Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2024; 30(12): 1663-1669
Published online Mar 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i12.1663
Published online Mar 28, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i12.1663
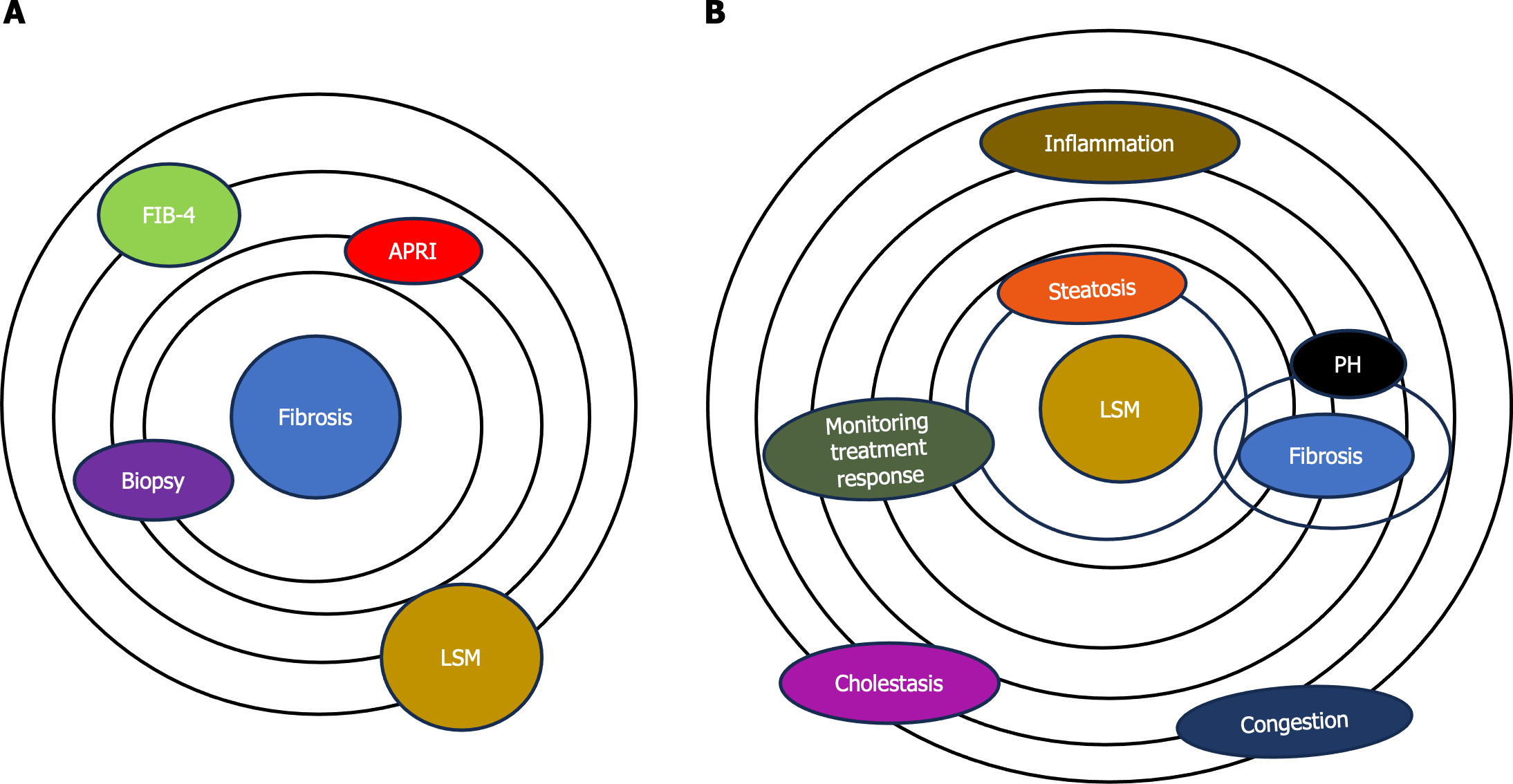
Figure 1 Role of elastography in assessing liver tissue health.
A: Model of assessment of fibrosis. Elastography, once primarily associated with fibrosis assessment (biopsy, different noninvasive scores like fibrosis index based on 4 factors, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet index, etc); B: Model of assessment of liver stiffness. Now, elastography has evolved into a versatile method offering assessment of the mechanical properties and dynamic nature of liver tissues such as the quantification of liver steatosis by providing a noninvasive means for evaluation of fat content and the detection of inflammatory changes within liver tissues. Elastography may provide valuable insights into portal hypertension and monitor responses to therapeutic interventions. There are some confounding factors (cholestasis and heart congestion) that can contribute to increasing the liver stiffness. LSM: Liver stiffness measurement; FIB-4: Fibrosis index based on 4 factors; APRI: Aminotransferase-to-platelet index; PH: Portal hypertension.
- Citation: Peltec A, Sporea I. Multiparametric ultrasound as a new concept of assessment of liver tissue damage. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(12): 1663-1669
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i12/1663.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i12.1663