Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2022; 28(46): 6551-6563
Published online Dec 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6551
Published online Dec 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6551
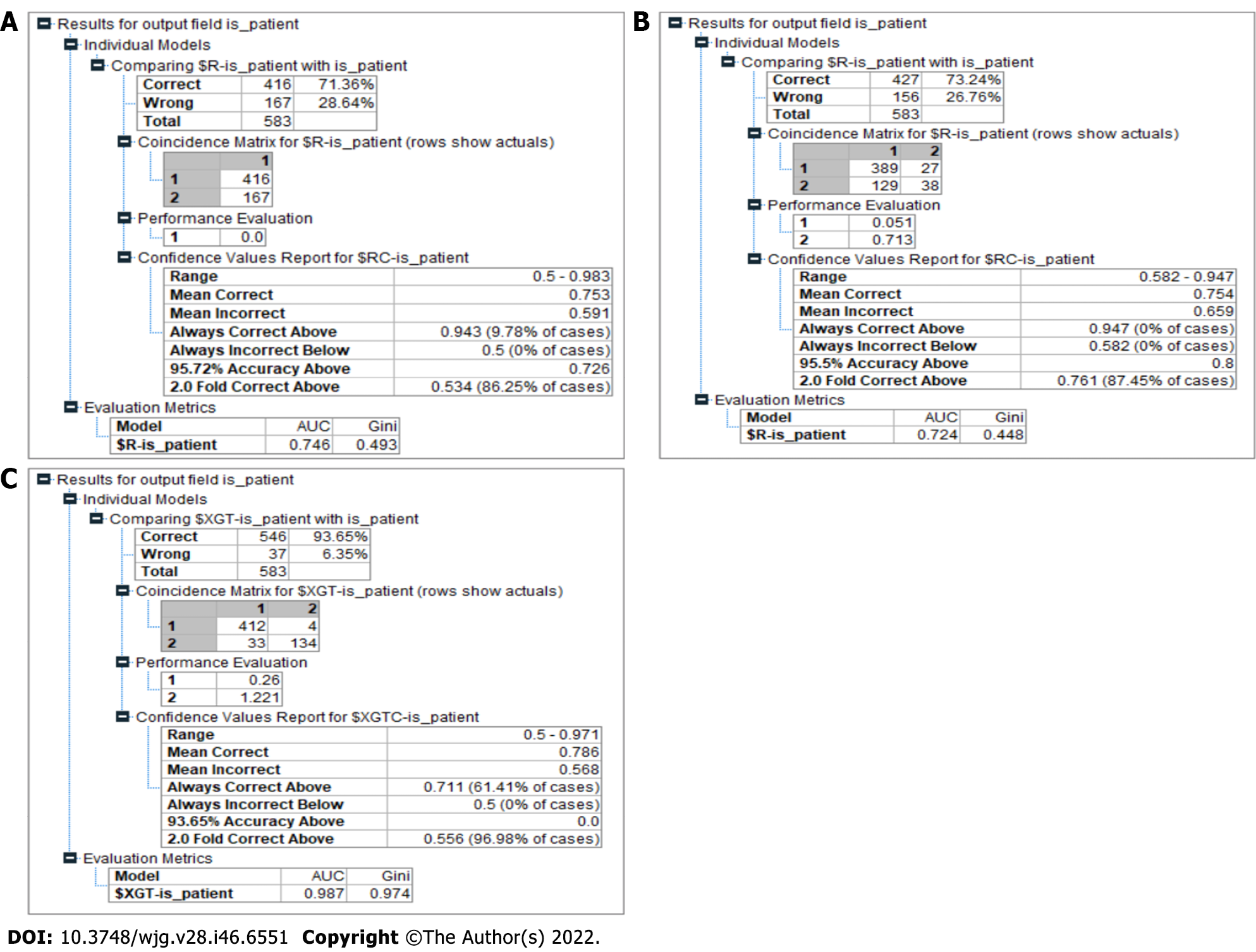
Figure 8 Model results.
A: Chi-square automated interaction detection (CHAID) results. The CHAID model had 71.36% accuracy in predicting liver disease. The area under the curve (AUC) and Gini values of this model were 0.746 and 0.493, respectively; B: Classification and regression tree results. The result for the classification and regression tree model showed a better accuracy at predicting the liver disease compared to the CHAID model at 73.24%. The AUC and Gini values of this model were 0.724 and 0.4448, respectively; C: Proposed model results. The model produced an accuracy of 93.65% in predicting liver disease, outperforming the other models significantly. It also recorded a Gini index of 0.97, categorizing it as a highly efficient model in making the distinction between a patient who has liver disease and a patient who is healthy in the given context.
- Citation: Dalal S, Onyema EM, Malik A. Hybrid XGBoost model with hyperparameter tuning for prediction of liver disease with better accuracy. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(46): 6551-6563
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i46/6551.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i46.6551