Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2020; 26(18): 2177-2186
Published online May 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2177
Published online May 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2177
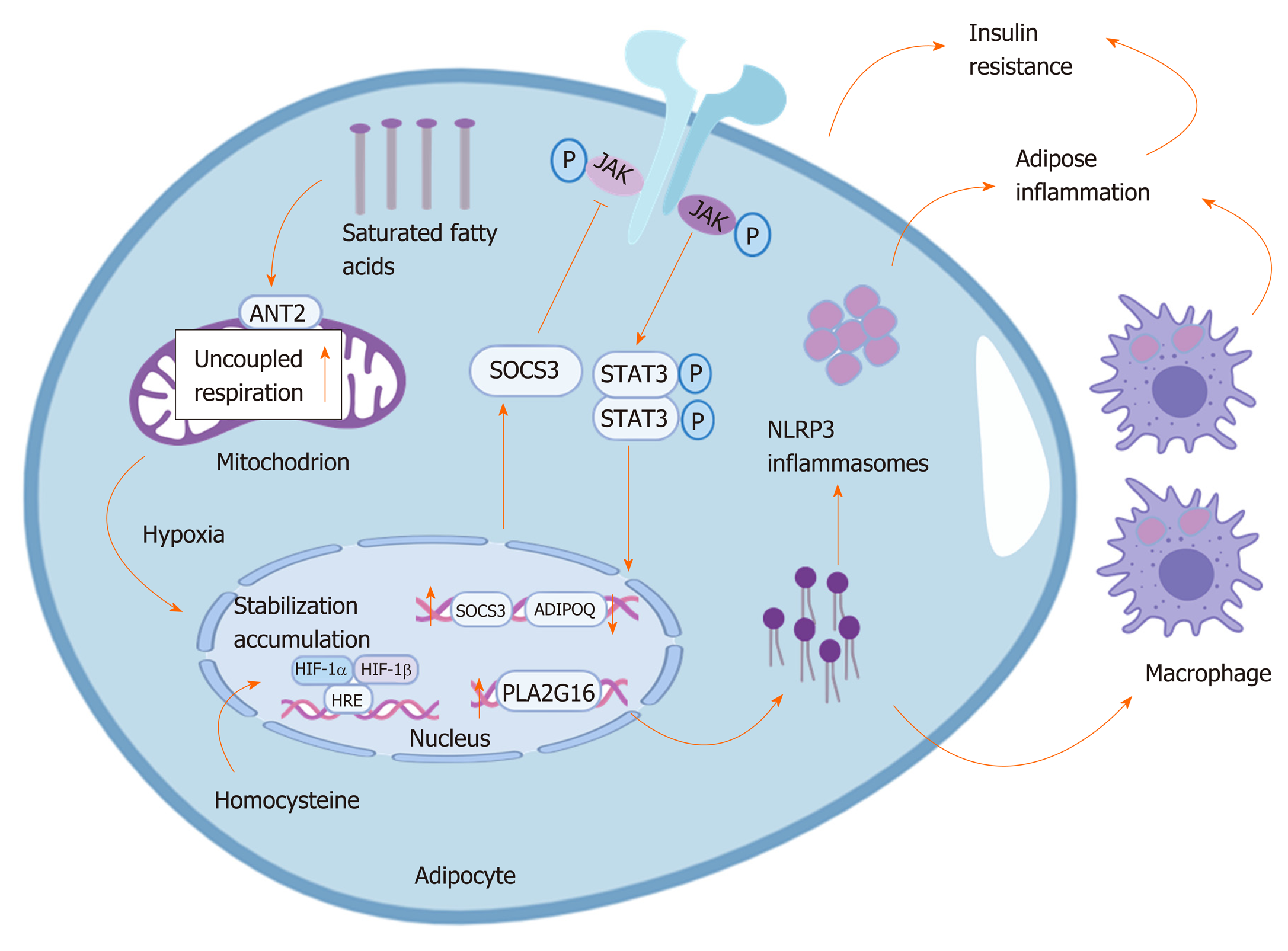
Figure 1 Accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α induces insulin resistance in hypoxic adipocytes.
Owing to excess saturated fatty acids binding to adenosine diphosphate/adenosine-triphosphate translocase 2 in mitochondria, which increases uncoupled respiration leading to hypoxia in adipose tissue, the stabilized and accumulated hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) further regulates relative target genes. On the one hand, HIF-1α induces expression of suppressor of cytokine signalling 3, which in turn activates signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, and dimerized signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 enters the cell nucleus and inhibits the transcription of ADIPOQ, resulting in insulin resistance. On the other hand, HIF-1α up-regulates the expression of pla2g16 to increase the level of lyso-PC, which in turn activates NLRP3 inflammasomes and stimulates NLRP3 inflammasomes in macrophages of adipose tissue, promoting insulin resistance. ANT2: Adenosine diphosphate/adenosine-triphosphate translocase 2; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; SOCS3: Suppressor of cytokine signalling 3; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; HRE: Hypoxia-inducible factor regulating element; P: Phosphate; lyso-PC: Lyso-phosphatidylcholine.
- Citation: Xia QS, Lu FE, Wu F, Huang ZY, Dong H, Xu LJ, Gong J. New role for ceramide in hypoxia and insulin resistance. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(18): 2177-2186
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i18/2177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2177