Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2021; 27(18): 2054-2072
Published online May 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2054
Published online May 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2054
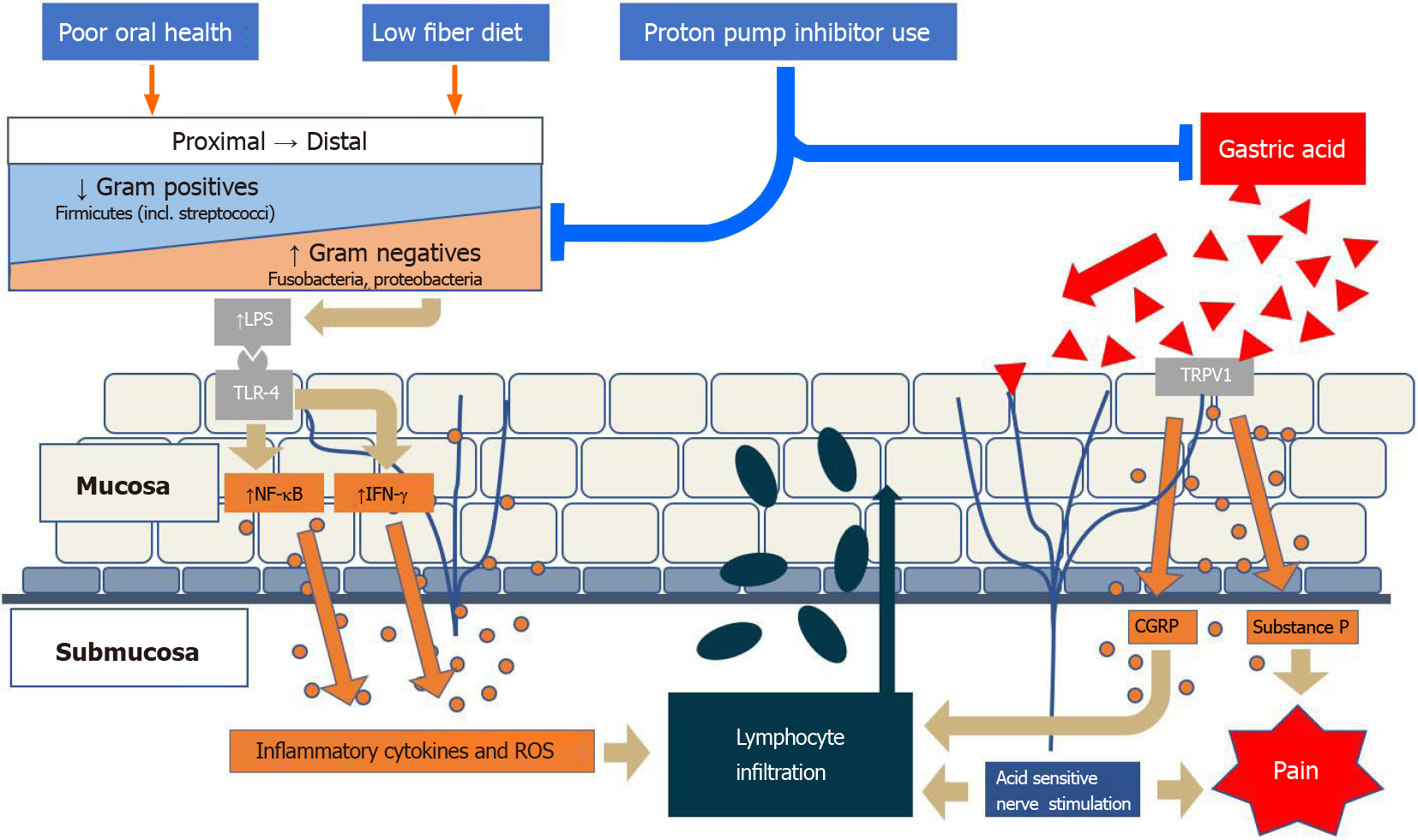
Figure 1 Environmental factors alter the local esophageal microbiome, which normally has a gram-positive to gram-negative gradient, towards increased proportion of gram-negatives.
Activation of Toll-like-receptor-4 by gram-negative lipopolysaccharide leads towards an inflammatory cascade that results in lymphocyte infiltration. In addition, gastric acid activates transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 on local nerve fibers and results in calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P expression, which contributes to the local inflammatory response as well as pain. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; TLR: Toll-like-receptor; NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa beta; IFN: Interferon; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TRPV1: Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1; CGRP: Calcitonin gene-related peptide.
- Citation: D'Souza SM, Houston K, Keenan L, Yoo BS, Parekh PJ, Johnson DA. Role of microbial dysbiosis in the pathogenesis of esophageal mucosal disease: A paradigm shift from acid to bacteria? World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(18): 2054-2072
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i18/2054.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2054