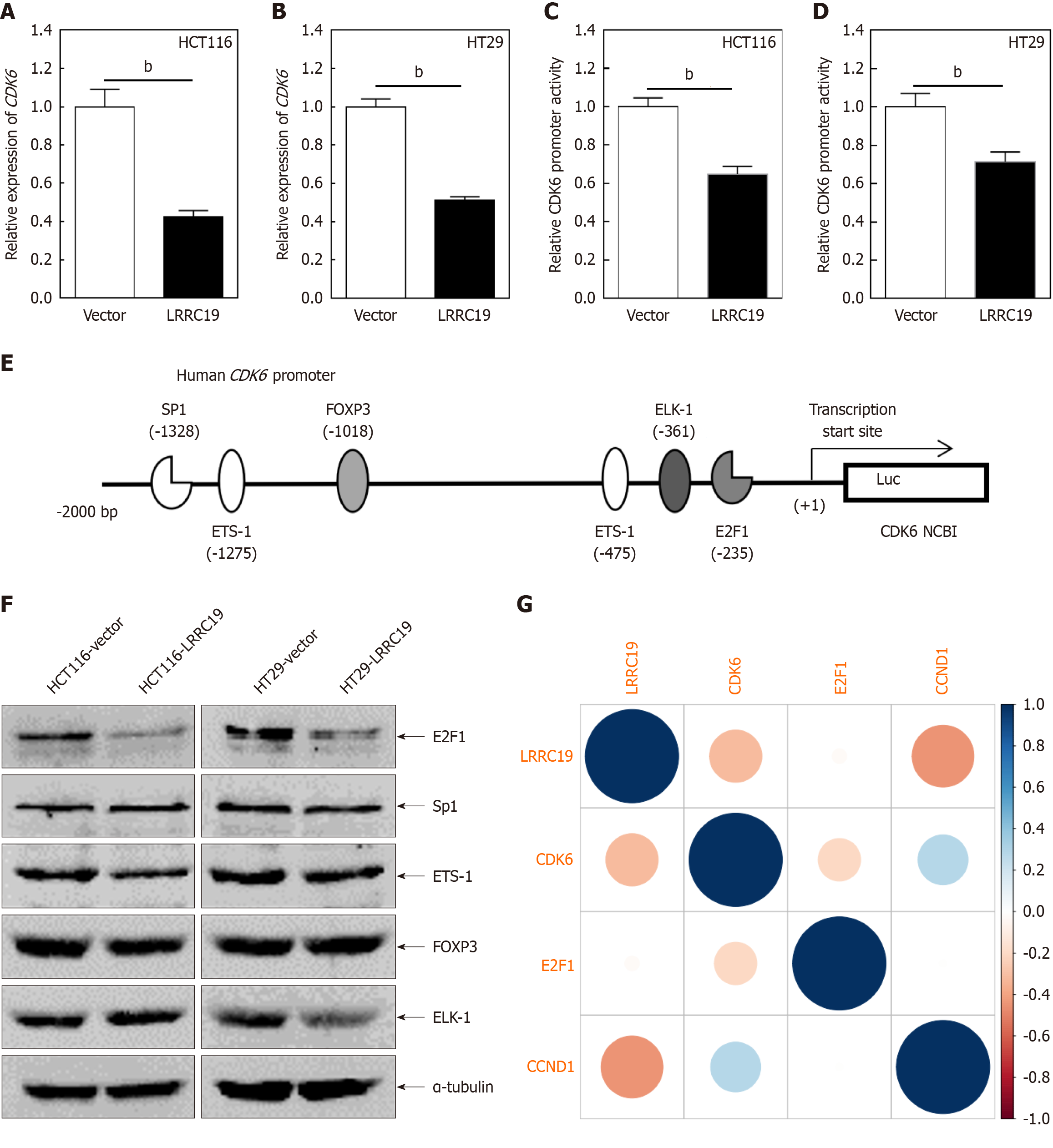
Figure 9 Leucine-rich repeat-containing 19 inhibits colorectal cancer proliferation via transcriptional suppression of E2F1 quantitative PCR analysis of cyclin-dependent kinase 6 mRNA expression levels in leucine-rich repeat-containing 19-overexpressing HCT116 and HT29 cells compared to vector controls.
A and B: Quantitative PCR analysis of cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) mRNA expression levels in leucine-rich repeat-containing 19 (LRRC19)-overexpressing HCT116 and HT29 cells compared to vector controls; C and D: Dual luciferase reporter assays evaluating CDK6 promoter activity; data are shown as the mean ± SD from triplicate experiments; E: Prediction of potential transcription factor binding sites within the CDK6 promoter region (-2000 to +1) using the TRANSFAC 8.3 engine; F: Western blot analysis of transcription factors Sp1, ETS-1, forkhead box P3 (FOXP3), ETS-like 1 (ELK-1), and E2F1; α-tubulin served as loading control; G: Scatter plots depicting correlation analyses between LRRC19 and key cell cycle-associated genes. bP < 0.05.
- Citation: Huang SS, Chen W, Vaishnani DK, Huang LJ, Li JZ, Huang SR, Li YZ, Xie QP. Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 19 suppresses colorectal cancer by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 6/E2F1 and remodeling the immune microenvironment. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(25): 107893
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i25/107893.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107893