Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2023; 29(29): 4499-4527
Published online Aug 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i29.4499
Published online Aug 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i29.4499
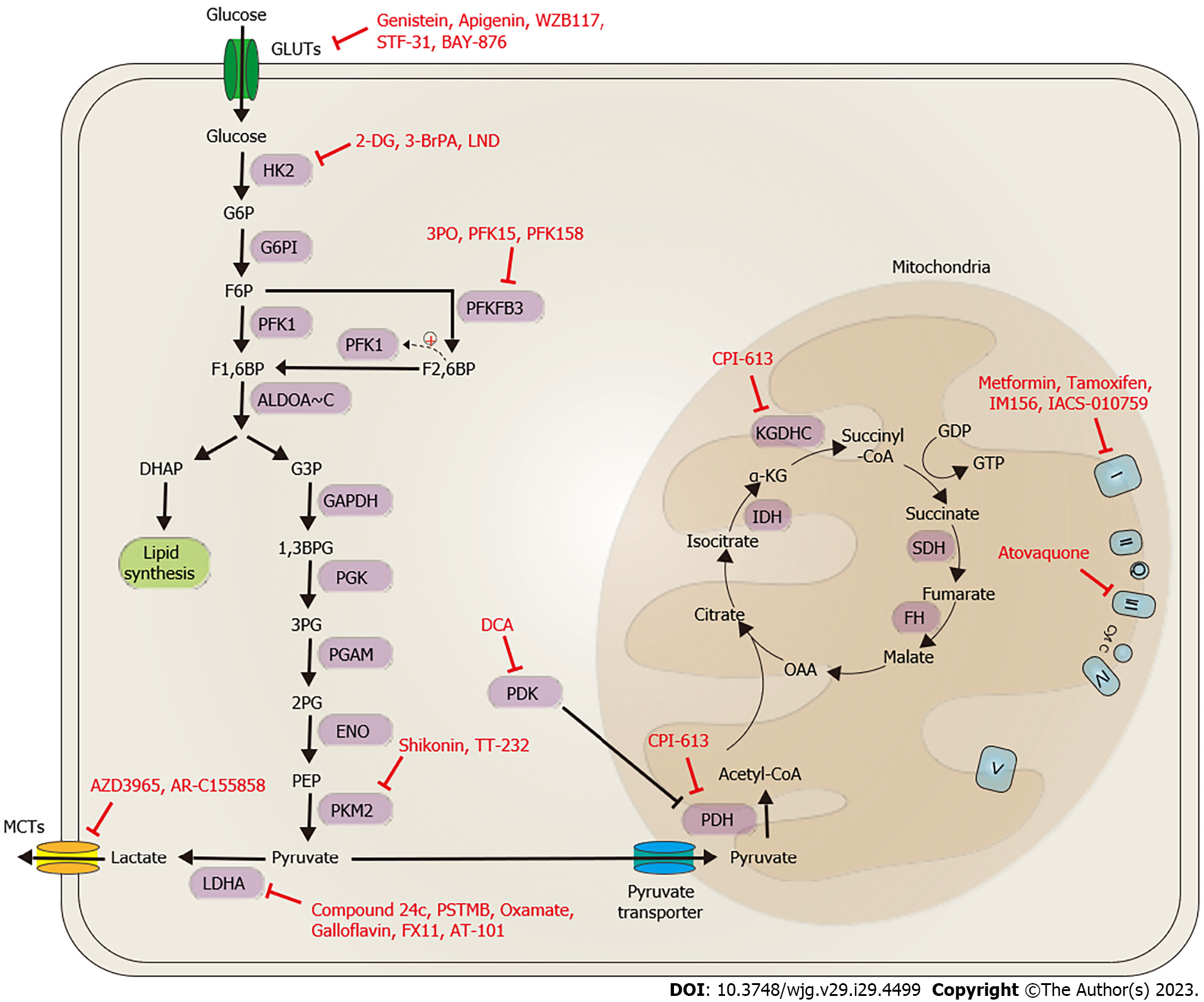
Figure 4 Potent bioenergetic-targeting drugs for gastrointestinal cancers.
Promising bioenergetic drugs for gastrointestinal cancers can be classified into two main categories based on their mode of action. The first category involves targeting aerobic glycolysis and lactate biosynthesis/transportation, while the second category involves targeting the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Strategies to target aerobic glycolysis include blocking glucose importation through the targeting of glucose transporter 1 with compounds such as genistein, apigenin, WZB117, STF-31, and BAY-876, reducing glycolysis activity by targeting HK2 with compounds such as 2-DG, 3-BrPA, and LND, and targeting PKMFB3 and PKM2 with compounds such as 3PO, PFK15, PFK158, shikonin, and TT-232. Lactate biosynthesis can be inhibited by targeting LDHA with compounds such as compound 24c, PSTMB, oxamate, galloflavin, FX11, and AT-101, and PDK with DCA. Lactate transportation can be blocked by targeting MCT1/2 with compounds such as AZD3965 and AR-C155858. Targeting the TCA cycle and OXPHOS involves using inhibitors of pyruvate dehydrogenase, such as CPI-613, and mitochondrial complex I with metformin, tamoxifen, IM156, IACS-010759, and complex III with atovaquone. GLUT: Glucose transporter; HK: Hexokinase; G6P: Glucose-6-phosphate; G6PI: Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; F6P: Fructose-6-phosphate; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; PFK1: Phosphofructokinase-1; F2,6BP: Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate; PFKBP3: Fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3; F1,6BP: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; G3P: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; DHAP: Dihydroxyacetone phosphate; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; 1,3BPG: 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; 3PG: 3-phosphoglycerate; PGK: Phosphoglycerate kinase; PGAM: Phosphoglycerate mutase; 2PG: 2-phosphoglycerate; ENO: Enolase; PEP: Phosphoenolpyruvate; PKM1/2: Pyruvate kinase isozyme M1/M2; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; MCT: Monocarboxylate transporter family; PDH: Pyruvate dehydrogenase; IDH: Isocitrate dehydrogenase; α-KG: α-ketoglutarate; OAA: Oxaloacetate; SDH: Succinate dehydrogenase; FH: Fumarate hydratase; I: Mitochondrial complex I; II: Mitochondrial complex II; III: Mitochondrial complex III; IV: Mitochondrial complex IV; V: Mitochondrial complex V; Q: Co-enzyme Q; cyto C: Cytochrome c; KGDHC: α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex.
- Citation: Chu YD, Chen CW, Lai MW, Lim SN, Lin WR. Bioenergetic alteration in gastrointestinal cancers: The good, the bad and the ugly. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(29): 4499-4527
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i29/4499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i29.4499