Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2025; 31(11): 102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
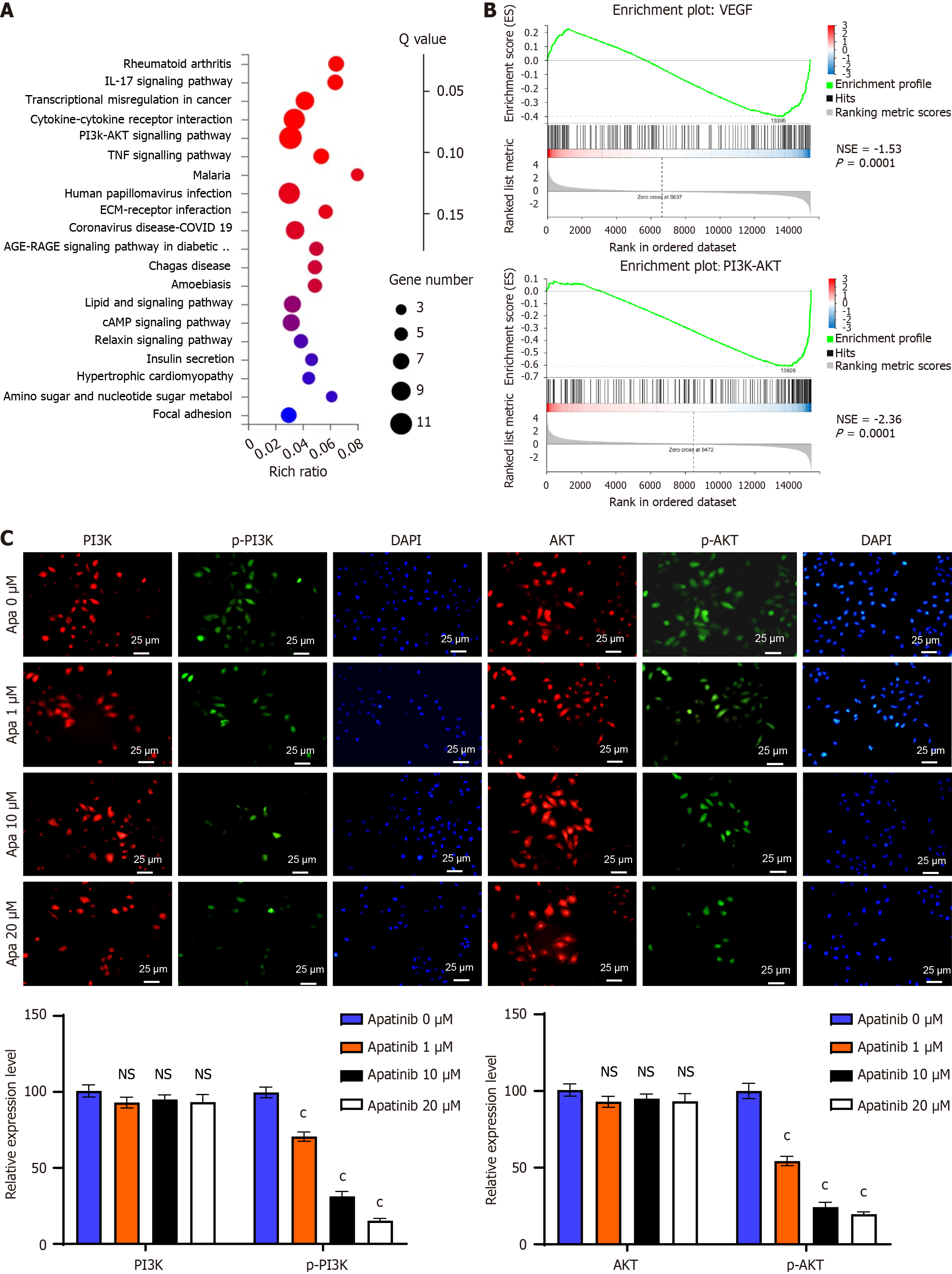
Figure 5 Apatinib suppresses the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathway.
A: Kyoto Encyclopedia of genes and genomes pathway analysis showed notable alterations in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway following apatinib administration; B: Results from gene set enrichment analysis indicated a significant inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor and PI3K/AKT pathways by apatinib; C: Immunofluorescence studies showed a marked reduction in PI3K and AKT protein expression after apatinib administration, as well as a diminished translocation of these proteins from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. cP < 0.001. IL: Interleukin; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; ECM: Extracellular matrix; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; NSE: Normalized enrichment score; Apa: Apatinib; NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Wu Y, Xie BB, Zhang BL, Zhuang QX, Liu SW, Pan HM. Apatinib regulates the glycolysis of vascular endothelial cells through PI3K/AKT/PFKFB3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(11): 102848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i11/102848.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848