Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2025; 31(20): 100192
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.100192
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.100192
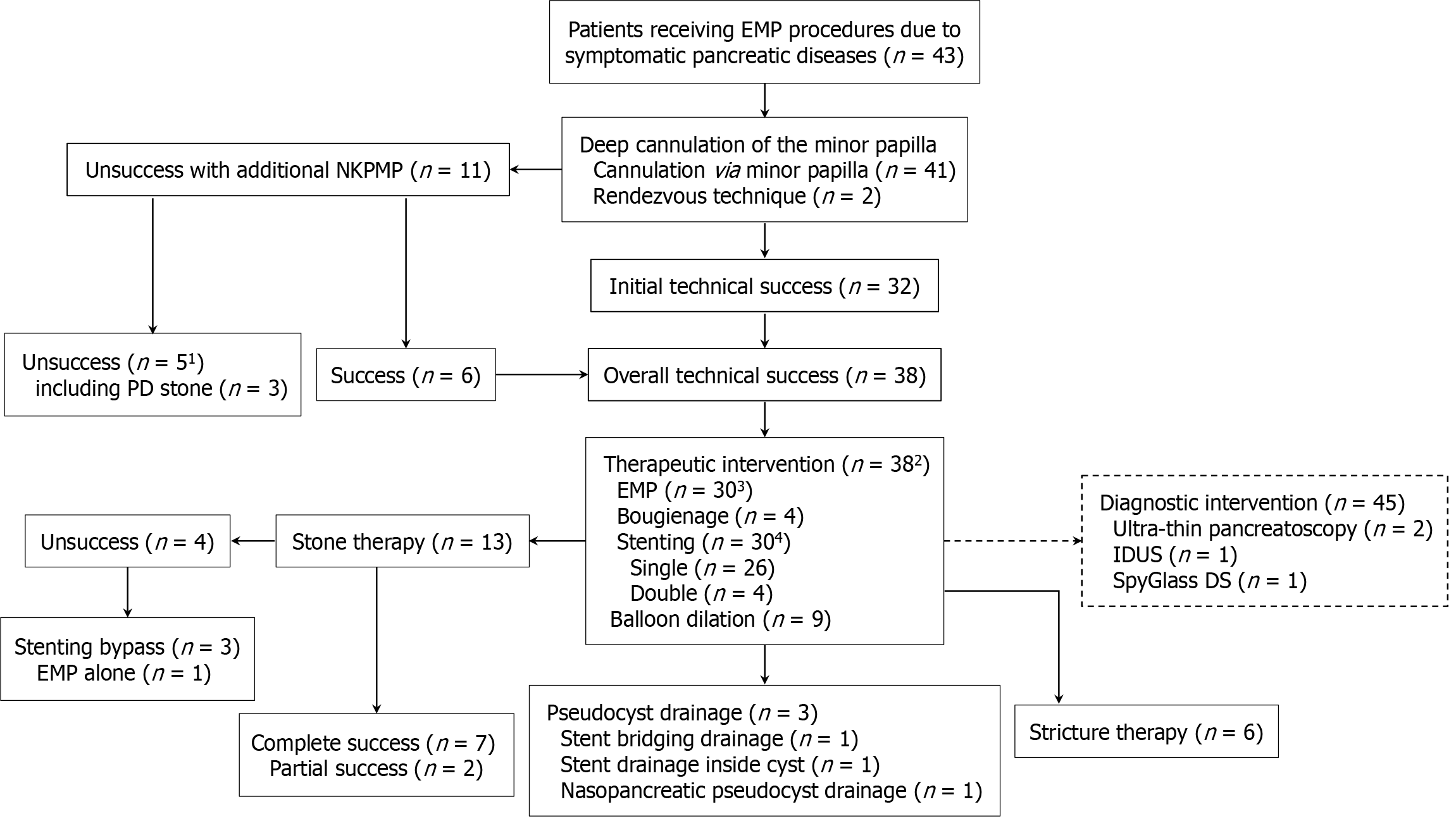
Figure 1 Technical details of endoscopic minor papilla intervention procedures in representative patients.
The solid line indicates therapeutic intervention and unsolid line indicates diagnostic intervention. 1Including 4 patients with obstructive chronic pancreatitis (3 of them with impacted stones) and 1 patient with pancreas divisum and chronic pancreatitis. 2Two or more interventional procedures were performed in some individual patients. 3Two patients received both needle-knife precut minor papillotomy (NKPMP) and endoscopic minor papillotomy (EMP). 4A 5 Fr stent (n = 10) or 7-8.5 Fr stent (n = 20) was used and ultimately exchanged in some cases with a single 10 Fr stent (n = 2) and double 7 Fr stents (n = 4) to treat the stricture. 5Four patients received diagnostic intervention after therapeutic intervention procedures including EMP (n = 4) and balloon dilation of the minor papilla and stricture (n = 1) for SpyGlass passing through the stricture and balloon sweep (n = 2) for mucin removal. IDUS: Intraductal ultrasound; PD: Pancreatic duct.
- Citation: Ren X, Qu YP, Xia T, Tang XF. Technical success, clinical efficacy, and safety of endoscopic minor papilla interventions for symptomatic pancreatic diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(20): 100192
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i20/100192.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.100192