Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2023; 29(22): 3422-3439
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3422
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3422
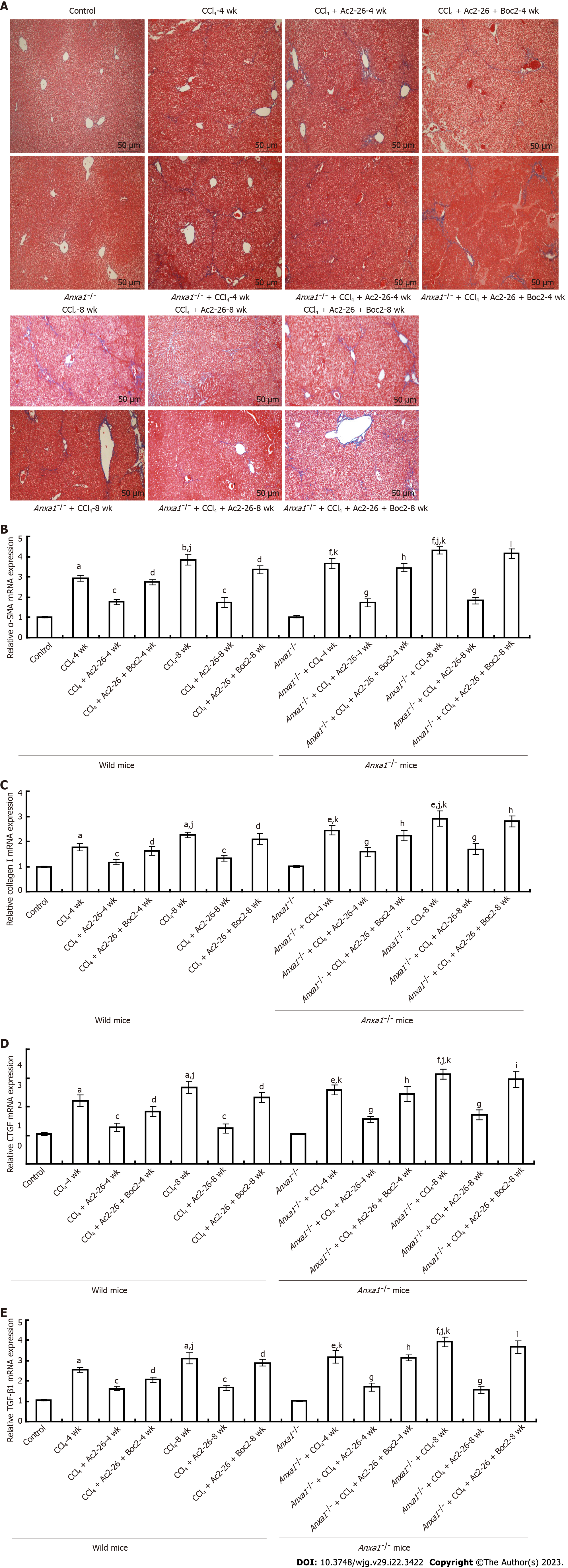
Figure 3 Annexin A1 inhibits CCl4 induced hepatic stellate cell activation in liver tissue.
A: Annexin A1 (AnxA1) inhibited collagen deposition induced by CCl4 in mouse liver tissue. Collagen was stained blue by Masson staining. The collagen content in the liver tissues in the control group was low, while collagen deposition in the liver of the CCl4-induced model group was high. Collagen deposition in the liver of the AnxA1-/- model group was significantly aggravated compared with that in the wild-type model group. Active N-terminal peptide of AnxA1 (Ac2-26) significantly reduced collagen deposition in the CCl4-induced model group, and the collagen deposition in the mice after the intervention of Ac2-26 + N-formylpeptide receptor antagonist N-Boc-Phe-Leu-Phe-Leu-Phe was similar to that in the CCl4-induced model group. Initial magnification: 100 ×; B: Effect of Ac2-26 on α-smooth muscle actin mRNA expression; C: Effect of Ac2-26 on collagen I mRNA expression; D: Effect of Ac2-26 on connective tissue growth factor mRNA expression; E: Effect of Ac2-26 on transforming growth factor-β1 mRNA expression; total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent and relative mRNA concentration was quantified using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (n = 8). Results are presented as ratios of target mRNA or protein normalized to internal GAPDH. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs CCl4; dP < 0.05 vs CCl4 + Ac2-26; eP < 0.05 and fP < 0.01 vs AnxA1-/- + control; gP < 0.05 vs AnxA1-/- + CCl4; hP < 0.05 and iP < 0.01 vs AnxA1-/- + CCl4 + Ac2-26; jP < 0.05 vs intra-group; kP < 0.05 vs inter-group. Ac2-26: Active N-terminal peptide of AnxA1; AnxA1: Annexin A1; Boc2: N-formyl peptide receptor antagonist N-Boc-Phe-Leu-Phe-Leu-Phe; CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor β1.
- Citation: Fan JH, Luo N, Liu GF, Xu XF, Li SQ, Lv XP. Mechanism of annexin A1/N-formylpeptide receptor regulation of macrophage function to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(22): 3422-3439
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i22/3422.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3422