Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2020; 26(36): 5420-5436
Published online Sep 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i36.5420
Published online Sep 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i36.5420
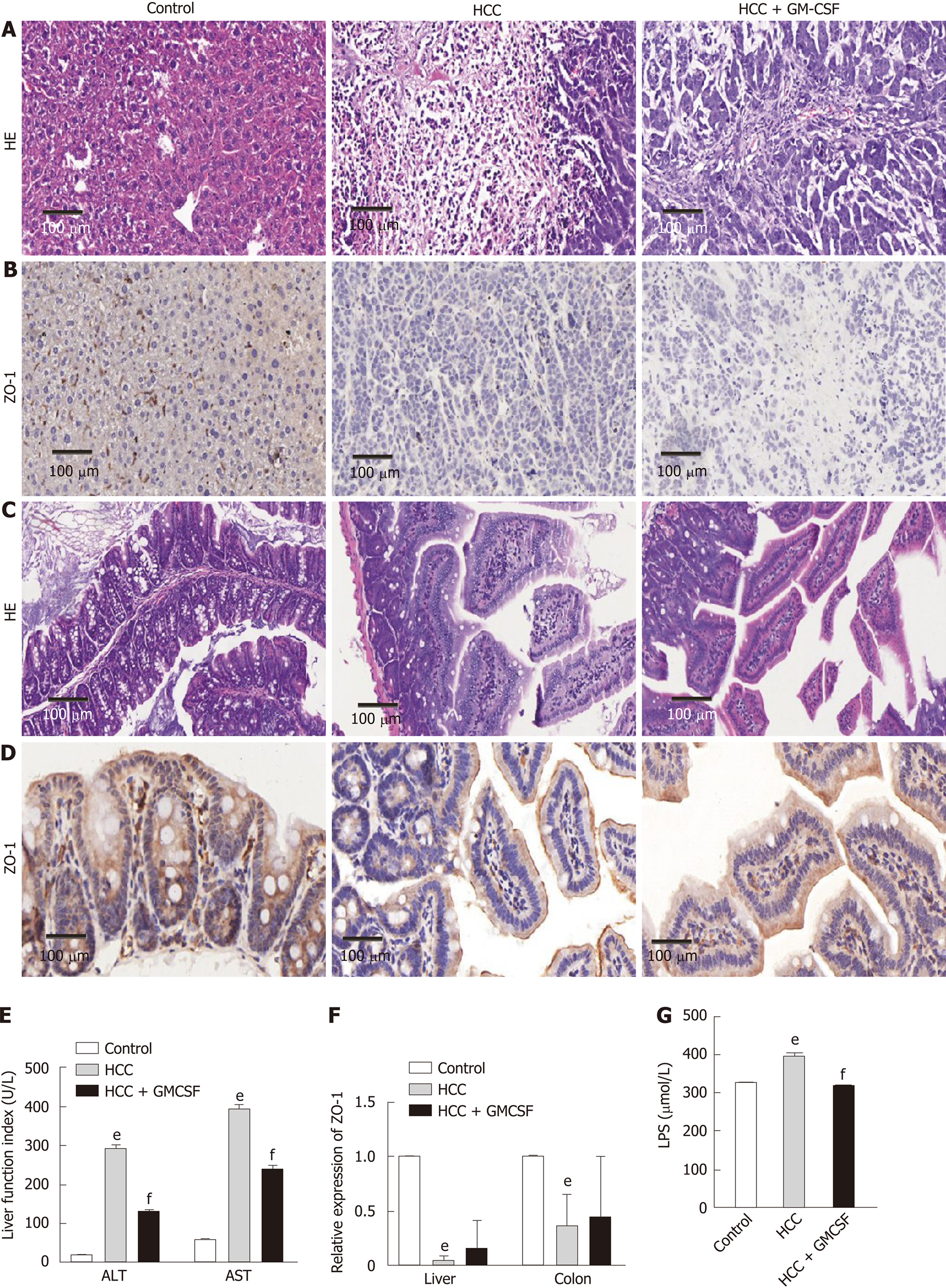
Figure 1 Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor alleviated hepatic injury, normalized liver function, improved intestinal barrier function, and reduced serum endotoxin levels detected in response to hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Liver histology was assessed by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, scale bar: 200 μm (200 ×); B: Liver histology was assessed via ZO-1 immunohistochemical staining (scale bar, 200 μm); C: Colon histology was assessed via H&E staining, scale bar: 200 μm (400 ×); D: Colon histology was assessed via ZO-1 immunohistochemical staining (scale bar, 200 μm); E: Serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) levels; F: Expression of the intestinal barrier function marker ZO-1 in the liver and colon; G: Serum lipopolysaccharide levels (µmol/L). Data are presented as the means ± SE, n = 11–13 mice per group detected via one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, and eP < 0.001, HCC vs control; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, and fP < 0.001, HCC + GM-CSF vs HCC. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin.
- Citation: Wu YN, Zhang L, Chen T, Li X, He LH, Liu GX. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor protects mice against hepatocellular carcinoma by ameliorating intestinal dysbiosis and attenuating inflammation. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(36): 5420-5436
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i36/5420.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i36.5420