Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2023; 29(46): 6060-6075
Published online Dec 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i46.6060
Published online Dec 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i46.6060
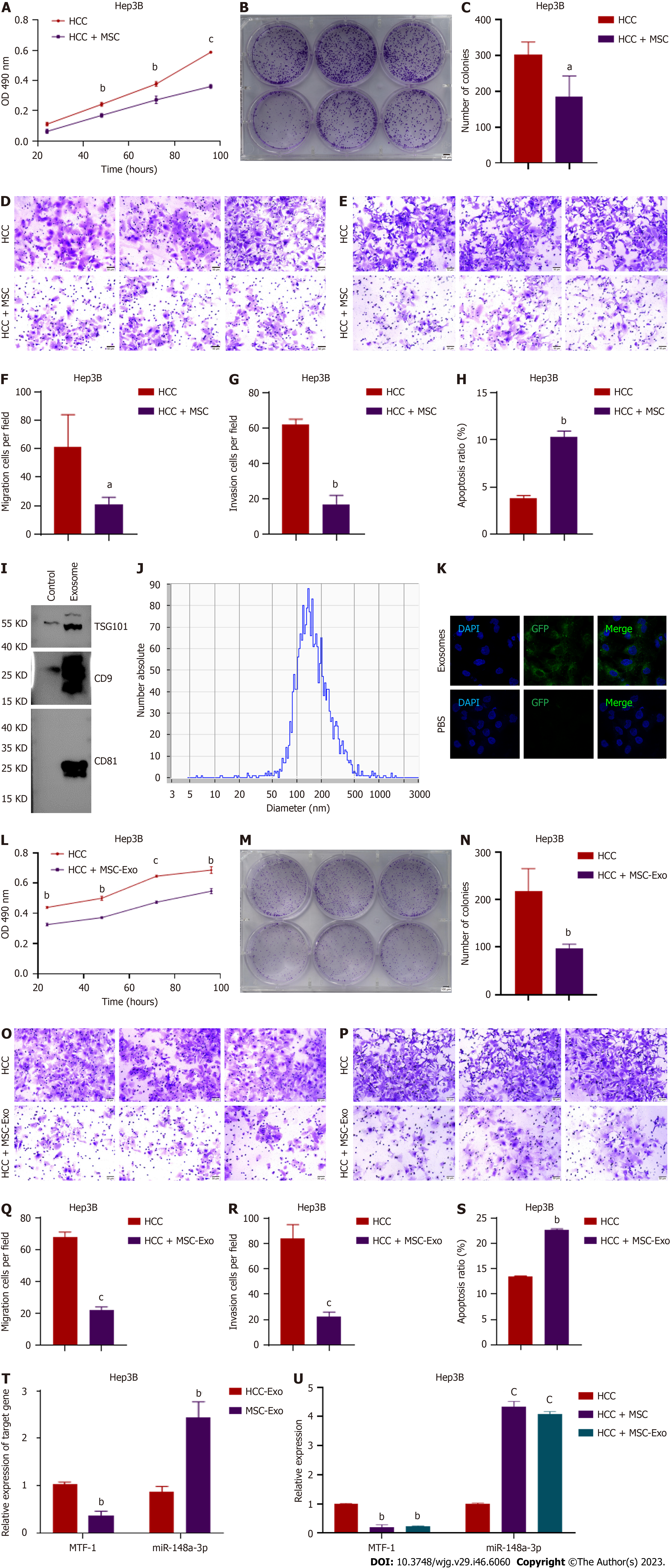
Figure 1 Effects of mesenchymal stem cells or mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome co-incubation on Hep3B cells.
A-C: The proliferation of Hep3B cells was measured using 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide and colony formation assays; D-G: Invasion and metastasis were determined using the Transwell assay. Scale bar = 500 μm; H: Cell apoptotic rates were detected after co-incubation using flow cytometry; I: Exosomes were isolated, and specific exosome markers were identified using western blotting; J: The particle size analyzer showed that the average diameter of the vesicles was within the diameter range of exosomes; K: The uptake of labeled exosomes was observed and verified; L-S: Hep3B cell viability and metastasis were both suppressed after exposure to mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes, and apoptosis was enhanced; T: Comparison of miR-148a-3p and metal-regulatory transcription factor-1 (MTF-1) expression levels in MSC- and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-derived exosomes; U: Assessment of miR-148a-3p and MTF-1 expression by real-time polymerase chain reaction in HCC cells co-cultured with MSC and MSC-derived exosomes. Quantitative data from three independent experiments are shown as the mean ± SD (error bars). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; miRNA: MicroRNA; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; MTF-1: Metal-regulatory transcription factor-1; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline.
- Citation: Lyu ZZ, Li M, Yang MY, Han MH, Yang Z. Exosome-mediated transfer of circRNA563 promoting hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the microRNA148a-3p/metal-regulatory transcription factor-1 pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(46): 6060-6075
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i46/6060.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i46.6060