Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2025; 31(24): 108234
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i24.108234
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i24.108234
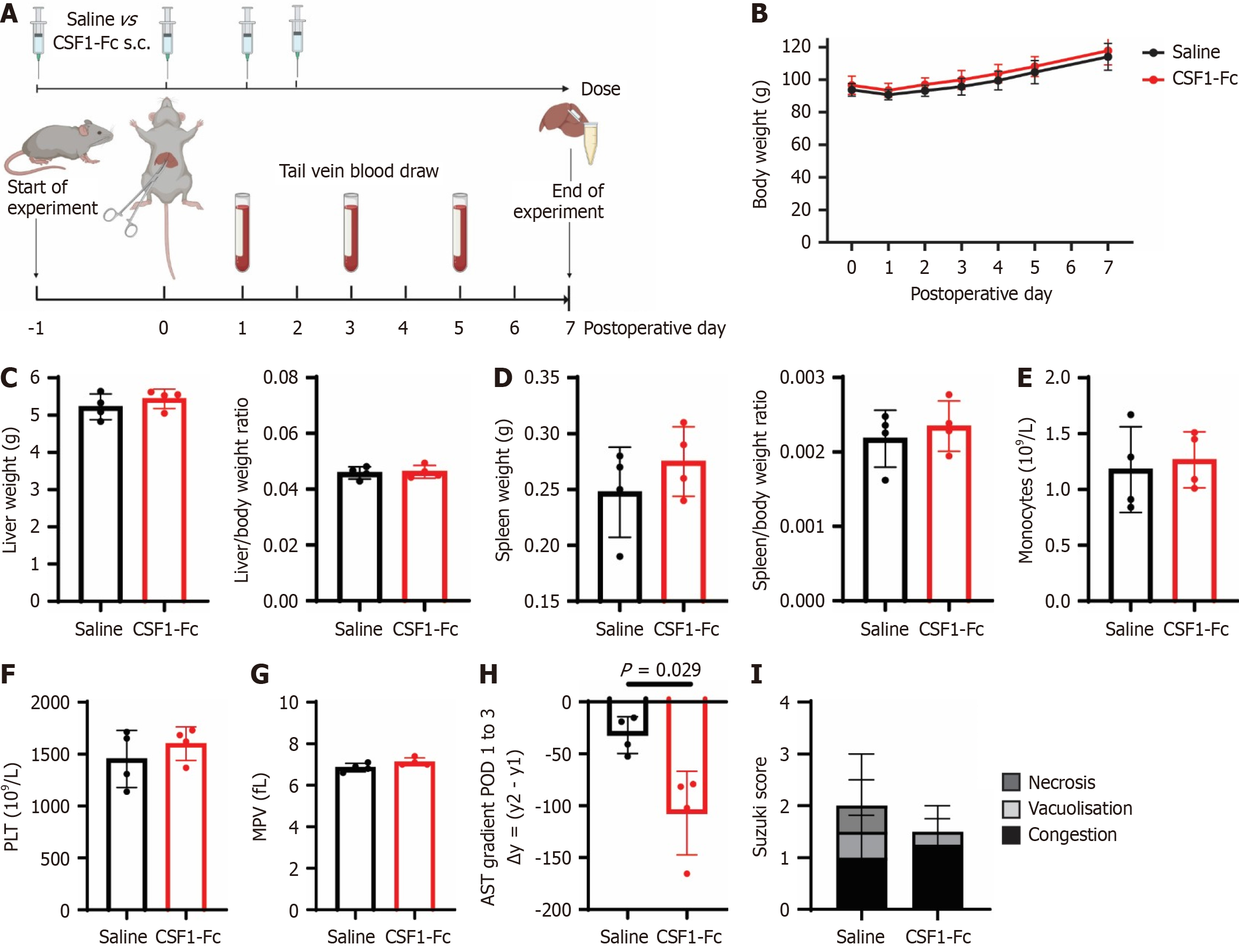
Figure 6 Colony stimulating factor 1-Fc treatment accelerates aspartate aminotransferase decline after ischemia-reperfusion injury.
A: Groups of male rats were subjected to 60 minutes of ischemia, followed by 7 days of reperfusion and treated with 4 × daily doses of 1 mg/kg of colony stimulating factor 1-Fc or saline control at postoperative day (POD) -1, 0, 1 and 2; B-D: Postoperative body weight (B), total liver weight, liver/body weight ratio (C) and total spleen and spleen/body weight ratio (D) were measured; E-G: Monocyte count (E), platelets (F) and mean platelet volume (G) in the peripheral blood were quantified; H: Aspartate aminotransferase gradient between POD 1 to 3; I: Suzuki scores on POD 7. n = 4 for all groups, results were analysed using the Mann Whitney test. Data show mean and standard deviation. Created in BioRender (Supplementary material). s.c.: Subcutaneous; CSF: Colony stimulating factor; PLT: Platelet; MPV: Mean platelet volume.
- Citation: Schulze S, Keshvari S, Miller GC, Bridle KR, Hume DA, Irvine KM. Perisurgical colony stimulating factor one treatment ameliorates liver ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(24): 108234
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i24/108234.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i24.108234