Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2025; 31(22): 108815
Published online Jun 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i22.108815
Published online Jun 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i22.108815
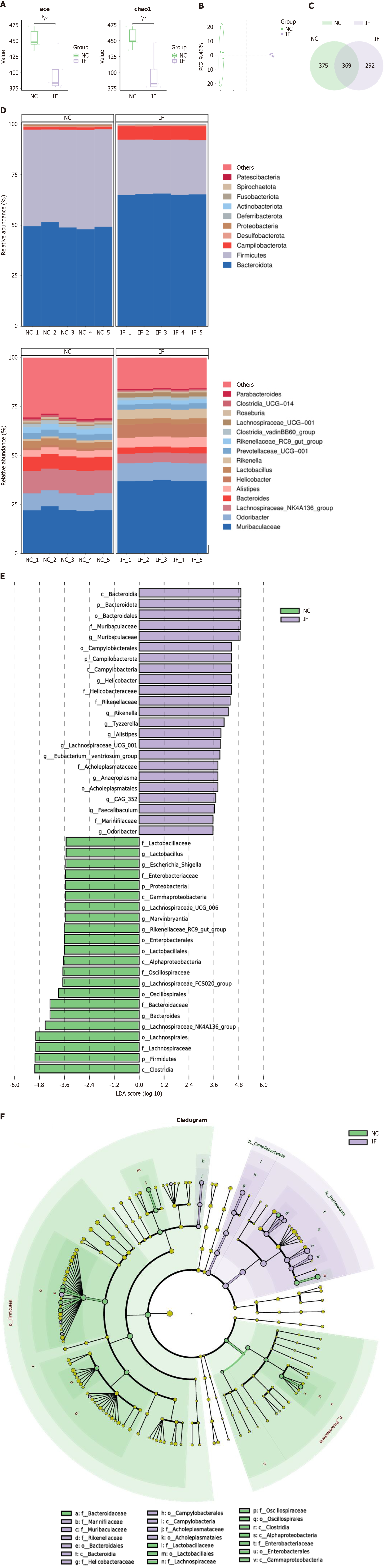
Figure 3 Restrictive diet is associated with gut microbiota dysbiosis.
A: The abundance-based coverage estimator and Chao1 index analysis, found significant differences in α diversity between the two groups; B: Principal component analysis showed significant differences in β diversity observed in the two groups; C: A total number of 369 species in both groups of gut microbiota, of the 375 species endemic to the normal control group, 292 species; D: At the gate level, Firmicutes (Firmicutes) decreased and Cyclospora (Campilobacterota) increased in the intermittent fasting group; At the genus level, the relative abundance of group F species (Rikenella) and murobacteria (Muribaculaceae) increased; E and F: Lefse further analyzed the microbial communities. bP < 0.01. NC: Normal control; IF: Intermittent fasting; PC: Principal component; LDA: Linear discriminant analysis.
- Citation: Fu R, Zhang P, Zhang JW, Hong Y, Chen B, Cao GD. Intermittent fasting exacerbates colon inflammation by promoting Th17 cell differentiation through inhibition of gut microbiota-derived indoleacrylic acid. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(22): 108815
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i22/108815.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i22.108815