Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2023; 29(34): 5038-5053
Published online Sep 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i34.5038
Published online Sep 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i34.5038
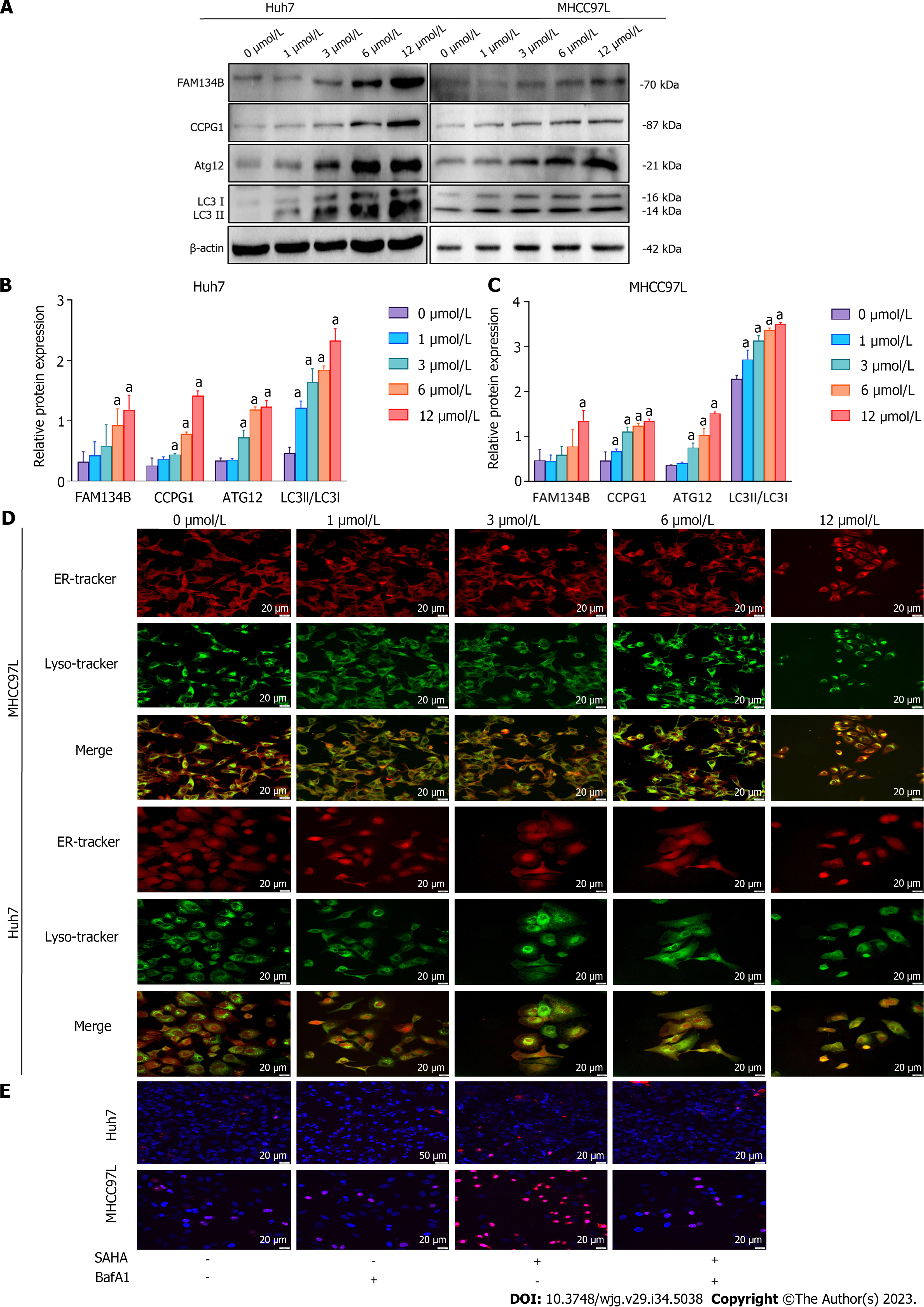
Figure 3 Impact of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid treatment on the level of endoplasmic reticulum-phagy and autophagy-mediated cell death in Huh7 and MHCC97L cells.
A-C: Huh7 and MHCC97L cells were exposed to 0, 1, 3, 6, and 12 μmol/L suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid for 48 h. Proteins related to the reticulophagy pathway were detected using western blotting. Relative protein expression levels were normalized to β-actin; D: The colocalization coverage of the endoplasmic reticulum and lysosomes were observed using a confocal microscope (× 400). Representative pictures from three independent replicate assays are exhibited; E: Huh7 and MHCC97L cells were pretreated with 0.5 nmol/L BafA1 for 12 h, followed by 12 μmol/L suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid treatment for 48 h. Hoechst 33342/propidium iodide (PI) double staining localization assay was utilized to observe nuclear coagulation. After Hoechst 33342/PI double staining, the death rate of hepatocellular carcinoma cells was quantified based on the ratio of pink cells/blue cells. Experiments were repeated thrice. Representative pictures from three independent replicate assays are shown. Data are exhibited as mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol/L group. SAHA: Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; FAM134B: Family with sequence similarity 134 member B.
- Citation: Li JY, Tian T, Han B, Yang T, Guo YX, Wu JY, Chen YS, Yang Q, Xie RJ. Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid upregulates reticulophagy receptor expression and promotes cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(34): 5038-5053
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i34/5038.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i34.5038