Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2024; 30(16): 2195-2208
Published online Apr 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i16.2195
Published online Apr 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i16.2195
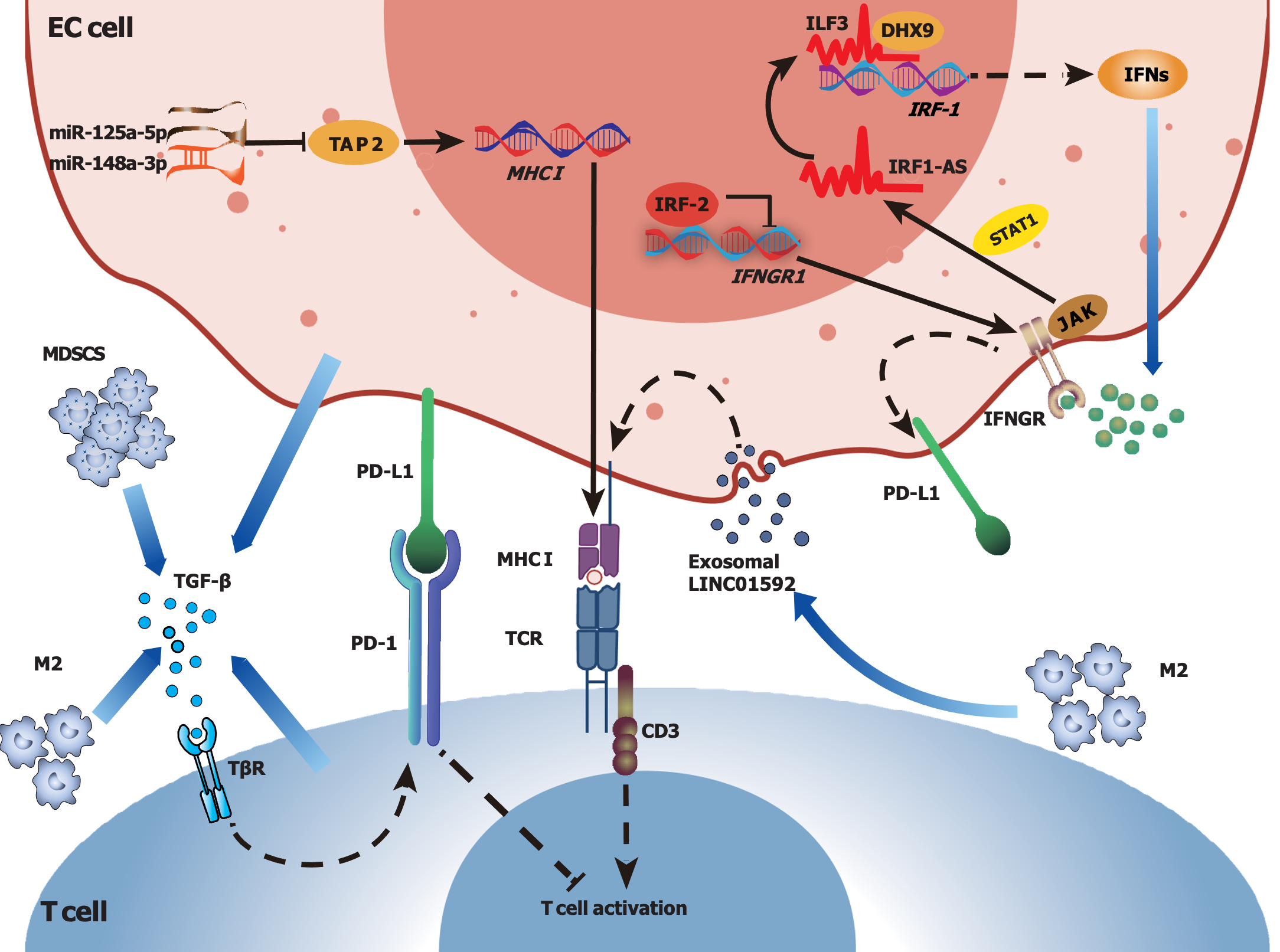
Figure 2 Potential mechanisms of tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment formation in esophageal cancer: Major histo-compatibility complex downregulation and immunosuppressive factors.
In esophageal cancer (EC) cells, miR-125a-5p and miR-148a-3p may downregulate ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 2 translation and major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-I expression, and exosomal LINC01592 released by M2 macrophages may also downregulate MHC-I expression. Transforming growth factor beta secreted by various cells can enhance programmed cell death protein 1 expression on T cells, and interferon (IFN)-γ can upregulate programmed cell death ligand 1 expression on EC cells, subsequently contributing to immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment. Additionally, EC cells may acquire immune resistance by downregulating the expression of IFN-γ receptors and suppressing the activation of Janus-activated kinase signaling. EC: Esophageal cancer; TCR: T-cell receptor; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand 1; MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cell; M2: Type 2 macrophage/suppressive macrophage; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; TβR: Transforming growth factor beta receptor; IFN: Interferon; IFNGR: Interferon gamma receptor; IRF-1: Interferon regulatory factor 1; IRF-2: Interferon regulatory factor 2; IRF1-AS: Interferon regulatory factor 1 antisense RNA; ILF3: Interleukin enhancer binding factor 3; DHX9: DExH-box helicase 9; STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; JAK: Janus-activated kinase; TAP2: ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 2.
- Citation: Zhang XJ, Yu Y, Zhao HP, Guo L, Dai K, Lv J. Mechanisms of tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment formation in esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(16): 2195-2208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i16/2195.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i16.2195