Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2022; 28(29): 3994-4006
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3994
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3994
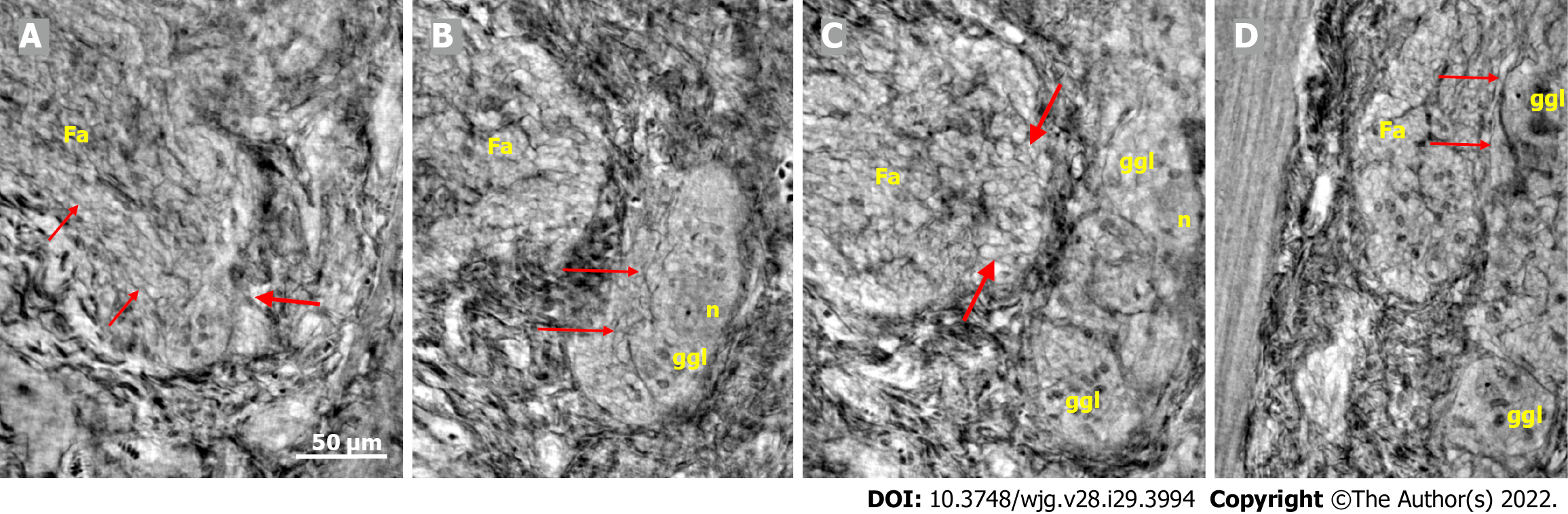
Figure 3 Series of virtual slices covering 113.
6 μm thickness at the border between the nerve fascicle and the ganglion. A: Thick fascicle with parallel telopodes (thin arrows). There is a small peripheral part of the ganglion (thick arrow); B: 62.2 μm deeper from Figure A. Connective tissue cells between the fascicle and the superficial part of the ganglion. Normal large neurons and nuclei of several glial cells in the ganglion. A network of telopodes is present on the surface of the ganglion (arrows); C: 11.5 μm deeper from Figure B. The thickness of the connective tissue is diminished between the fascicle and the periphery of the ganglion, with two neurons and small glial cells. Transversally cut vesicle-like axons (between the arrows) on the right end of the fascicle; D: 39.9 μm deeper from Figure C, the fascicle and ganglion are united. Thin arrows show telopodes. The scale bar (50 µm) applies to all the subfigures. Fa: Fascicle; ggl: Ganglion; n: Neuron.
- Citation: Veress B, Peruzzi N, Eckermann M, Frohn J, Salditt T, Bech M, Ohlsson B. Structure of the myenteric plexus in normal and diseased human ileum analyzed by X-ray virtual histology slices. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(29): 3994-4006
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i29/3994.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3994