Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2024; 30(10): 1431-1449
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1431
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1431
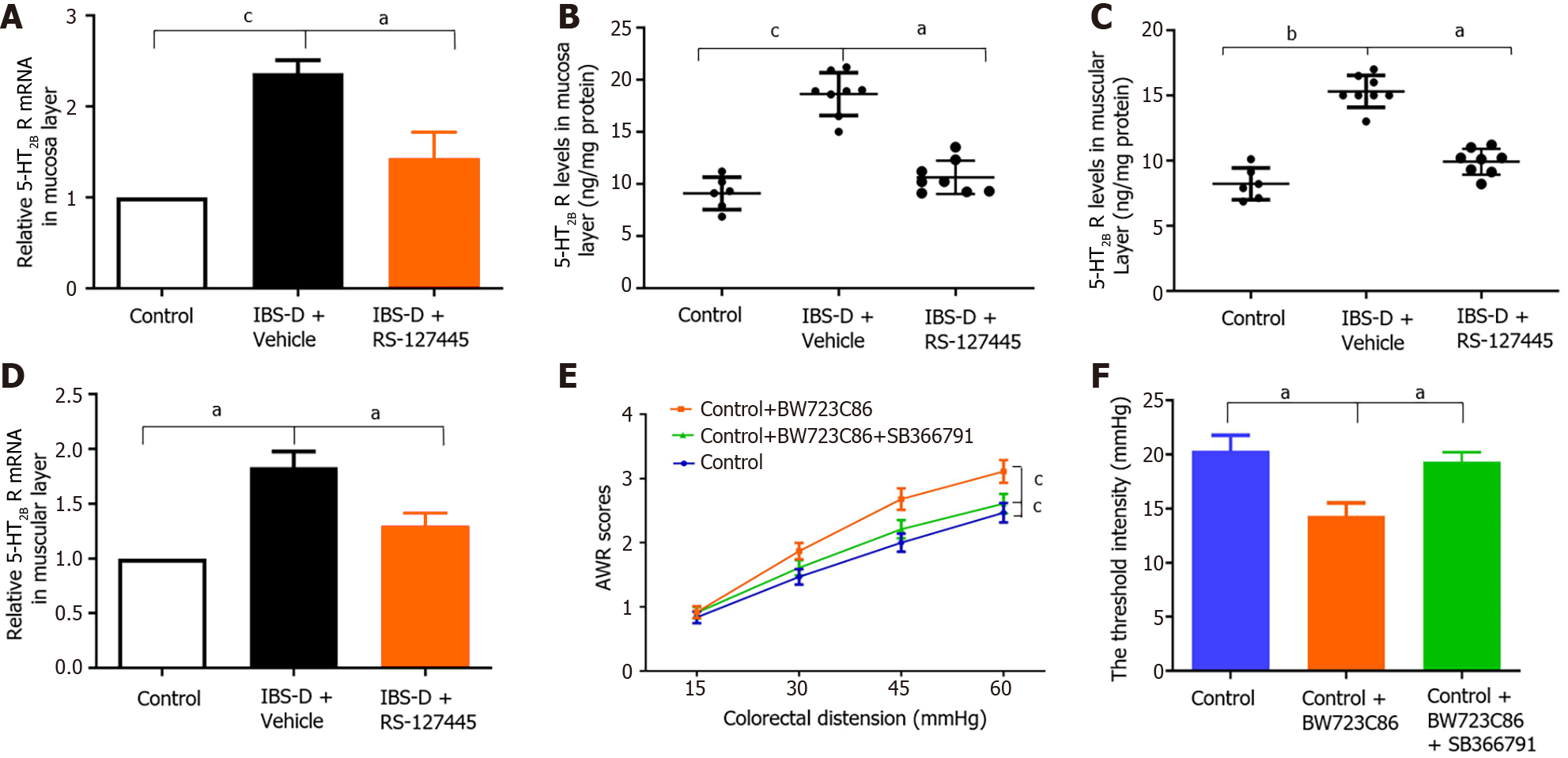
Figure 5 RS12-7445 decreased the serotonin receptor 2B levels in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea rats.
Visceral sensitivity was detected by the colorectal distension. A: Serotonin receptor 2B (5-HT2B receptor) mRNA levels in the colonic mucosa layer were detected via quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR); B: Expression of the 5-HT2B receptor in colon mucosa tissues from each group was detected by ELISA; C: Expression of the 5-HT2B receptor in colon muscular tissues from each group was detected by ELISA; D: 5-HT2B receptor mRNA levels in the colonic muscular layer were detected via qRT-PCR; E: The Control + BW723C86 group had higher abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores than did the Control group, with colorectal distension (CRD) pressures of 30, 45 and 60 mmHg but not 15 mmHg. Similarly, the Control + BW723C86 group had increased AWR scores with the same CRD pressure compared with those of the Control + BW723C86 + SB366791 group; F: The Control + BW723C86 group had a decreased threshold pressure compared with that of the Control group. Similarly, the Control + BW723C86 group had reduced threshold pressure with the same CRD pressure compared with those of the Control + BW723C86 + SB366791 group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. IBS-D: Irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea; 5-HT2B: Serotonin receptor 2B; AWR: Abdominal withdrawal reflex.
- Citation: Li ZY, Mao YQ, Hua Q, Sun YH, Wang HY, Ye XG, Hu JX, Wang YJ, Jiang M. Serotonin receptor 2B induces visceral hyperalgesia in rat model and patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(10): 1431-1449
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i10/1431.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1431