Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2022; 28(45): 6314-6327
Published online Dec 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i45.6314
Published online Dec 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i45.6314
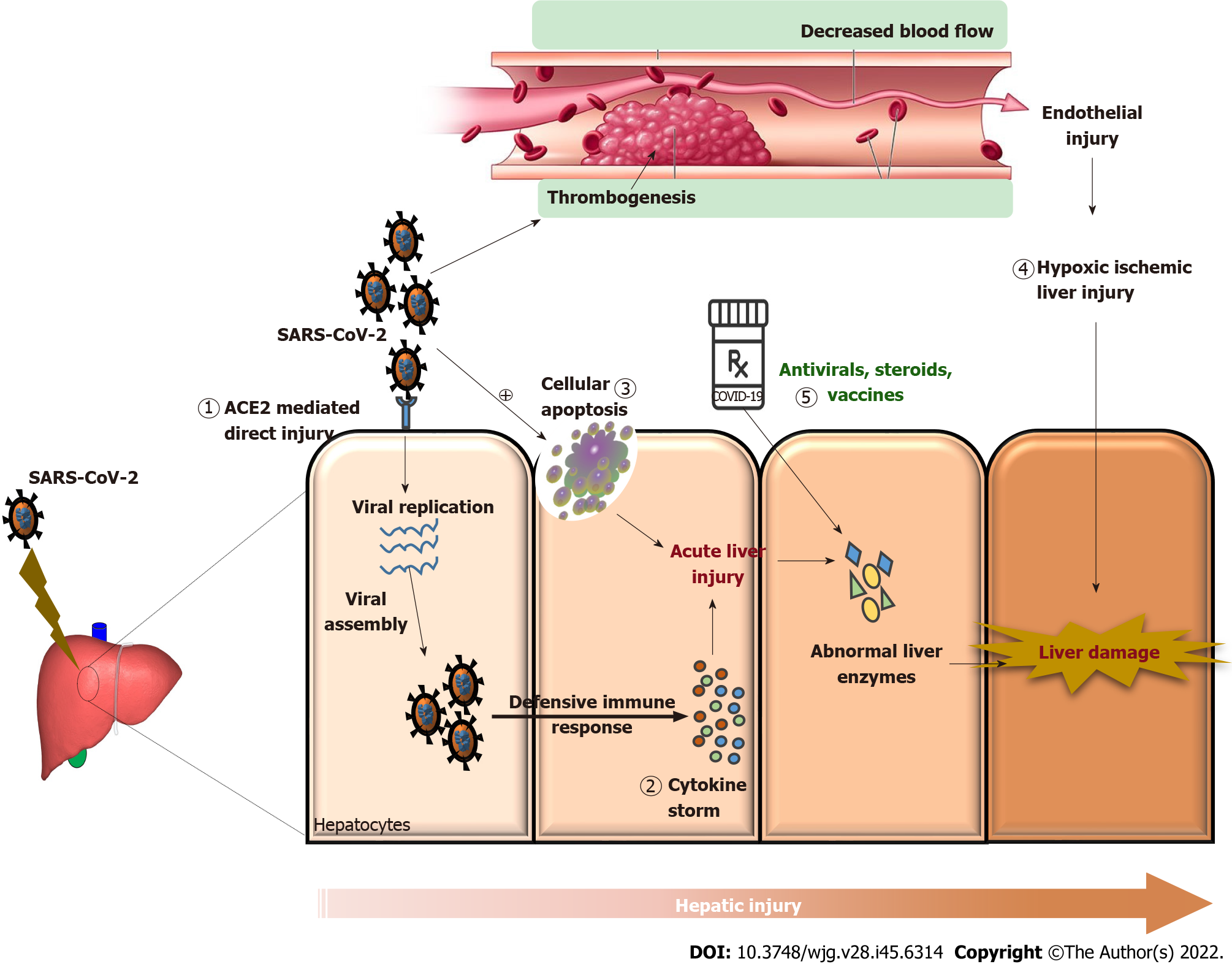
Figure 1 Molecular mechanisms of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and coronavirus disease 2019 drug-induced liver injury.
1: Direct action of the virus, i.e., angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor mediated action; 2: Immuno-inflammation caused by cytokine storm leading to liver damage; 3: Hepatocellular apoptosis induced by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection; 4: SARS-CoV-2-induced thrombosis leading to vascular endothelial damage and causing hypoxic-ischemic liver injury; 5: Several drugs and therapies used to counteract coronavirus disease 2019 including antivirals, immunomodulatory agents, and vaccines reportedly led to abnormal liver enzymes causing drug-induced liver injury. All these mechanisms aggravate liver injury by causing abnormal liver enzymes like increasing the levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate transaminase, alkaline phosphate, gamma-glutamyl transferase, lactate dehydrogenase, and total bilirubin and reducing the albumin levels. ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme-2; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019.
- Citation: Saha L, Vij S, Rawat K. Liver injury induced by COVID 19 treatment – what do we know? World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(45): 6314-6327
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i45/6314.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i45.6314