Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2020; 26(21): 2781-2791
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2781
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2781
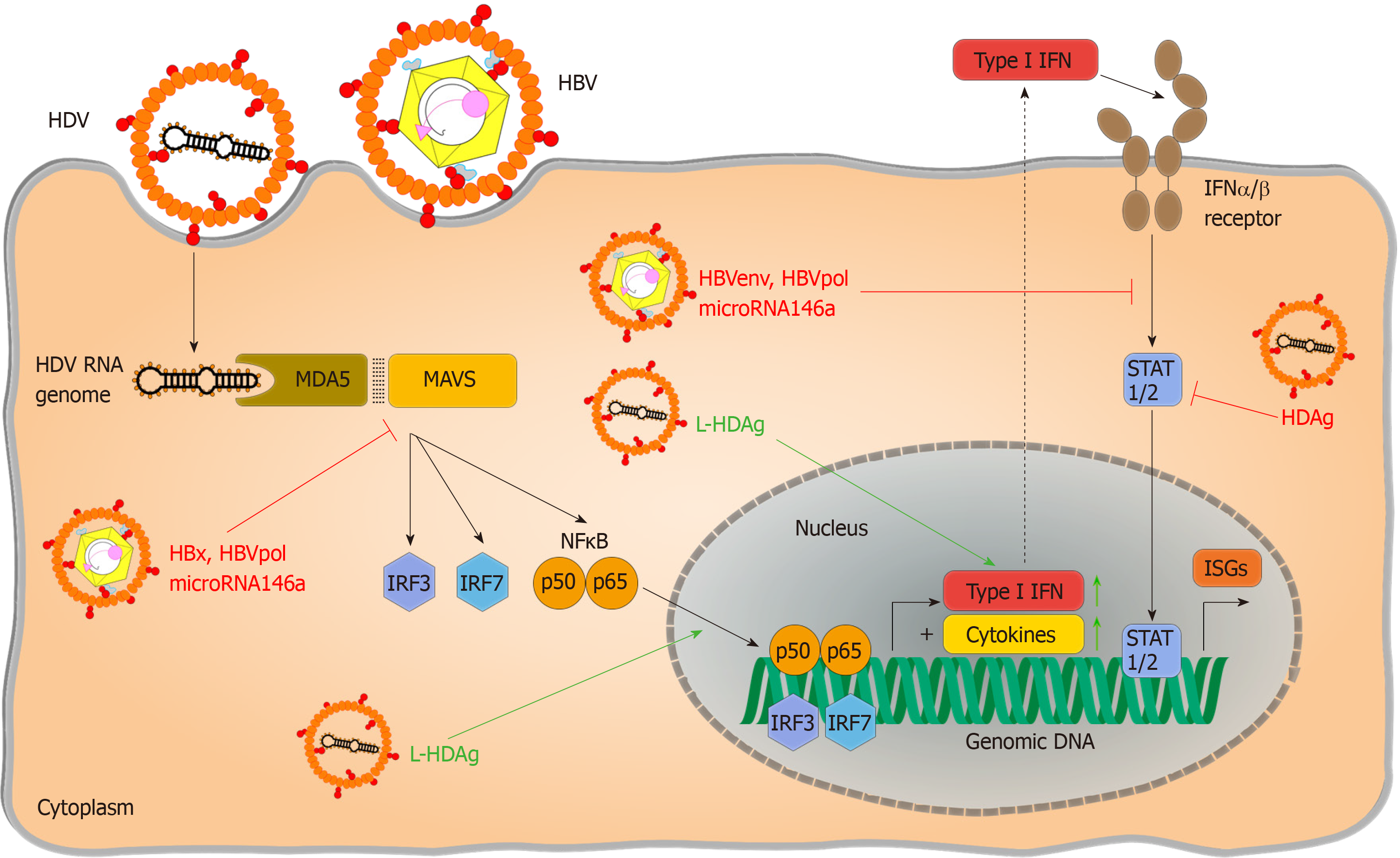
Figure 2 Immune evasion and immunomodulation in hepatitis D virus infection.
Pattern recognition of hepatitis D virus RNA was reported to be both inhibited by hepatitis B virus (HBV) specific proteins like HBV X protein, HBV envelope proteins, HBV polymerase as well as the hepatitis delta antigen and in particular its large variant. Inhibitions of major pathways are indicated with red flat arrows, activation of cytokine response is indicated in green pointed arrows. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HDV: Hepatitis D virus; HBx: Hepatitis B virus X protein; HBV env: Hepatitis B virus envelope proteins; HBV pol: Hepatitis B virus polymerase; HDAg: Hepatitis delta antigen; L-HDAg: Large hepatitis delta antigen; TLRs: Toll-like receptors; RIG I: Retinoic acid inducible gene I; LGP2: Laboratory of genetics and physiology 2; ssRNA: Single-stranded RNA; CTD: C-terminal domain; RLRs: RIG I like receptors; NF-κB: Nuclear factor “kappa-light-chain-enhancer” of activated B-cells; MAVS: Mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein; TIR: Toll/interleukin-1 receptor; dsRNA: Double-stranded RNA; MDA5: Melanoma differentiation antigen 5; CARDs: Caspase activation and recruitment domains; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; STAT1/2: Signal transducers and activators of transcription 1/2; Type I IFN: Type I interferon; ISGs: Interferon-stimulated genes.
- Citation: Jung S, Altstetter SM, Protzer U. Innate immune recognition and modulation in hepatitis D virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(21): 2781-2791
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i21/2781.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2781