Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2025; 31(19): 106814
Published online May 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i19.106814
Published online May 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i19.106814
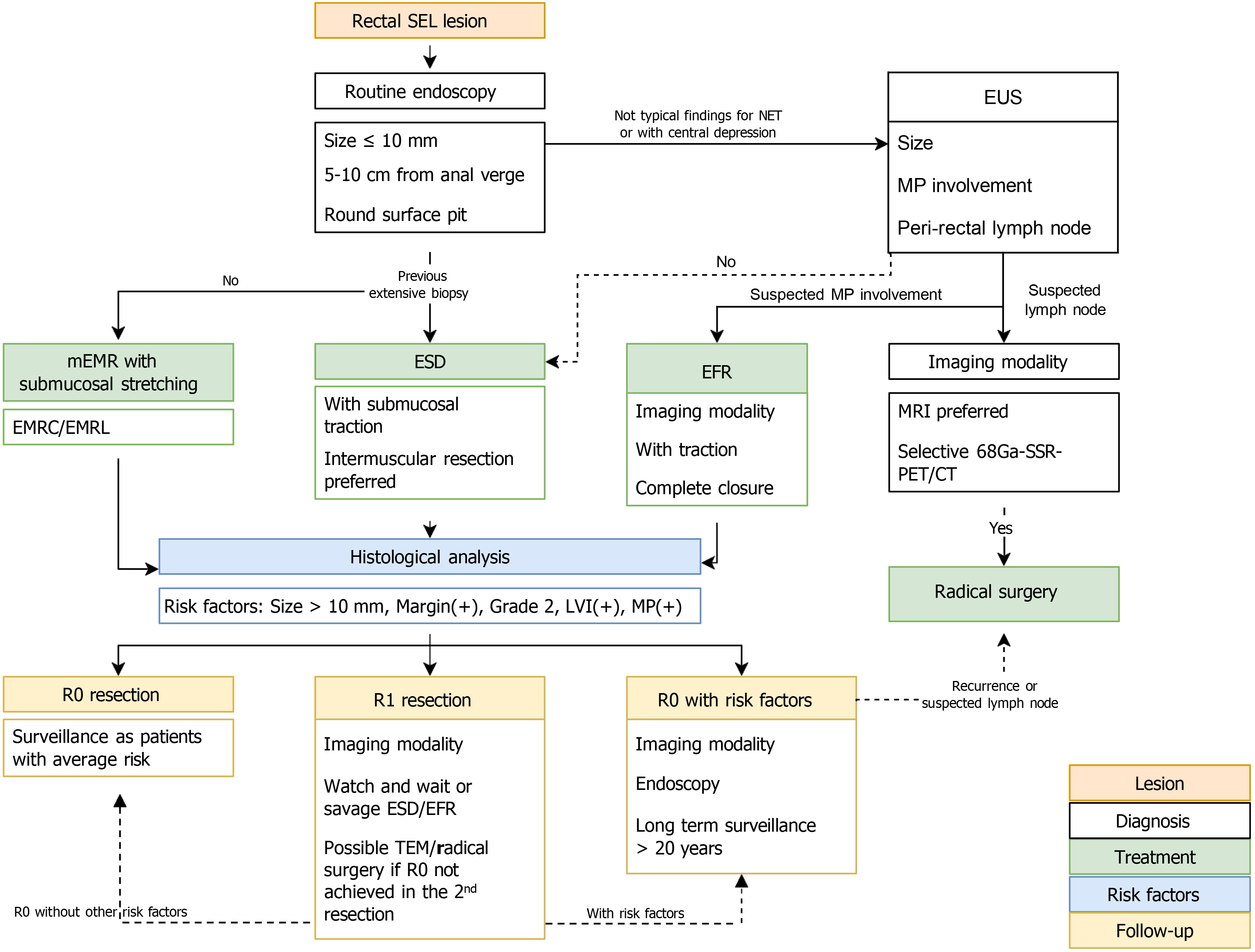
Figure 5 Proposed algorithm for the management of rectal neuroendocrine tumors.
SEL: Subepithelial lesion; NET: Neuroendocrine tumor; EUS: Endoscopic ultrasound; MP: Muscularis propria; mEMR: Modified endoscopic submucosal resection; ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; EFR: Endoscopic full-thickness resection; EMRC: Cap-assisted endoscopic submucosal resection; EMRL: Endoscopic submucosal resection with a ligation device; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; 68Ga-SSR-PET/CT: Gallium-68-somatostatin receptor-positron emission tomography/computed tomography; R0 resection: Complete resection; R1 resection: Incomplete resection; TEM: Transanal endoscopic microsurgery.
- Citation: Liu JN, Chen H, Fang N. Current status of endoscopic resection for small rectal neuroendocrine tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(19): 106814
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i19/106814.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i19.106814