Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2022; 28(34): 5007-5022
Published online Sep 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.5007
Published online Sep 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.5007
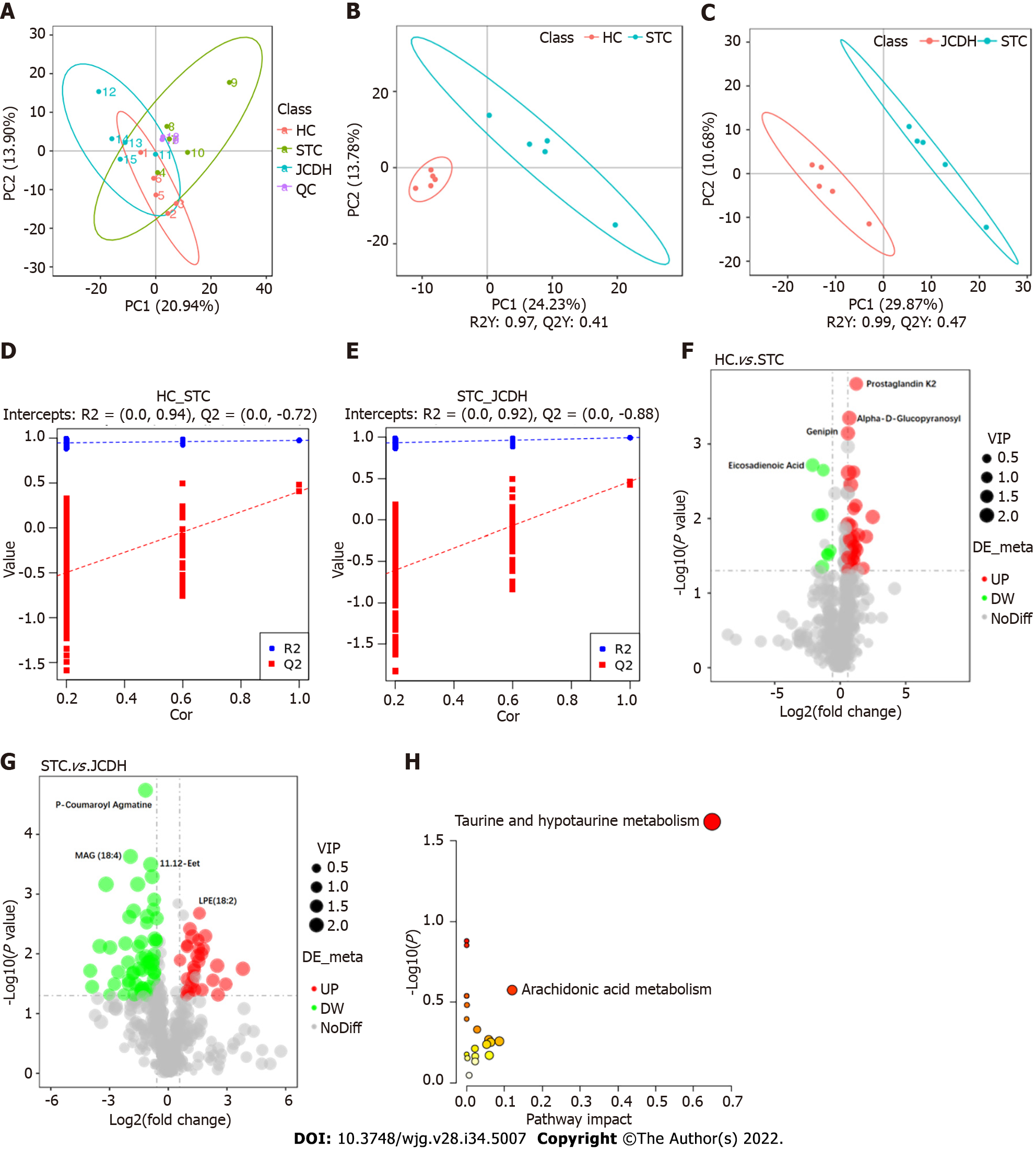
Figure 3 Different intestinal metabolites detected by ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry.
A: Principal component analysis; B: Orthogonal partial least squares discrimination analysis score plots of intestinal metabolic profiling in the healthy control (HC) vs slow transit constipation (STC) groups; C: STC vs high-dose Ji-Chuan decoction (JCDH) treatment groups under negative ion mode; D: Permutation test in negative ion mode of the HC vs STC groups; E: Permutation test in negative ion modes of the STC vs JCDH groups; F: Volcano plot of the different metabolites between the STC and HC groups; G: Volcano plot of the different metabolites between the JCDH and STC groups; H: Critical metabolic pathways of the STC vs JCDH groups. HC: Healthy control; STC: Slow transit constipation; JCD: Ji-Chuan decoction; JCDL: Low-dose Ji-Chuan decoction treatment; JCDM: Middle-dose Ji-Chuan decoction treatment; JCDH: High-dose Ji-Chuan decoction treatment; MSP: Mosapride treatment; MAG: 1-(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z-Octadecatetraenoyl)-sn-glycerol; 11.12-EET: (5Z,8Z,14Z)-11,12-Epoxyeicosa-5,8,14-trienoic acid; LPE: 2-(9Z,12Z-octadecadienoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; QC: Quality control.
- Citation: Wang XM, Lv LX, Qin YS, Zhang YZ, Yang N, Wu S, Xia XW, Yang H, Xu H, Liu Y, Ding WJ. Ji-Chuan decoction ameliorates slow transit constipation via regulation of intestinal glial cell apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(34): 5007-5022
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i34/5007.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.5007