Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2025; 31(23): 106949
Published online Jun 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.106949
Published online Jun 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.106949
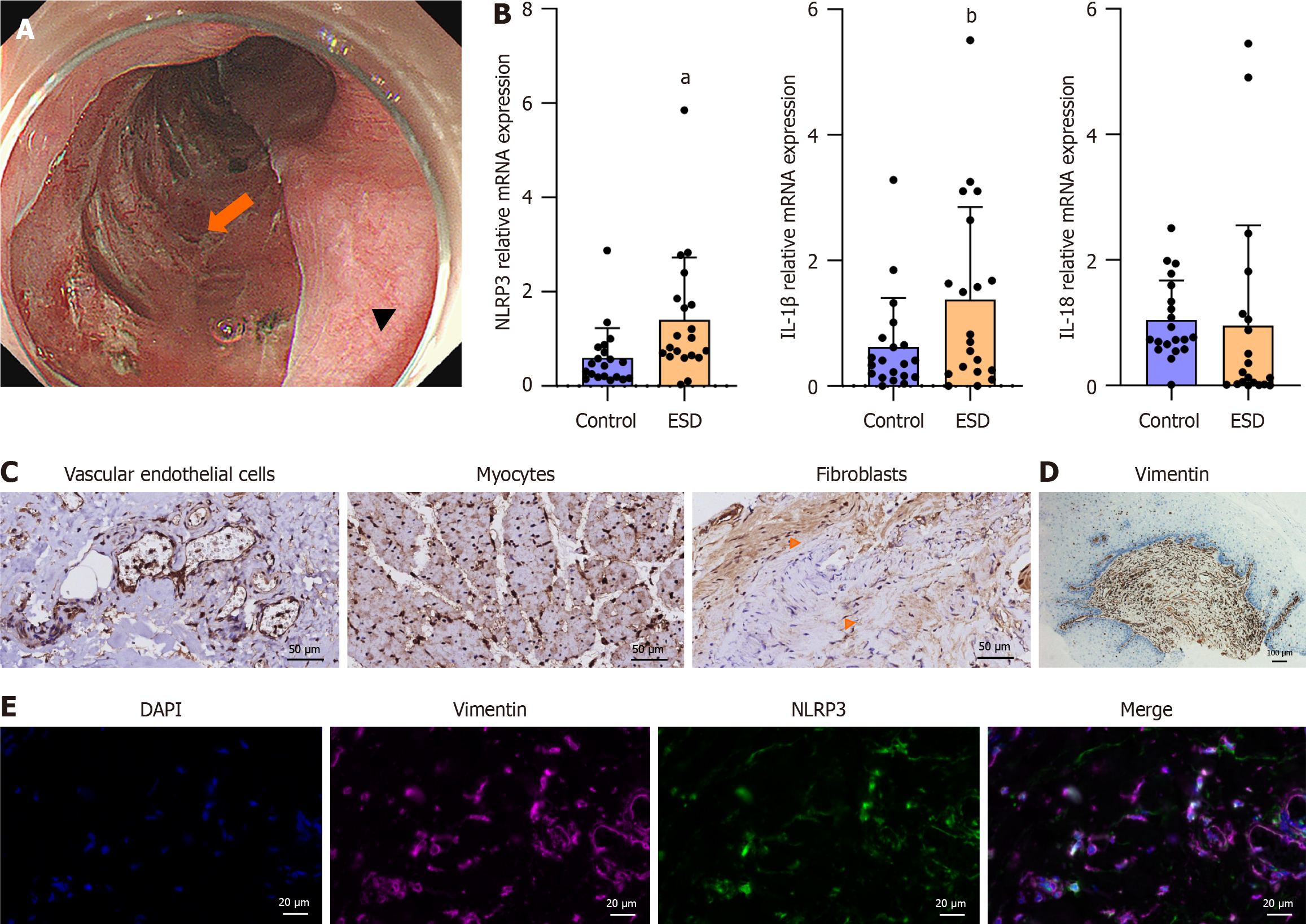
Figure 2 NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 associated inflammatory mediators in the endoscopic submucosal dissection resection bed.
A: Tissue acquisition site in the post-endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) esophagus. Arrowhead: The ESD resection bed; Arrow: The normal esophageal mucosa; B: mRNA levels of NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3), interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-18 (presented as the mean ± SD). Control: Tissues from normal esophageal mucosa; ESD: Tissues from the resection bed. Statistical analysis was performed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, aP = 0.009; bP = 0.02; C: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) of NLRP3 in the post-ESD resection bed: Vascular endothelial cells, myocytes, and fibroblasts (arrows). Scale bar = 50 μm; D: IHC of vimentin in human tissues from post-ESD esophageal stricture. Scale bar = 100 μm; E: Dual labeling for NLRP3 and vimentin was performed in human tissues from the resection bed. Scale bar = 20 μm. ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; IL: Interleukin; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3.
- Citation: Zhang MX, Wu C, Feng XX, Tian W, Zhao NH, Lu PP, Ding Q, Liu M. Celastrol alleviates esophageal stricture in rats by inhibiting NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 activation. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(23): 106949
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i23/106949.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.106949