Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2025; 31(22): 106937
Published online Jun 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i22.106937
Published online Jun 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i22.106937
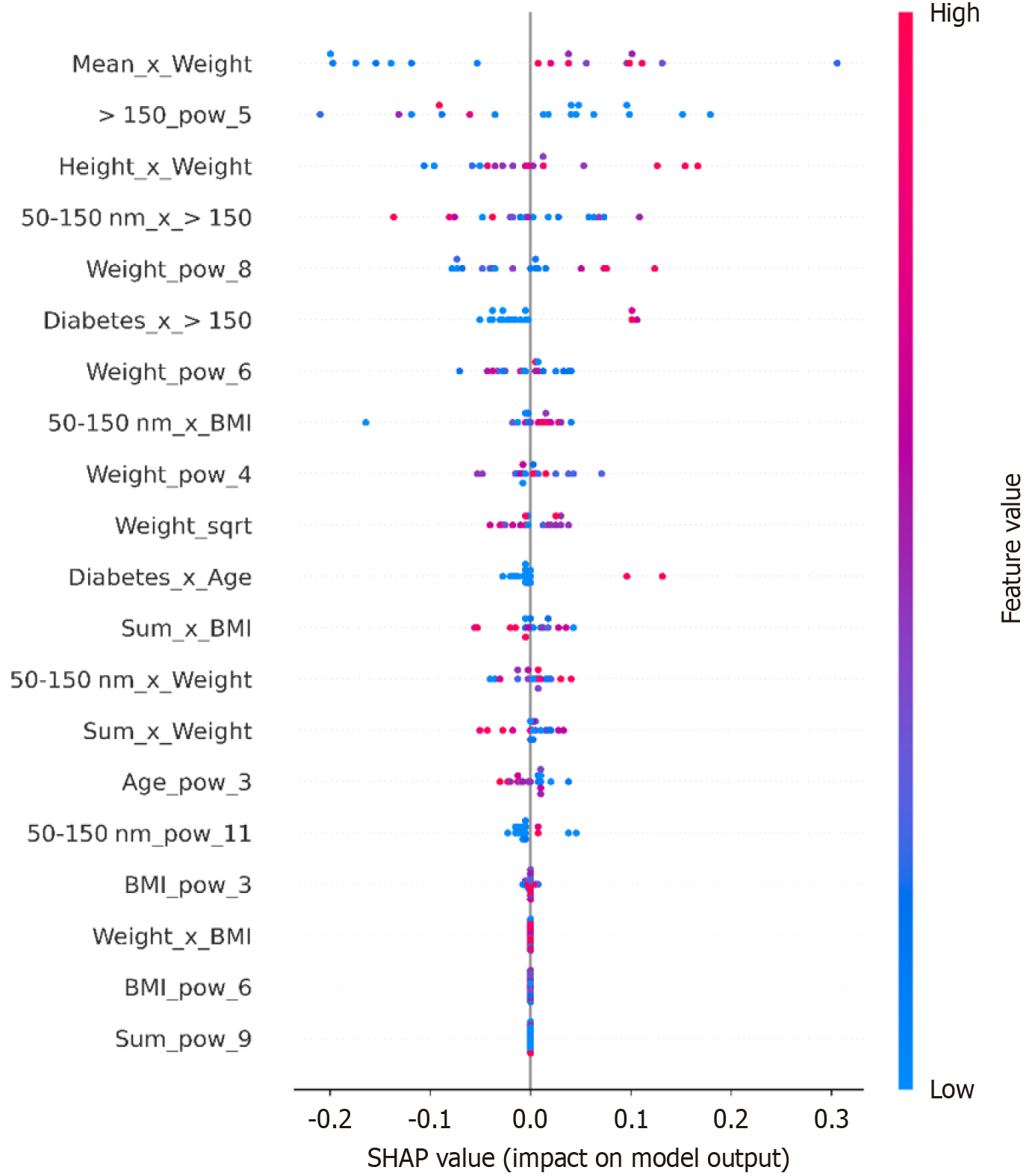
Figure 6 Each dot represents an individual prediction, with the X-axis denoting the SHapley Additive exPlanations value (impact on model output), while the color gradient indicates the feature value (blue for low values, red for high values).
Features such as > 150_pow_5, Height_x_Weight, and Sum_x_BMI also significantly contribute to the predictive capability of the model, showcasing complex interactions between anthropometric, clinical, and extracellular vesicle features. In Supplementary Table 2 we demonstrate the information regarding all the machine learning models of C2 and in Table 3 performances on the CB-C1a and CB-C2h-21, using ten times iterative 5CV and 3CV for C1 and C2, respectively. SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations; BMI: Body mass index.
- Citation: Trifylli EM, Angelakis A, Kriebardis AG, Papadopoulos N, Fortis SP, Pantazatou V, Koskinas J, Kranidioti H, Koustas E, Sarantis P, Manolakopoulos S, Deutsch M. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease staging using explainable artificial intelligence. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(22): 106937
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i22/106937.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i22.106937