Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2021; 27(30): 5060-5075
Published online Aug 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.5060
Published online Aug 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.5060
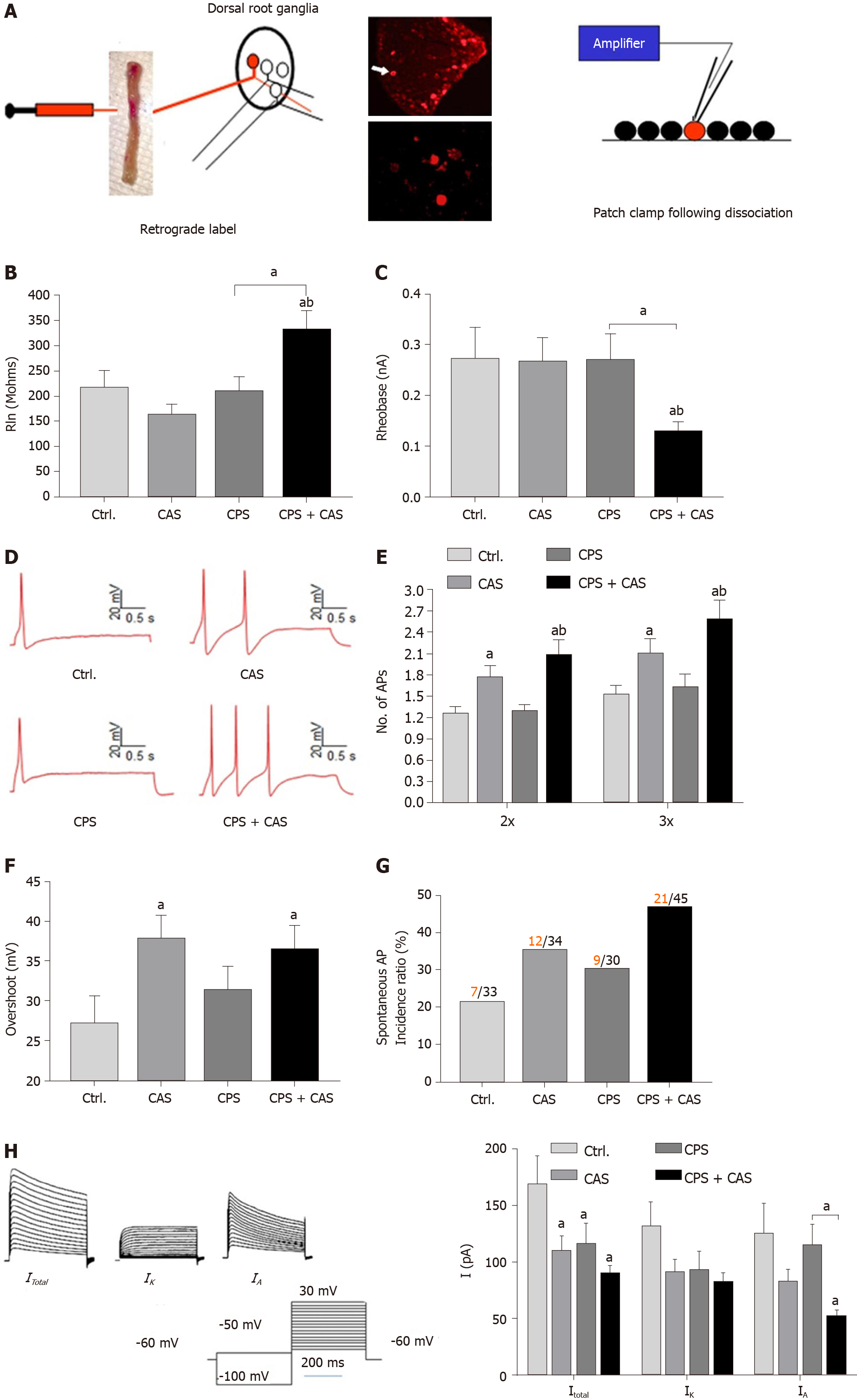
Figure 2 Patch clamp recording in colonic dorsal root ganglion neurons from female rats.
A: Patch clamp process of cell labeling. Under isoflurane anesthesia, the lipid soluble fluorescent dye 9-DiI was injected into muscularis externa of the exposed distal colon (left figure). Lumbosacral (L6–S2) dorsal root ganglions (upper photograph) were isolated and DiI-labeled neurons were identified by fluorescence microscopy (lower photograph). Electrophysiological properties of each neuron were measured using whole-cell current and voltage clamp protocols (right figure); B: Rheobase from all four experimental groups (n = 5 rats, 45 cells in each group, one-way ANOVA, aP < 0.05 vs control or bP < 0.05 vs CAS); C: Representative action potentials (APs) elicited by current injection at 2 × the rheobase in neurons from control, chronic adult stress (CAS), chronic prenatal stress (CPS) and CPS + CAS female rats; D: Membrane input resistance from all four groups (n = 5 rats, 45 cells in each group, one-way ANOVA, aP < 0.05 vs control; bP < 0.05 vs CPS); E: Number of APs elicited by current injection at either 2 × and 3 × the rheobase in all four experimental groups (two-way ANOVA, aP < 0.05 vs control; bP < 0.05 vs CPS); F: AP overshoot recorded from all four experimental groups (aP < 0.05 vs control); G: The proportion of neurons from each experimental group exhibiting spontaneous APs. Red numbers represent spontaneous AP firing cells; black numbers represent total cells; H: Representative total, IK and IA current tracings and average values of potassium currents: Itotal, IK and IA are shown in female CPS + CAS, CAS, CPS (n = 15 neurons, from 5 rats in each group), and control groups (n = 12 neurons from 5 rats); two-way ANOVA, aP < 0.05 vs each control group.
- Citation: Chen JH, Sun Y, Ju PJ, Wei JB, Li QJ, Winston JH. Estrogen augmented visceral pain and colonic neuron modulation in a double-hit model of prenatal and adult stress. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(30): 5060-5075
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i30/5060.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.5060