Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2025; 31(23): 103848
Published online Jun 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.103848
Published online Jun 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.103848
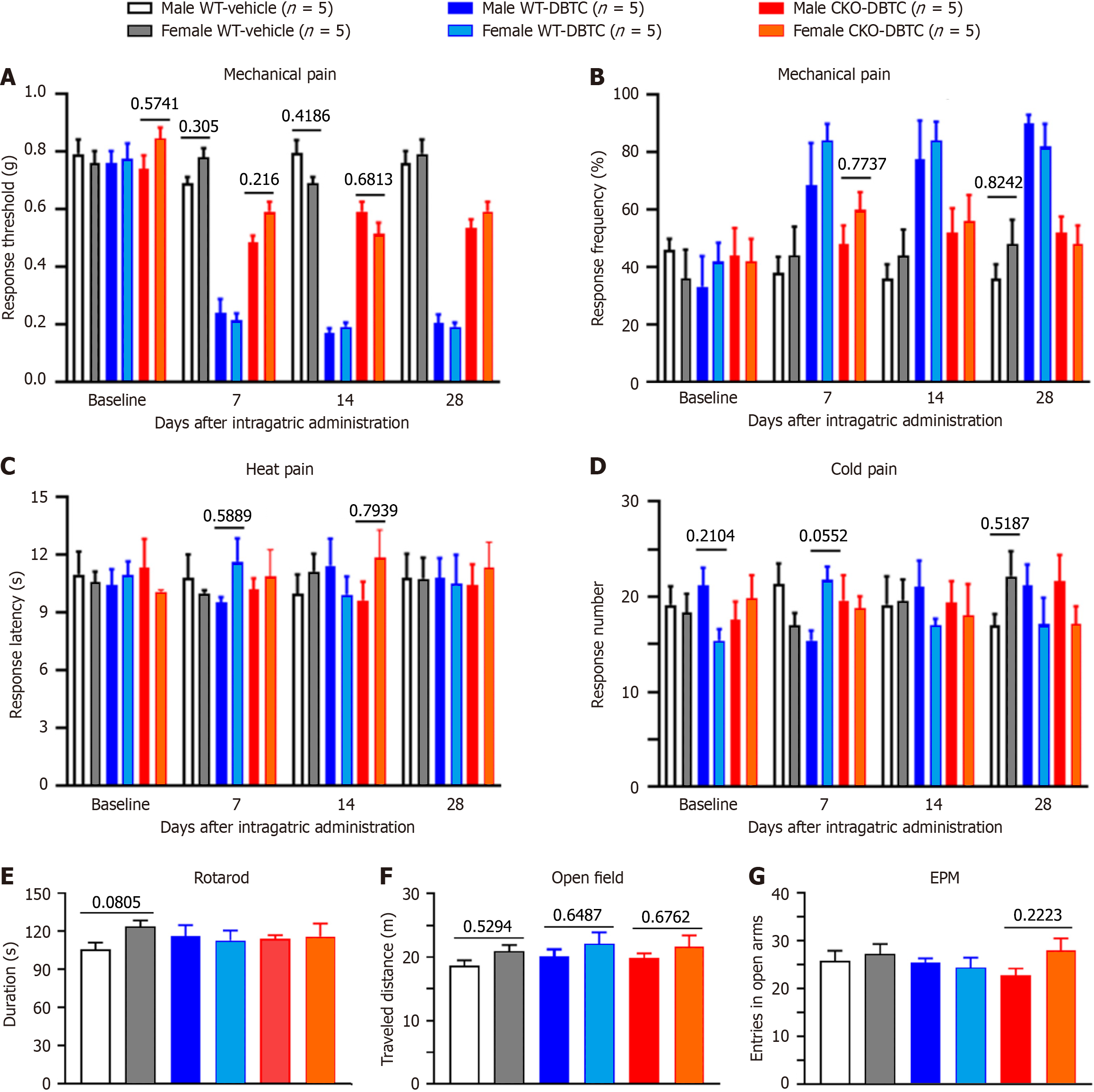
Figure 6 Gender differences in behavioral phenotypes of dibutyltin dichloride -induced chronic pancreatitis model.
A and B: No gender difference was observed in mechanical pain sensitivity in experimental mice before and after chronic pancreatitis (CP); C and D: No gender differences were observed in heat pain sensitivity (C) and cold allodynia (D) in experimental mice before and after CP; E and F: No gender differences were observed in motor function (E) and autonomous activities (F) in experimental mice before and after CP; G: No gender differences were observed in emotional state in experimental mice before and after CP. n = 5 mice. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were conducted with unpaired two-way analysis of variance (A-D) or one-way analysis of variance (E-G) with Sidak’s post hoc test. WT: Wild type; CKO: Conditional knockout; DBTC: Dibutyltin dichloride; EPM: Elevated plus maze.
- Citation: Wang B, Ge JY, Wu JN, Xu JH, Cao XH, Chang N, Zhou X, Jing PB, Liu XJ, Wu Y. Endothelin A receptor in nociceptors is essential for persistent mechanical pain in a chronic pancreatitis of mouse model. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(23): 103848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i23/103848.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i23.103848