Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2021; 27(9): 815-834
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.815
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.815
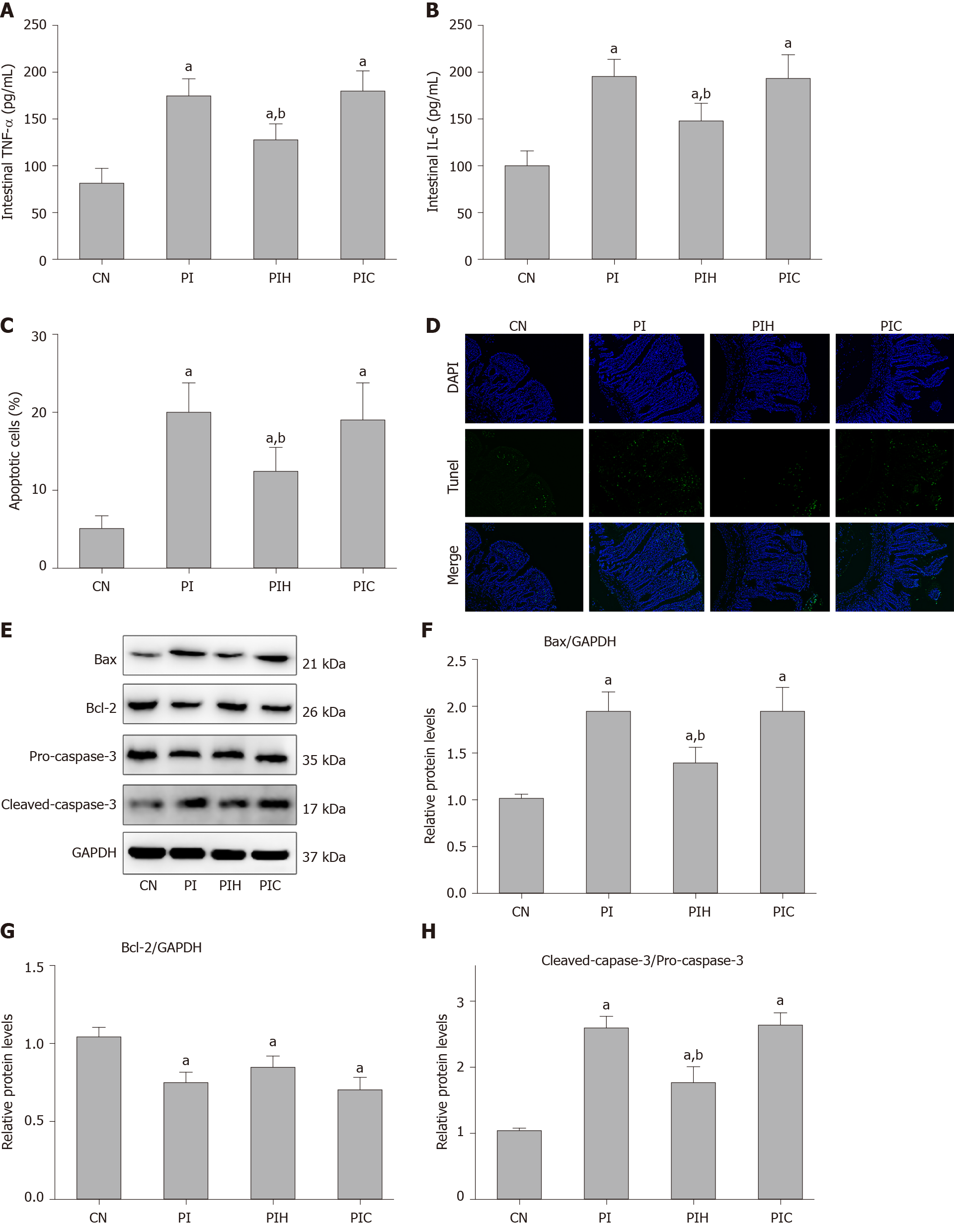
Figure 6 Effects of intraperitoneal pancreatitis-associated ascitic fluid injection with or without anti-high mobility group box protein 1 neutralizing antibody on intestinal inflammation and cell apoptosis in cerulein-treated rats.
A: Intestinal tumor necrosis factor-α; B: Intestinal interleukin-6; C: Statistical results of the number of apoptotic intestinal mucosal cells in each group; D: Representative images (400 × magnification) of terminal deoxynucleotidyl-transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay; E: Immunoblotting of Bax, Bcl-2, pro-caspase-3 and cleaved-caspase-3 protein expression from intestinal samples; F-H: Densitometry analysis of the immunoblotting data of apoptosis-related proteins in intestinal tissue. Data are expressed as means ± SD, n = 6 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and TUNEL assay results per group; means ± SD, n = 3 immunoblotting results per group. aP < 0.05 vs control group; bP < 0.05 vs pancreatitis-associated ascitic fluid group. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; CN: Control; PI: Pancreatitis-associated ascitic fluid (PAAF) injection; PIH: PAAF and 200 μg anti-high mobility group box protein 1 neutralizing antibody; PIC: PAAF + control lgY; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl-transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Huang SQ, Wen Y, Sun HY, Deng J, Zhang YL, Huang QL, Wang B, Luo ZL, Tang LJ. Abdominal paracentesis drainage attenuates intestinal inflammation in rats with severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting the HMGB1-mediated TLR4 signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(9): 815-834
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i9/815.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.815