Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2025; 31(24): 108234
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i24.108234
Published online Jun 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i24.108234
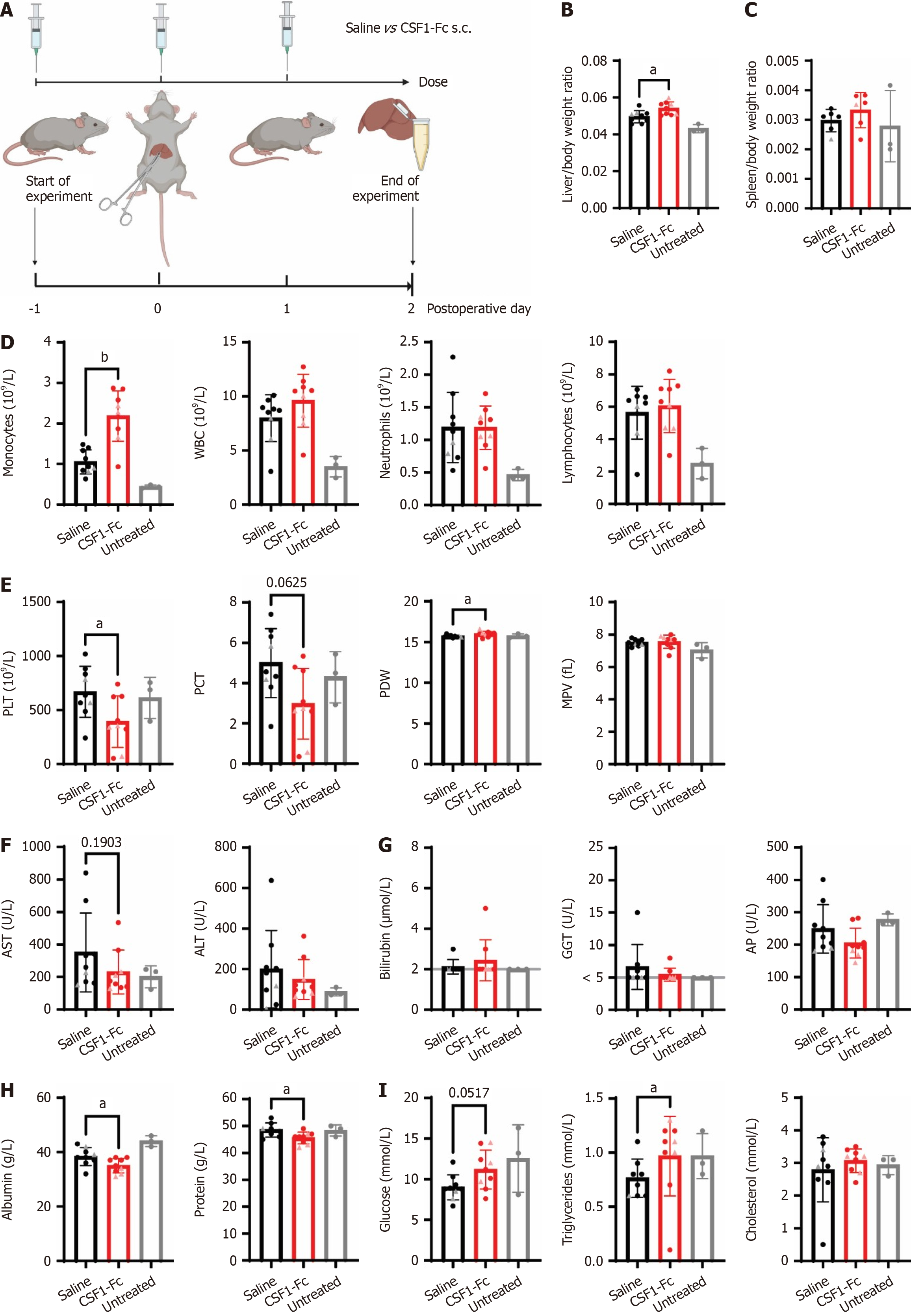
Figure 2 Perisurgical colony stimulating factor 1-Fc treatment increased circulating monocytes and promoted liver growth after ischemia-reperfusion injury.
A: Groups of rats (n = 9/group except spleen weight n = 6/group, females indicated by triangle symbol) were subjected to 60 minutes of ischemia, followed by 48 hours of reperfusion and treated with 3 × daily doses of 1 mg/kg of a human colony stimulating factor (CSF)1-Fc or saline control on postoperative day (POD) -1, 0 and 1; B: Liver/body weight ratio; C: Spleen/body weight ratio; D and E: Blood monocyte, white blood cell, neutrophil and lymphocyte count (D), platelets, plateletcrit, platelet distribution width and mean platelet volume (E) in the peripheral blood quantified using a haematology analyser; F-I: Aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase (F), bilirubin, gamma glutamyl transferase and alkaline phosphatase levels (G), albumin and total protein (H) and glucose, triglycerides and cholesterol (I) were measured in the serum. Data show mean and standard deviation. Data were analysed using the Mann Whitney test for saline vs CSF1-Fc-treated groups. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001. Data from age-matched Dark Agouti rats (n = 3) that had not been subjected to ischemia-reperfusion surgery collected at a different time are shown for reference (grey bars), but not included in statistical analysis. Grey line indicates limit of detection. s.c.: Subcutaneous; WBC: White blood cell; PLT: Platelet; PCT: Plateletcrit; PDW: Platelet distribution width; MPV: Mean platelet volume; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; GGT: Gamma glutamyl transferase; AP: Alkaline phosphatase; CSF: Colony stimulating factor.
- Citation: Schulze S, Keshvari S, Miller GC, Bridle KR, Hume DA, Irvine KM. Perisurgical colony stimulating factor one treatment ameliorates liver ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(24): 108234
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i24/108234.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i24.108234