Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2025; 31(11): 102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
Published online Mar 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848
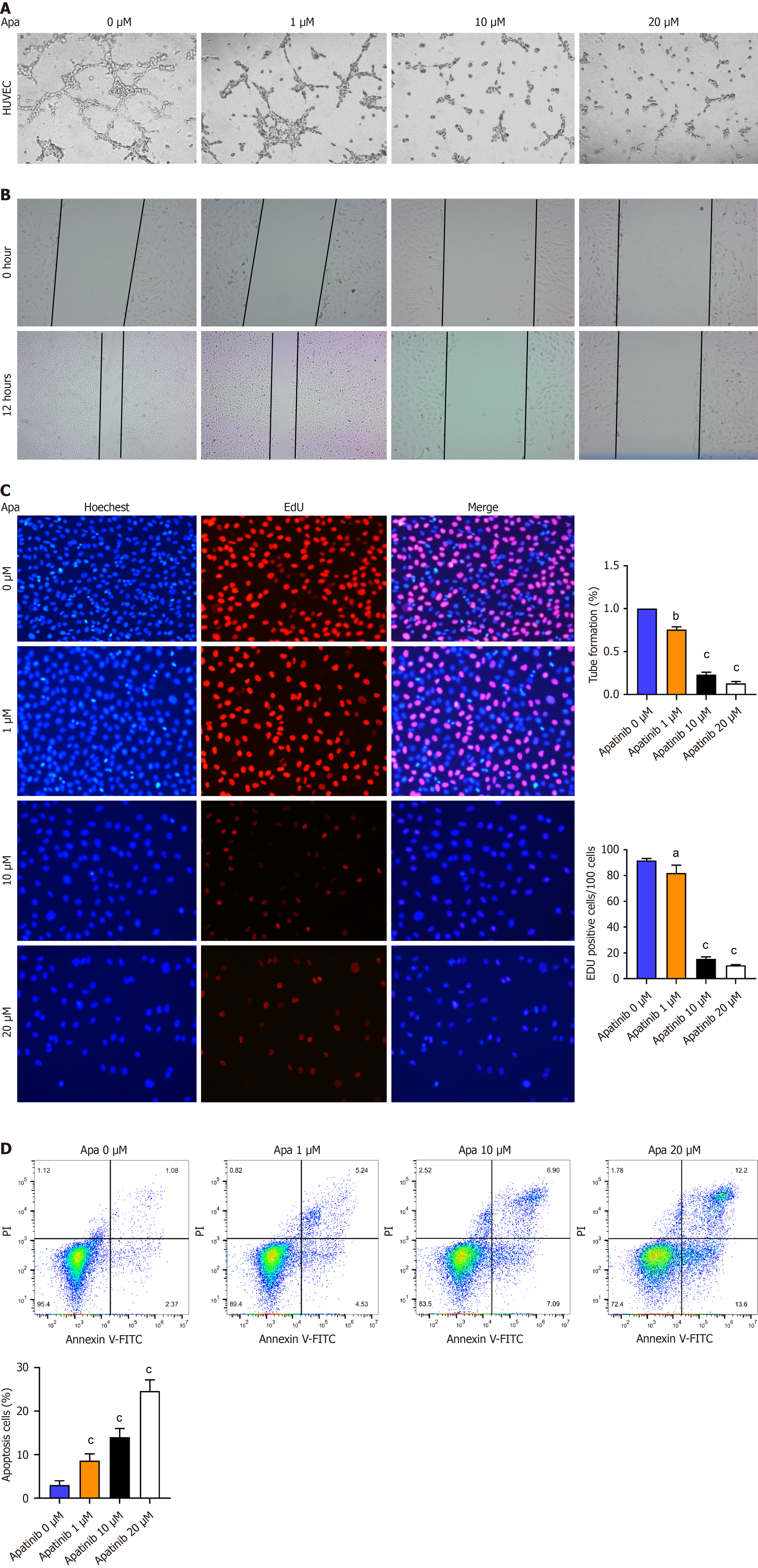
Figure 4 Apatinib inhibits tube formation, proliferation, and migration but induces apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells.
A: Influence of diverse apatinib levels on the capability of vascular endothelial cells (VECs) to form tubes; B: How varying concentrations of apatinib influence the migration patterns of VECs; C: The role of different apatinib doses in altering the proliferation capacity of VECs; D: Annexin V/ propidium iodide staining indicates that apatinib treatment triggers apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. aP< 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Apa: Apatinib; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells; PI: propidium iodide; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate.
- Citation: Wu Y, Xie BB, Zhang BL, Zhuang QX, Liu SW, Pan HM. Apatinib regulates the glycolysis of vascular endothelial cells through PI3K/AKT/PFKFB3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(11): 102848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i11/102848.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i11.102848