Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2025; 31(25): 107893
Published online Jul 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107893
Published online Jul 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107893
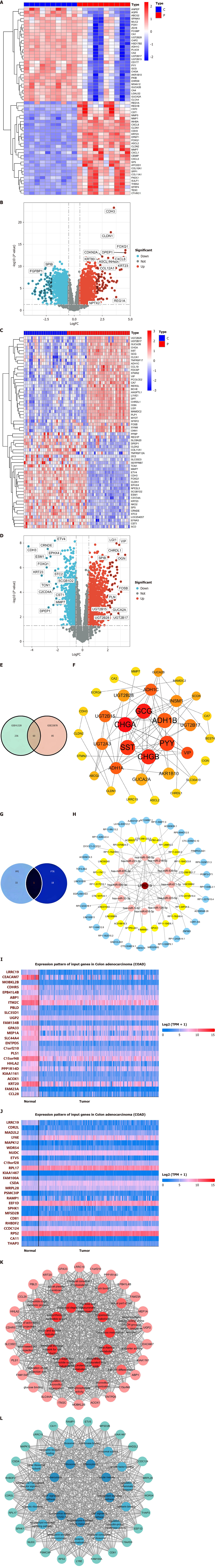
Figure 1 Colorectal cancer differentially expressed gene analysis.
A: Sample gene expression heterogeneity (heatmap); B: Genome-wide expression changes (volcano plot); C: Representative differentially expressed gene (DEG) expression distribution (heatmap); D: DEG statistical significance with key genes; E: Common DEGs between GSE41328 and GSE23878; F: Core gene interactions [streamlined protein-protein interaction (PPI)]; G: Leucine-rich repeat-containing 19 (LRRC19) overlap in transmembrane receptors and PPI network; H: Potential microRNAs/long non-coding RNAs regulating LRRC19; I: LRRC19-positively correlated genes; J: LRRC19-negatively correlated genes; K: Positive correlation gene enrichment [Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)/Gene Ontology (GO)]; L: Negative correlation gene enrichment (KEGG/GO). FTR: Functional transmembrane receptor.
- Citation: Huang SS, Chen W, Vaishnani DK, Huang LJ, Li JZ, Huang SR, Li YZ, Xie QP. Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 19 suppresses colorectal cancer by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 6/E2F1 and remodeling the immune microenvironment. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(25): 107893
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i25/107893.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i25.107893