Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2020; 26(45): 7153-7172
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7153
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7153
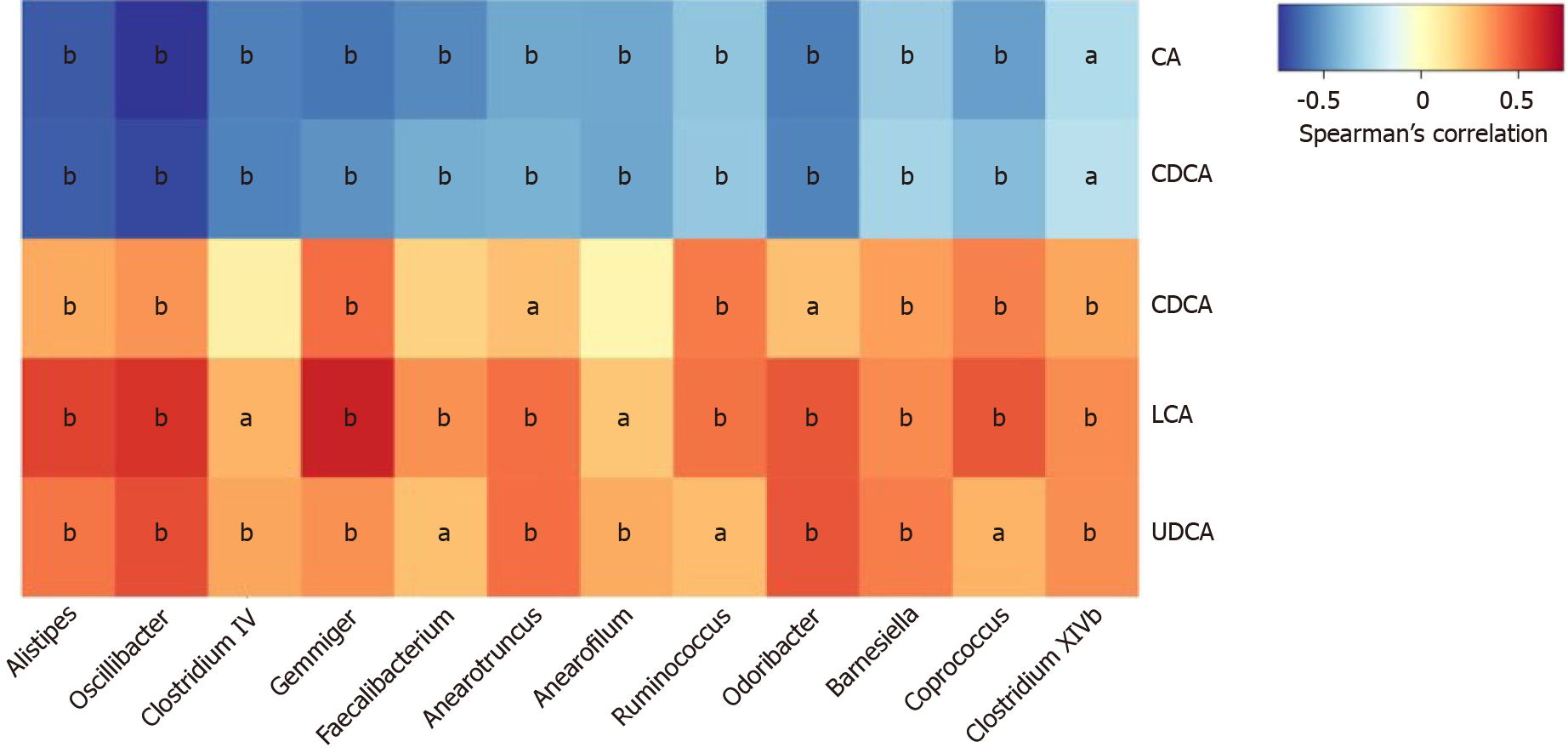
Figure 5 Correlations between fecal bile acids and microbiota composition in all subjects.
The heatmap presents the Spearman correlation coefficients between unconjugated fecal bile acids and the distinguishing genera in all subject. Seven genera belong to the family Ruminococcaceae (Oscillibacter, Clostridium IV, Gemmiger, Anaerofilum, Anaerotruncus, Faecalibacterium, and Ruminococcus); one genus belongs to the family Rikenellaceae (Alistipes); two genera belong to the family Porphyromonadaceae (Odoribacter and Barnesiella); two genera belong to the family Lachnospiraceae (Coprococcus and Clostridium XlVb). All of the genera were decreased significantly in the IBS-D group except for Ruminococcus. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. CA: Cholic acid; CDCA: Chenodeoxycholic acid; DCA: Deoxycholic acid; LCA: Lithocholic acid; UDCA: Ursodeoxycholic acid.
- Citation: Wei W, Wang HF, Zhang Y, Zhang YL, Niu BY, Yao SK. Altered metabolism of bile acids correlates with clinical parameters and the gut microbiota in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(45): 7153-7172
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i45/7153.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7153