Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2023; 29(22): 3422-3439
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3422
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3422
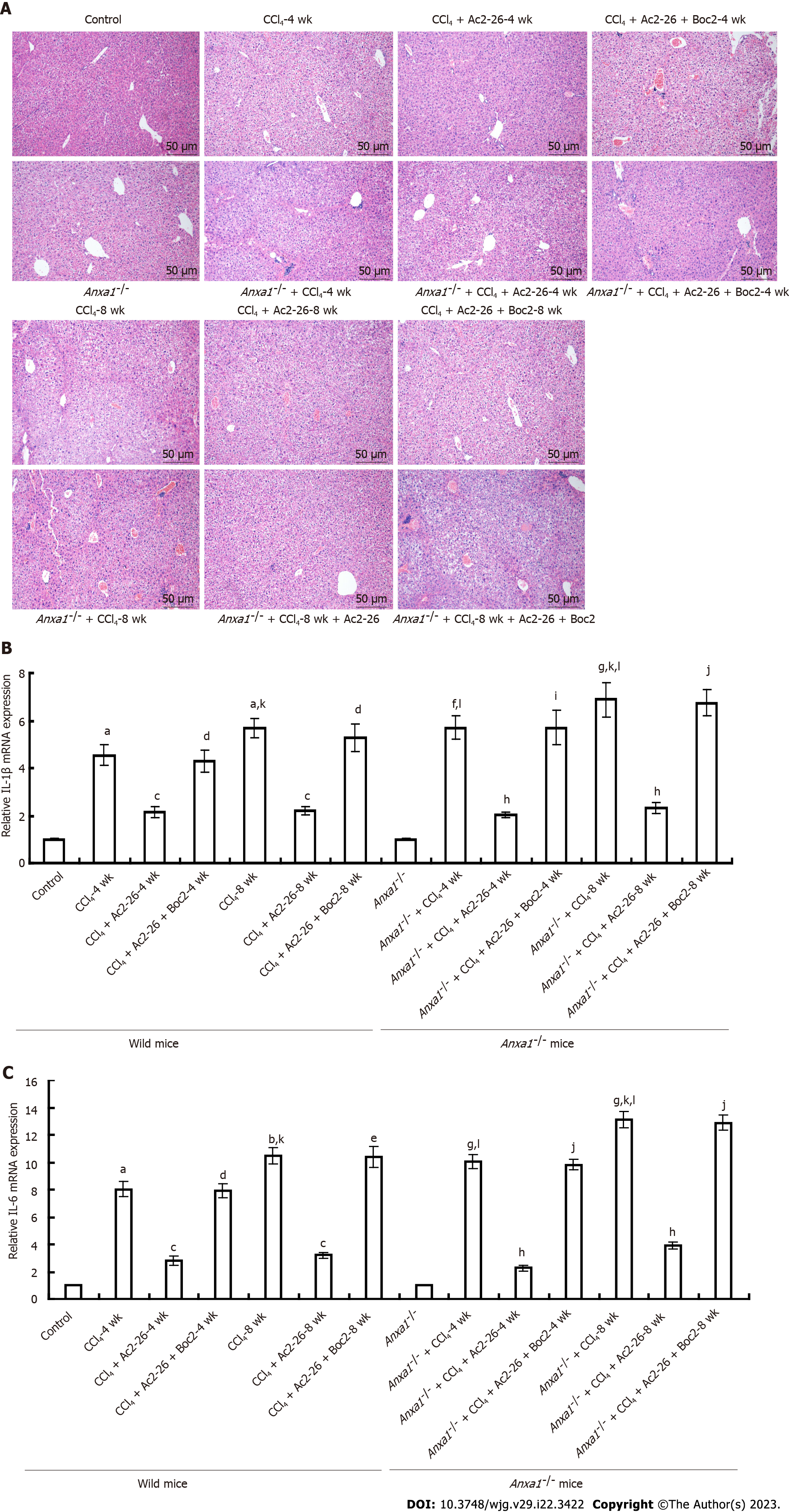
Figure 2 Annexin A1 inhibits CCl4-induced hepatic inflammatory cytokines release.
A: Annexin A1 (AnxA1) inhibited CCl4-induced liver injury and inflammatory cell infiltration in mice. Normal mouse liver lobule structure was clear, with no obvious vacuole formation or inflammatory cell infiltration. In the wild-type model group, hepatic lobules were severely damaged; a large number of hepatic nuclei were shrunken, hepatocytes were vacuolated, and inflammatory cells infiltrated. AnxA1-/- mice had more severe vacuolation and extensive inflammatory cell infiltration than wild-type mice had. After treatment with active N-terminal peptide of AnxA1 (Ac2-26), the damage to hepatic lobules was reduced, hepatocyte vacuolation was reduced but necrosis was observed, clusters of regenerated hepatocytes were observed in some tissues, and inflammatory cell infiltration was also reduced. N-formylpeptide receptor antagonist N-Boc-Phe-Leu-Phe-Leu-Phe almost reversed the therapeutic effect of Ac2-26, but the inflammatory infiltration and damage to hepatic lobule structure were not significantly improved. Initial magnification: 200 ×; B: Effect of Ac2-26 on interleukin (IL)-1β mRNA expression; C: Effect of Ac2-26 on IL-6 mRNA expression; total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent and relative concentration of mRNA was quantified using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (n = 8). Results are presented as ratios of target mRNA or protein normalized to internal GAPDH. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs CCl4; dP < 0.05 and eP < 0.01 vs CCl4 + Ac2-26; fP < 0.05 and gP < 0.01 vs AnxA1-/- + control; hP < 0.05 vs AnxA1-/- + CCl4; iP < 0.05 and jP < 0.01 vs AnxA1-/- + CCl4 + Ac2-26; kP < 0.05 vs intra-group; lP < 0.05 vs inter-group. Ac2-26: Active N-terminal peptide of AnxA1; AnxA1: Annexin A1; Boc2: N-formyl peptide receptor antagonist N-Boc-Phe-Leu-Phe-Leu-Phe; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Fan JH, Luo N, Liu GF, Xu XF, Li SQ, Lv XP. Mechanism of annexin A1/N-formylpeptide receptor regulation of macrophage function to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(22): 3422-3439
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i22/3422.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3422