Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2024; 30(11): 1588-1608
Published online Mar 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1588
Published online Mar 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1588
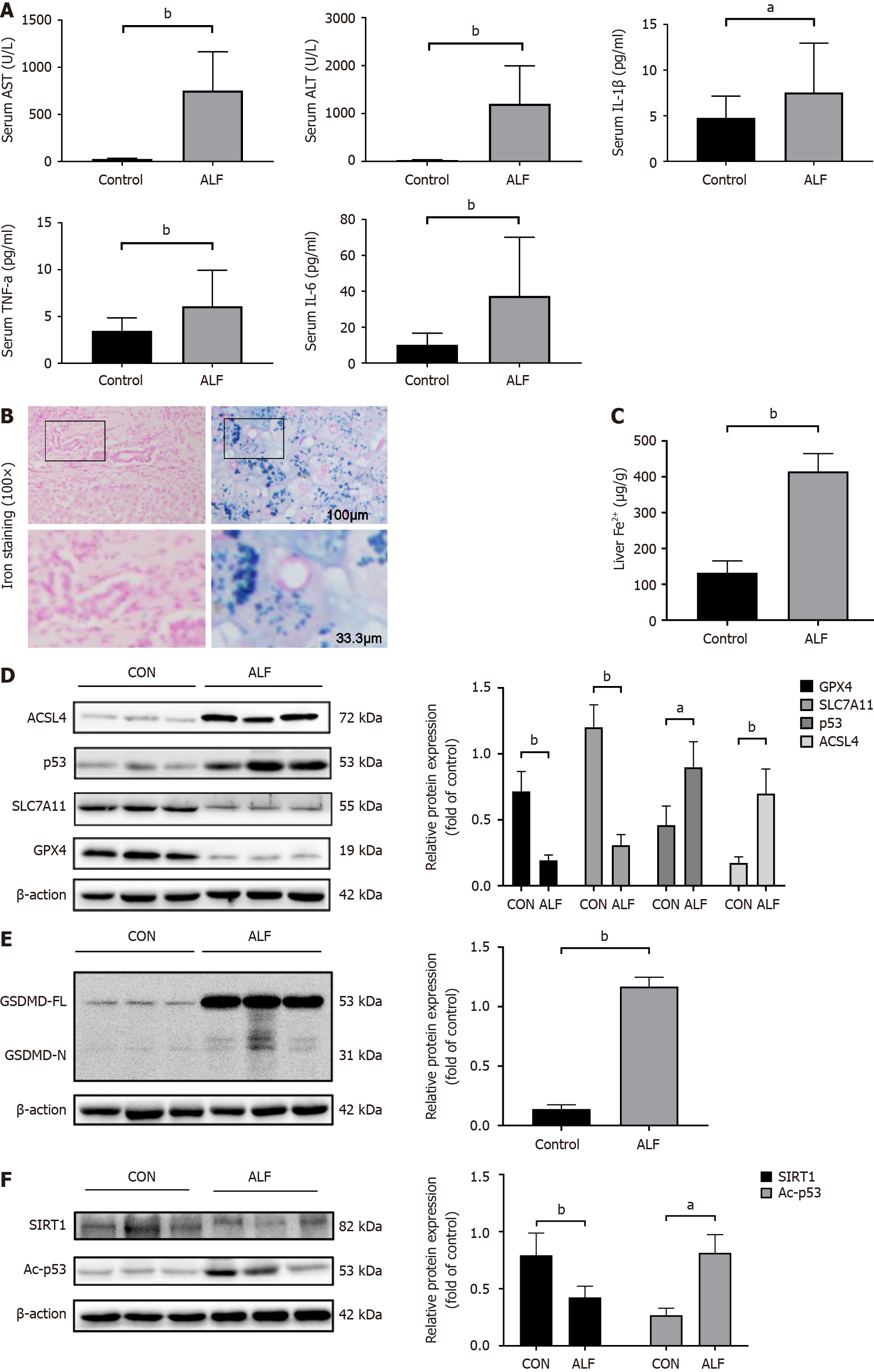
Figure 1 Ferroptosis and pyroptosis occur in human acute liver failure.
A: The levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 were changed in serum samples of healthy individuals and patients with acute liver failure (ALF) (n = 30 in each group); B: Iron staining (scale bar: 100 µm and 33.3 µm) of normal liver tissue and ALF liver tissue; C: Detection of iron in normal liver tissue and ALF; D: Western blot analyses of glutathione peroxidase 4, solute carrier family 7a member 11, p53, and acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 proteins were performed in healthy individuals and patients with ALF. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments; E: Western blot analysis of gasdermin D protein expression (n = 3); F: Western blot analysis of silent information regulator sirtuin 1 and Ac-p53 protein expression in healthy individuals and patients with ALF (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. ALF: Acute liver failure; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; IL: Interleukin; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; SLC7A11: Solute carrier family 7a member 11; ACSL4: Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; GSDMD: Gasdermin D; SIRT1: Silent information regulator sirtuin 1.
- Citation: Zhou XN, Zhang Q, Peng H, Qin YJ, Liu YH, Wang L, Cheng ML, Luo XH, Li H. Silent information regulator sirtuin 1 ameliorates acute liver failure via the p53/glutathione peroxidase 4/gasdermin D axis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(11): 1588-1608
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i11/1588.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1588