Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2019; 25(5): 567-583
Published online Feb 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i5.567
Published online Feb 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i5.567
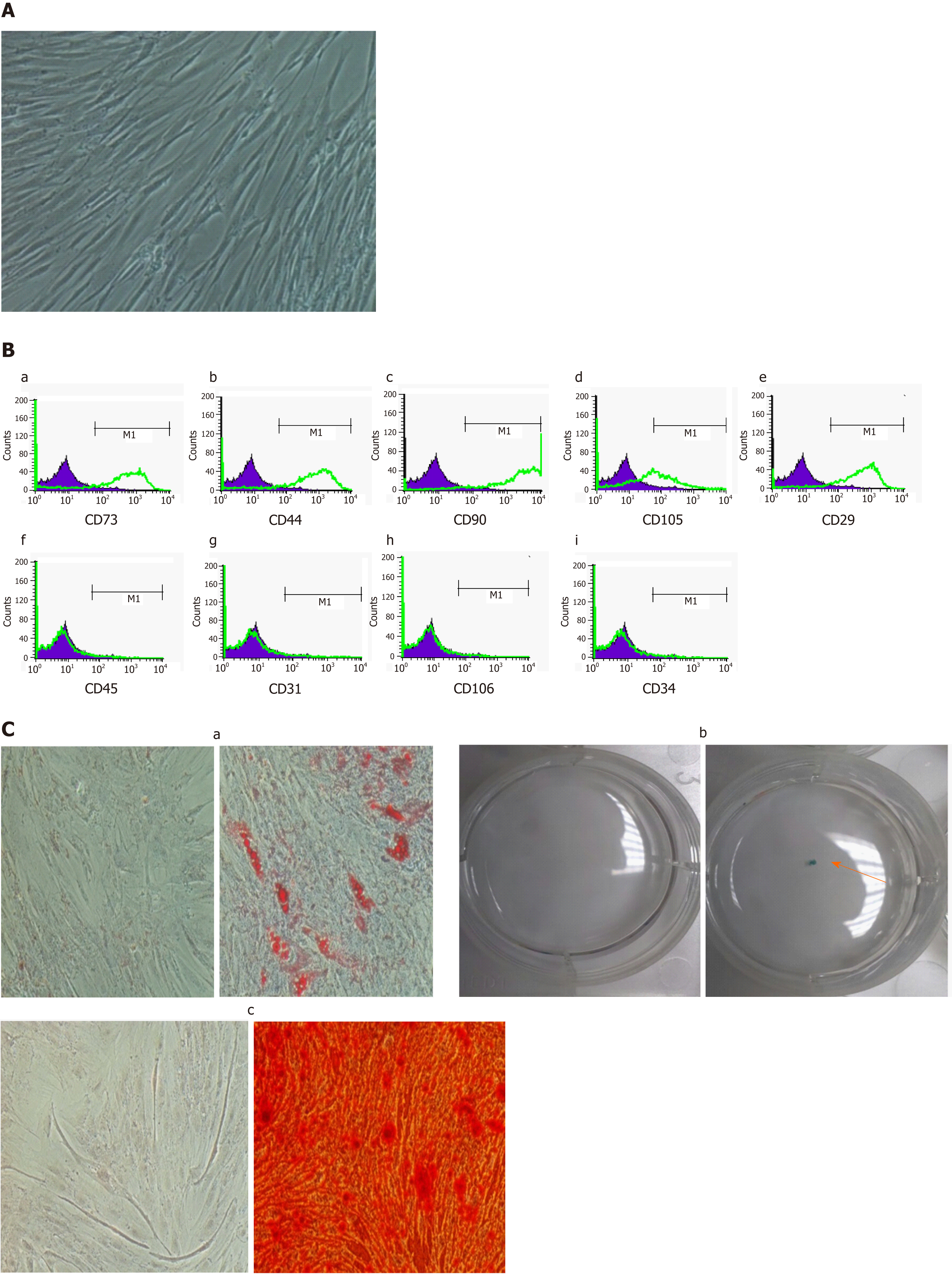
Figure 1 Characterization of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Microscopic observation (magnification 100 ×) showed that isolated ADMSCs have a fibroblast-like morphology; B: Immunophenotyping of ADMSCs using flow cytometry analysis. The flow cytometry histograms of the ADMSCs at passage 1 for a representative donor are displayed. The percentage of positively stained cells is indicated in the middle right section of each histogram. The green line indicates the positively stained cells; whereas the purple line indicates the isotype-matched monoclonal antibody control. Histograms showed that ADMSCs were positive for (B-a) CD73, (B-b) CD44, (B-c) CD90, (B-d) CD105, (B-e) CD29, and were negative for (B-f) CD45, (B-g) CD31, (B-h) CD106, (B-i) CD34; C: Differentiation capacity of ADMSCs incubated for 3 wk in adipogenic, chondrogenic and osteogenic medium. (C-a) Representative images of adipogenic differentiation marked by the formation of intracellular lipid droplets colored using Oil Red O compared to control. (C-b) Solid chondrogenic micromass colored by Alcian blue, indicating the presence of glycosaminoglycans. (C-c) Representative images of osteogenic differentiation confirmed by the presence of calcium deposits colored by Alizarin Red. All immunophenotyping and differentiation experiments were repeated four times. ADMSCs: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Serhal R, Saliba N, Hilal G, Moussa M, Hassan GS, El Atat O, Alaaeddine N. Effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on hepatocellular carcinoma: In vitro inhibition of carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(5): 567-583
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i5/567.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i5.567