Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2023; 29(18): 2733-2746
Published online May 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i18.2733
Published online May 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i18.2733
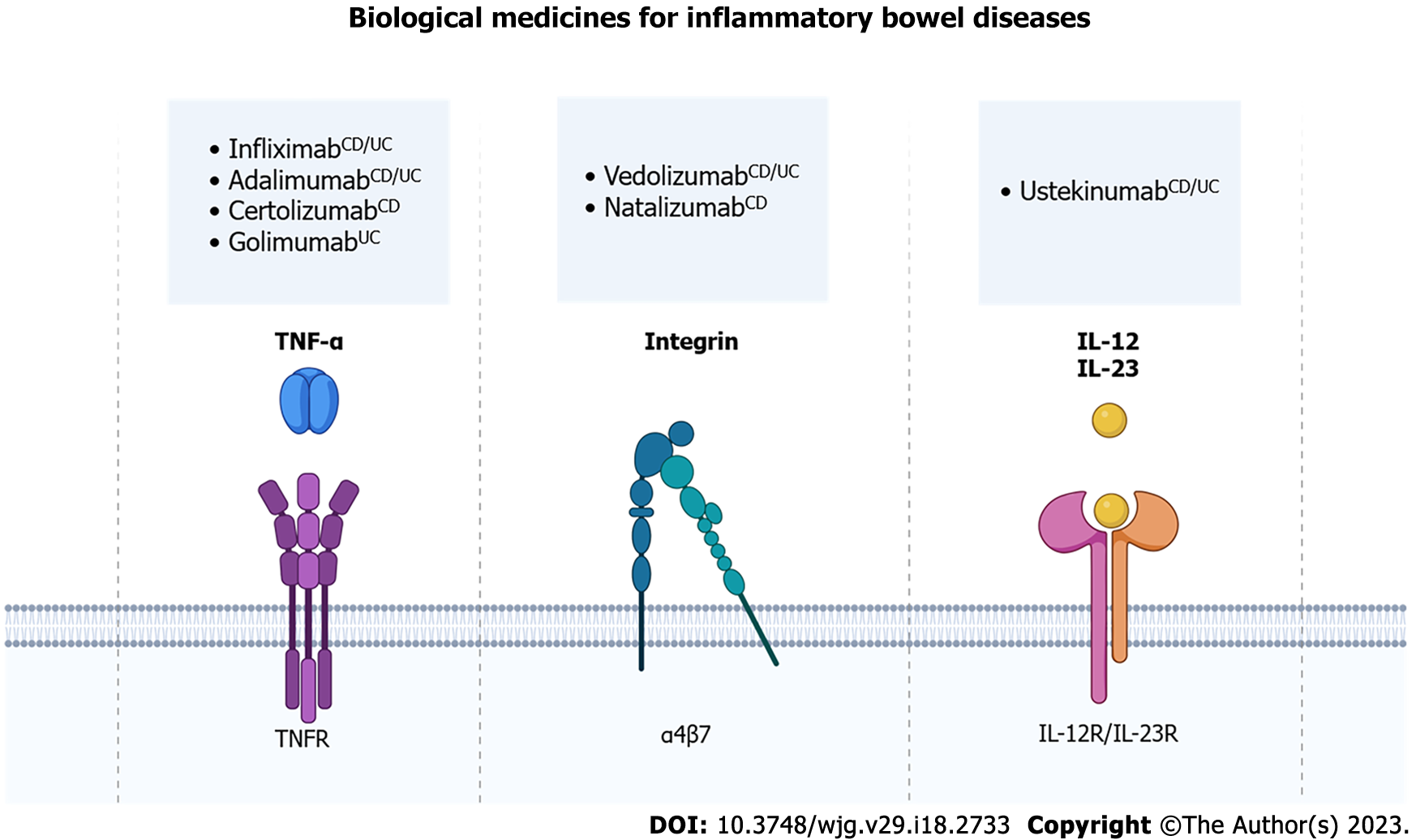
Figure 2 Biological medicines for inflammatory bowel diseases.
Biological medicines used for the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) can be classified into anti- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, anti-integrin and anti-interleukin therapies. Anti-TNF-α binds to TNF-α and inhibits TNF receptor activation. Infliximab, adalimumab, certolizumab pegol and golimumab are examples of anti-TNF-α used in the treatment of IBD. Vedolizumab and natalizumab are anti-integrin agents, which bind to the α4β7 integrin and prevent the migration of inflammatory cells into the intestinal tissue. Ustekinumab is an anti-interleukin that blocks interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23, which cannot bind to IL-12 receptor and IL-23 receptor on T and B lymphocytes, thus reducing the inflammatory response in the gut. CDindication only for Crohn’s Disease; UCindication only for Ulcerative Colitis; CD/UCindication both for Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL: Interleukin. Created with BioRender.com.
- Citation: Souza RF, Caetano MAF, Magalhães HIR, Castelucci P. Study of tumor necrosis factor receptor in the inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(18): 2733-2746
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i18/2733.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i18.2733