Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2025; 31(20): 104891
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.104891
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.104891
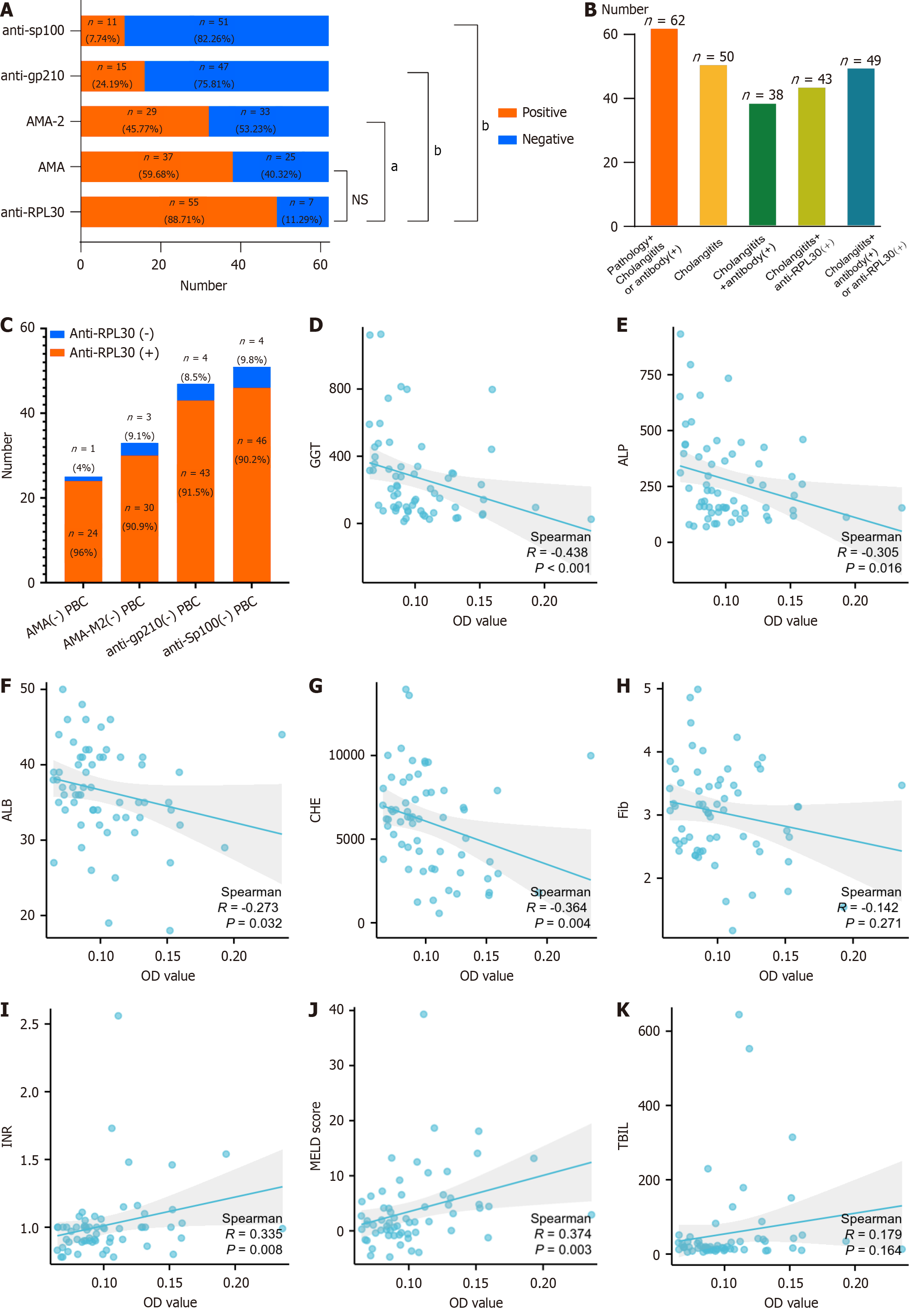
Figure 5 Analysis of clinical characteristics of patients with primary biliary cholangitis.
A: Autoantibody analysis of 62 patients with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC); B: Increased detection of PBC in patients with cholangitis features and anti-RPL30, even without liver biopsy; C: High anti-RPL30 positivity in patients with PBC negative for anti-mitochondrial antibody, anti-mitochondrial E2 subunit antibody, anti-glycoprotein 210, and anti-speckled protein 100; D–K: Correlation between anti-RPL30 optical density values and clinical indicators gamma-glutamyl transferase (D), alkaline phosphatase (E), albumin (F), cholinesterase (G), fibrinogen (H), international normalized ratio (I), Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score (J), and total bilirubin (K). aP < 0.01; bP < 0.0001. OD: Optical density; AMA: Anti-mitochondrial antibody; AMA-M2: Anti-mitochondrial E2 subunit antibody; Anti-gp210: Anti-glycoprotein 210; Anti-Sp100: Anti-speckled protein 100; PBC: Primary biliary cholangitis; AMA: Anti-mitochondrial antibody; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transferase; ALB: Albumin; CHE: Cholinesterase; FIB: Fibrinogen; TBIL: Total bilirubin; INR: International normalized ratio; MELD: Model for End-Stage Liver Disease.
- Citation: Zeng ZY, Huang ZX, Wang YR, Xie LK, Lin YP, Liang Y, Liu ZY, Li DL, Zhang XY. Anti-RPL30 as a novel biomarker for enhanced diagnosis of autoantibody-negative primary biliary cholangitis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(20): 104891
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i20/104891.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.104891