Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2025; 31(15): 103773
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.103773
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.103773
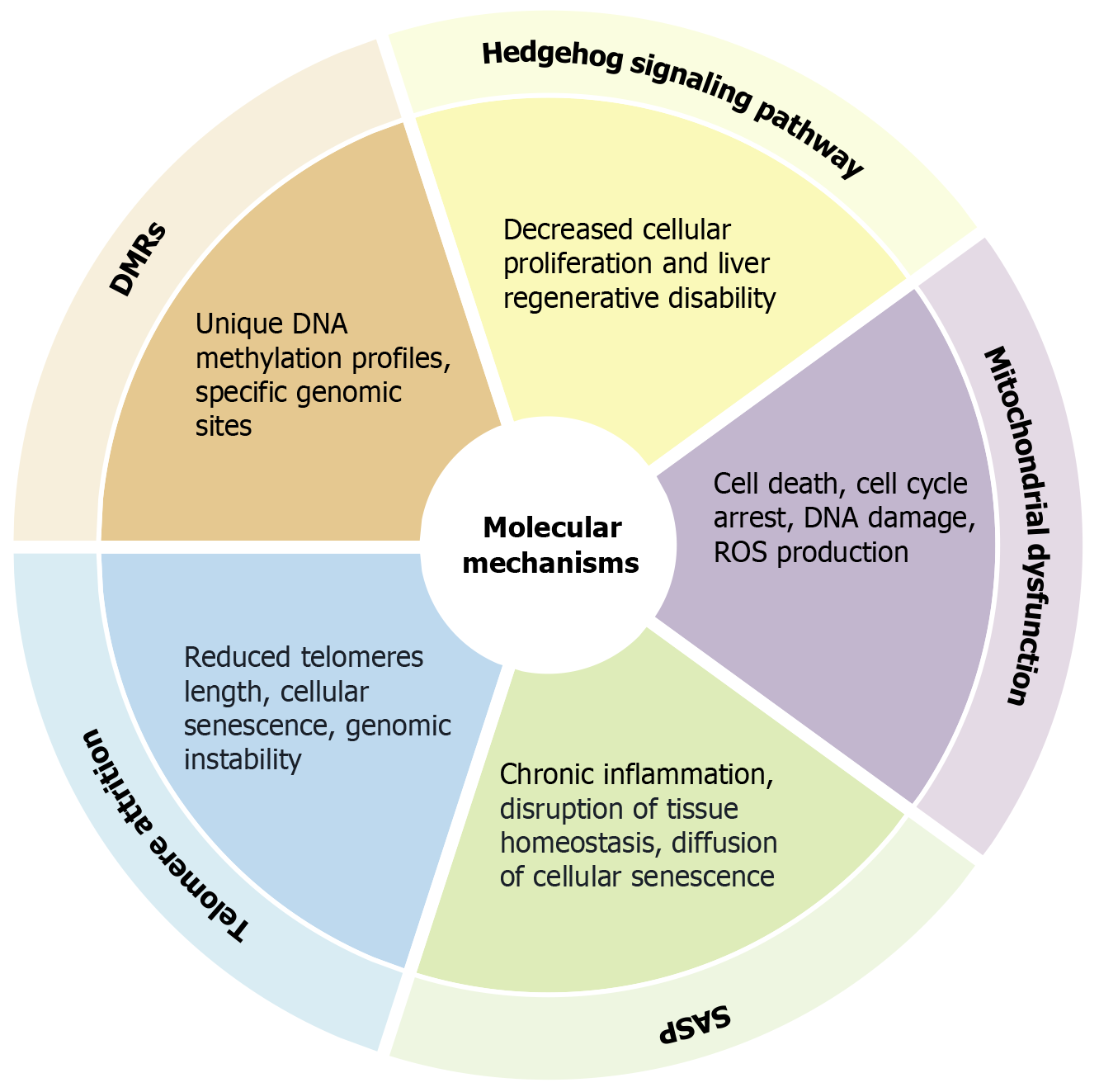
Figure 1 Summary of molecular mechanisms in liver aging.
Cellular senescence is linked to changes and effects at the molecular level. These include the role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in inhibiting liver regeneration and cellular proliferation, the effects of mitochondrial dysfunction, such as reactive oxygen species production and apoptosis, the link between senescence-associated secretory phenotype and the spread of senescence and chronic inflammation, the traits of telomere attrition that cause genomic instability, and the distinct DNA methylation profiles in differentially methylated regions. DMRs: Differentially methylated regions; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SASP: Senescence-associated secretory phenotype.
- Citation: Yao YQ, Cao QY, Li Z. Delaying liver aging: Analysis of structural and functional alterations. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(15): 103773
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i15/103773.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.103773