Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2023; 29(22): 3385-3399
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3385
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3385
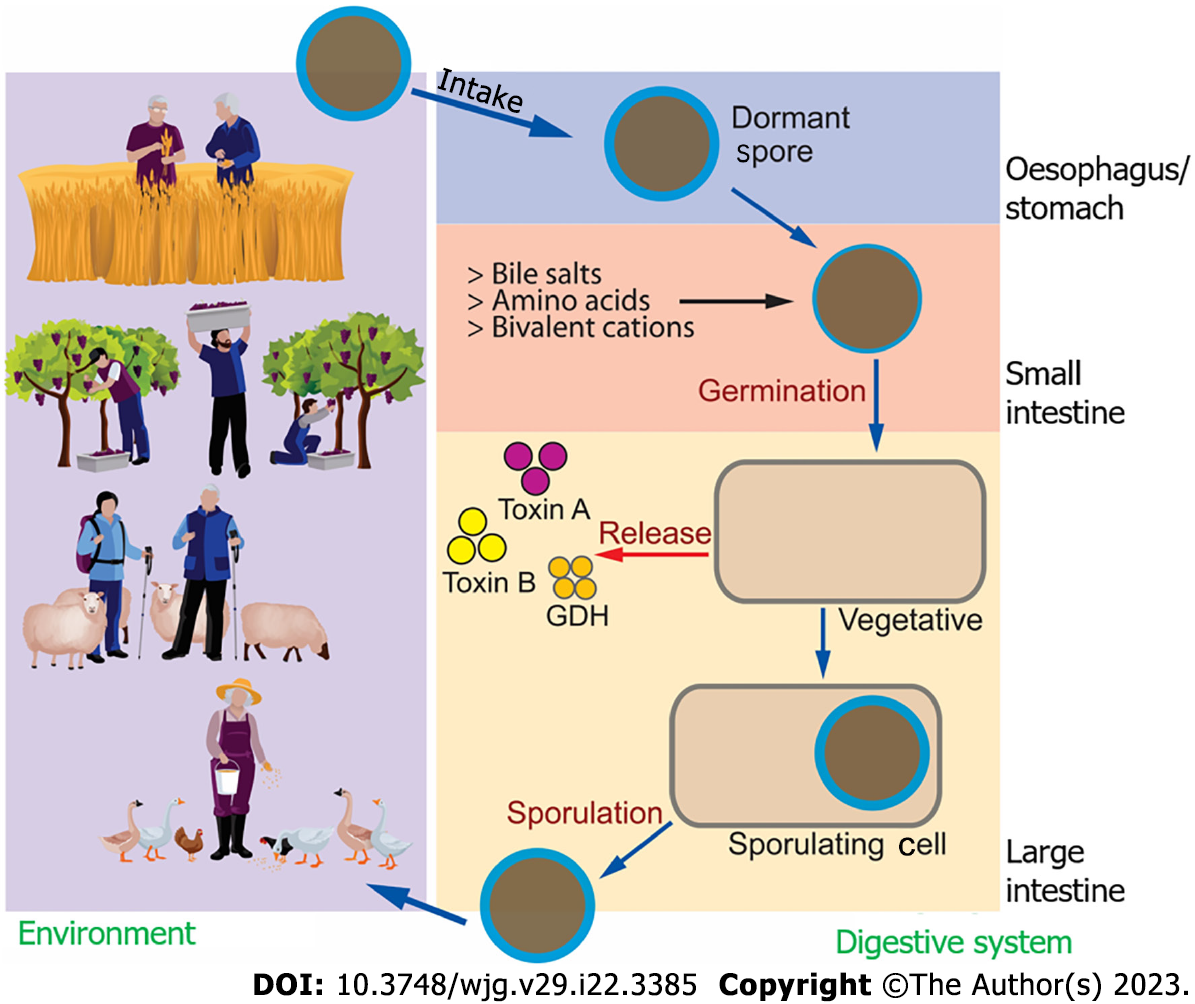
Figure 1 Clostridioidesdifficile life cycle.
Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile) can be found in soil and is transmitted to humans (as well as animals) through different daily activities. Besides hospital-acquired C. difficile infections, community-acquired C. difficile infections are also known, with agriculture being one of the main sources, from the spore stage into the human digestive system. Once stable, C. difficile may repopulate and release toxins that can affect intestinal health. C. difficile may go back to the environment and repeat the life cycle. GDH: Glutamate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Bocchetti M, Ferraro MG, Melisi F, Grisolia P, Scrima M, Cossu AM, Yau TO. Overview of current detection methods and microRNA potential in Clostridioides difficile infection screening. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(22): 3385-3399
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i22/3385.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3385