Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2025; 31(11): 102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
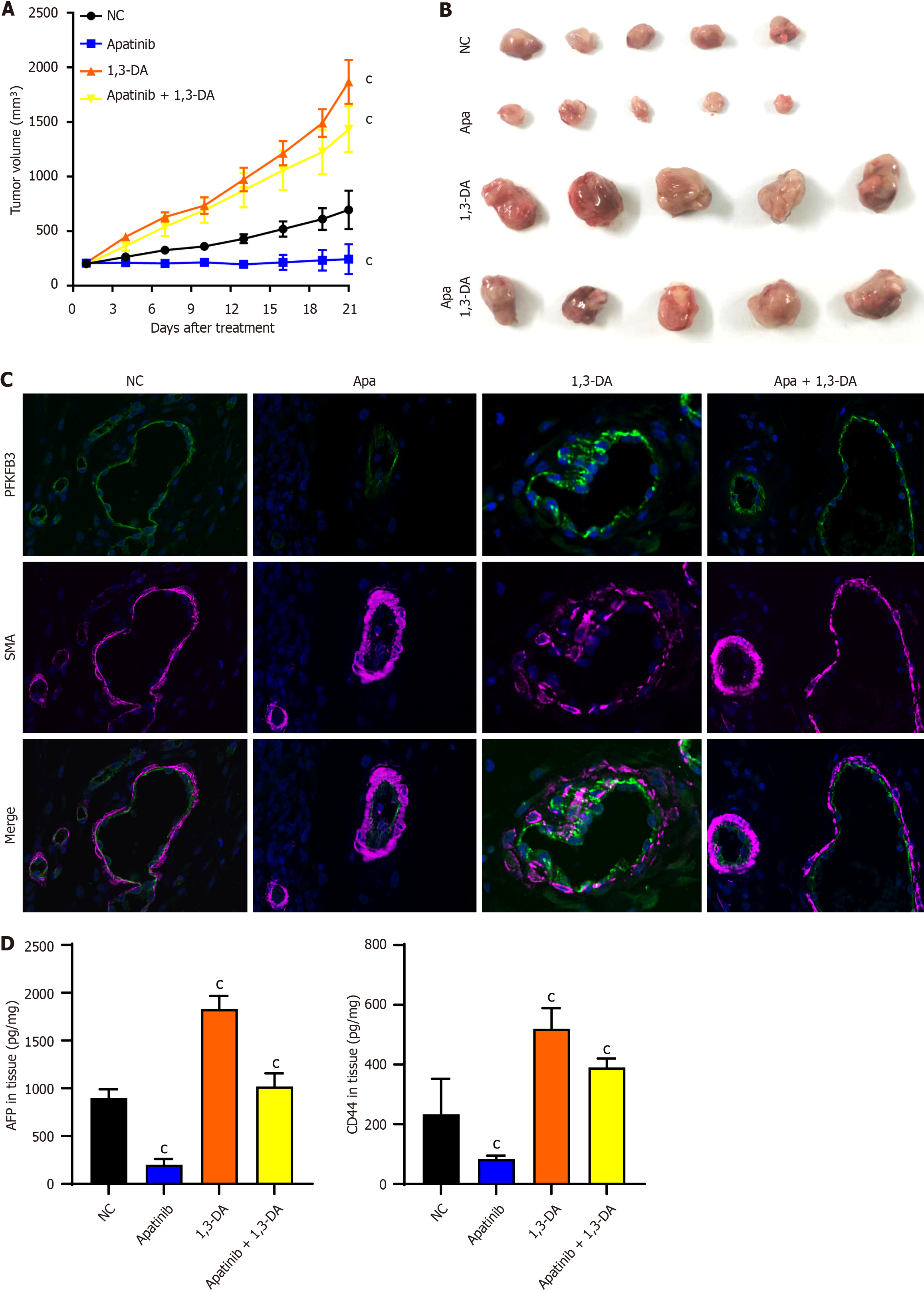
Figure 7 Apatinib inhibits liver cancer angiogenesis and suppresses glycolysis in vascular endothelial cells in vivo.
A: Tumor growth curve of mice treated with apatinib and 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid; B: Tumor size after 21 days of treatment with apatinib and 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid in mice; C: Immunofluorescence staining of mouse tissues treated with apatinib and 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid; D: The contents of alpha-fetoprotein and CD44 in animal tissues were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. cP < 0.001. Apa: Apatinib; DA: Dicaffeoylquinic acid; SMA: Smooth muscle actin; PFKFB3: 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein.
- Citation: Wu Y, Xie BB, Zhang BL, Zhuang QX, Liu SW, Pan HM. Apatinib regulates the glycolysis of vascular endothelial cells through PI3K/AKT/PFKFB3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(11): 102848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i11/102848.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848