Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2025; 31(25): 107893
Published online Jul 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107893
Published online Jul 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107893
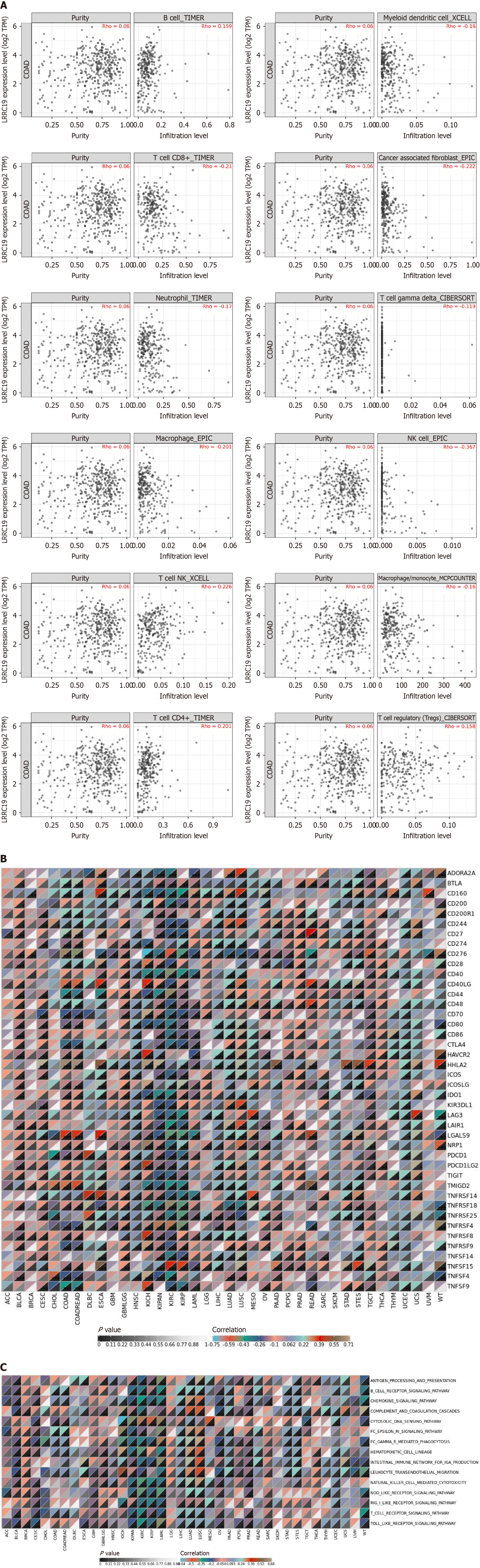
Figure 5 Leucine-rich repeat-containing 19 expression correlates with immune cell infiltration and immune checkpoint genes in colorectal cancer.
A: Leucine-rich repeat-containing 19 (LRRC19) expression correlates with immune cell infiltration levels, showing positive correlations with B cells, T cells/natural killer (NK) cells, and CD4+ T cells, and negative correlations with macrophages, myeloid dendritic cells, γδ T cells, neutrophils, NK cells, and CD8+ T cells. A weak positive correlation is observed with regulatory T cells (Tregs); B: LRRC19 gene correlates significantly with immune checkpoint genes, particularly in colorectal cancer (CRC), showing significant correlations with cluster of differentiation 40 ligand (CD40 LG), galectin-9 (LGALS9), transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing 2 (TMIGD2), CD44, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA4); C: LRRC19 expression correlates with immune-inflammatory pathways, with significant positive correlations in CRC for pathways like B cell receptor signaling, chemokine signaling, and T cell receptor signaling.
- Citation: Huang SS, Chen W, Vaishnani DK, Huang LJ, Li JZ, Huang SR, Li YZ, Xie QP. Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 19 suppresses colorectal cancer by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 6/E2F1 and remodeling the immune microenvironment. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(25): 107893
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i25/107893.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107893