Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2023; 29(3): 450-468
Published online Jan 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i3.450
Published online Jan 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i3.450
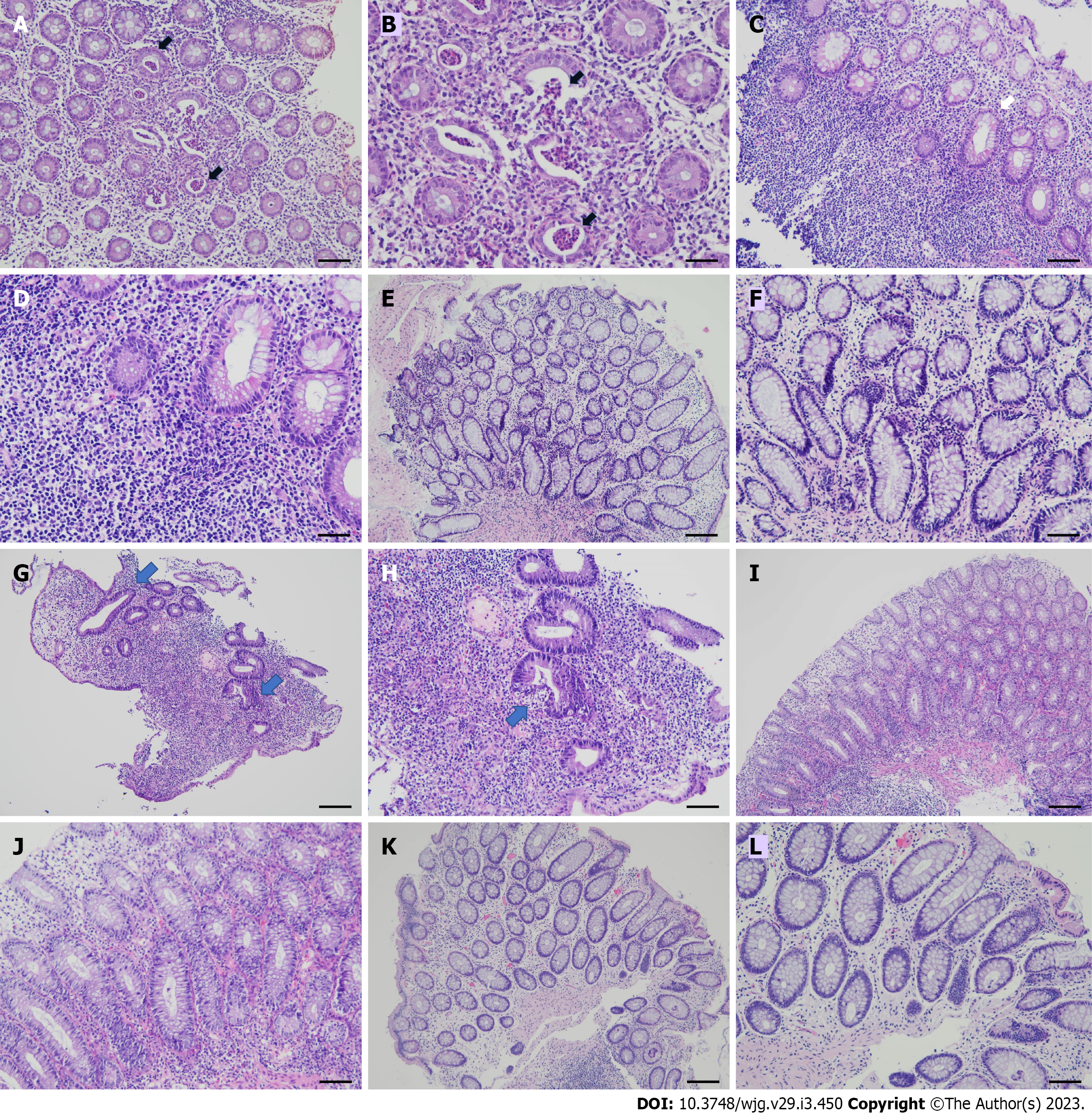
Figure 1 Serial histopathological findings of ulcerative proctitis before and after therapy from rectum biopsy specimens.
Hematoxylin and eosin stain. A and B: Rectal mucosa before therapy shows acute rectitis with neutrophilic infiltrates and crypt abscess in case No. 1 (arrows), 100 × (A) and 200 × (B); C and D: Rectal mucosa shows features of chronicity including dense lymphocytic infiltration, basal lymphoplasmacytosis and crypt distortion in case No. 1 (arrow), 100 × (C) and 200 × (D); E and F: Rectal mucosa after adalimumab therapy shows mild non-specific lymphocytic infiltration in case No. 1, 100 × (E) and 200 × (F); G and H: Colonic mucosa before therapy shows crypt distortion (arrows) and lymphoplasmacytic infiltration in the lamina propria in case No. 2, 100 × (G). The crypt shows distortion and neutrophilic infiltration (arrow), 200 × (H); I and J: Colonic mucosa shows less crypt distortion and lymphoplasmacytic infiltration as compared with (G and H) before adalimumab (ADA) therapy in case No. 2, 100 × (I) and 200 × (J); K and L: Colonic mucosa after ADA 40 mg injection once every 2 wk shows mild non-specific lymphocytic infiltration in case No. 2, 100 × (K) and 200 × (L). Bars shown on 100 × and 200 × photomicrographs correspond to 100 µm and 50 µm, respectively.
- Citation: Wang CR, Tsai HW. Seronegative spondyloarthropathy-associated inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(3): 450-468
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i3/450.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i3.450