Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2019; 25(44): 6527-6540
Published online Nov 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i44.6527
Published online Nov 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i44.6527
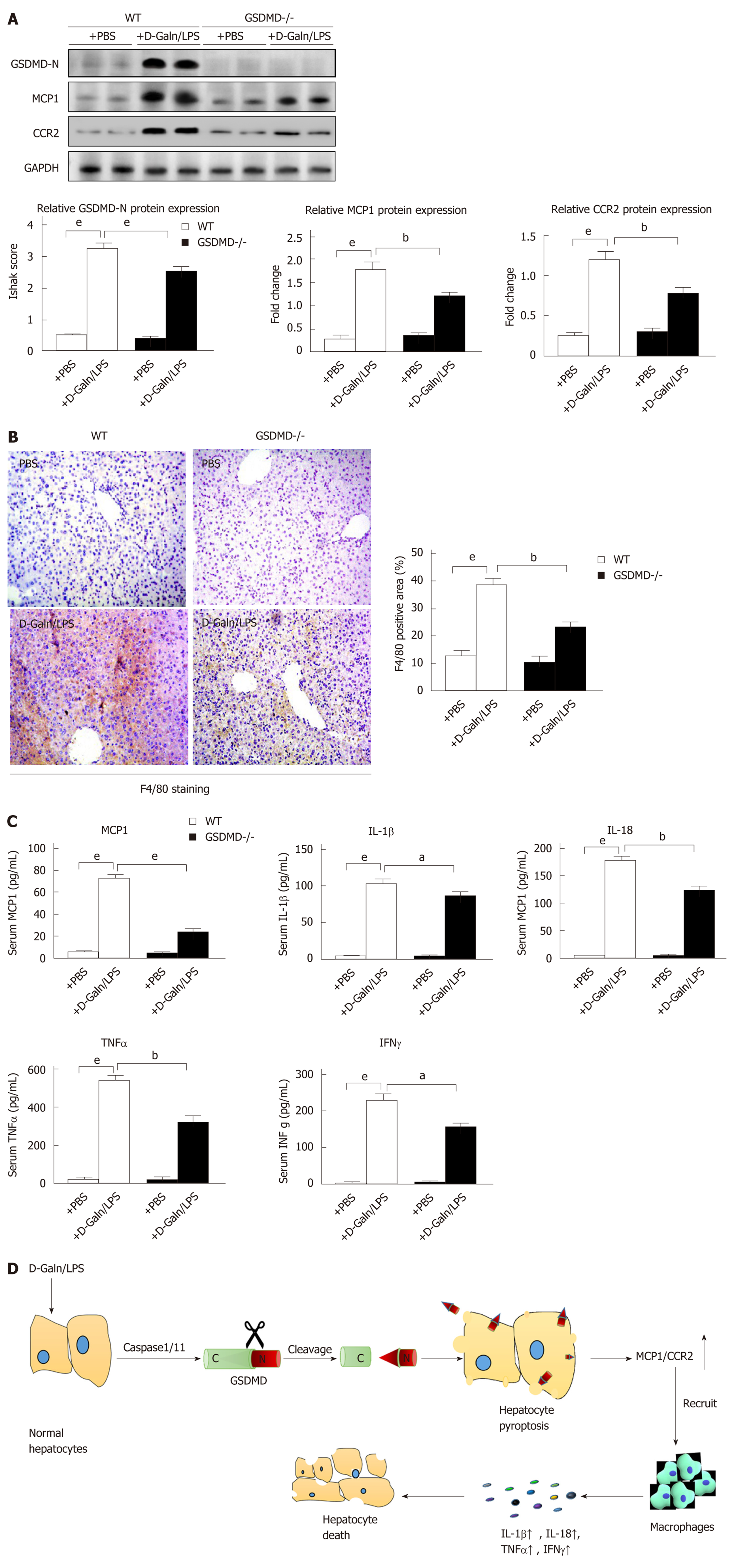
Figure 5 Gasdermin D knockout significantly decreases the expression of monocyte chemotactic protein 1/ CC chemokine receptor-2 and macrophage infiltration in D-galactose/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure mice.
A: Protein expression levels of cleaved N-terminal fragment of gasdermin D, monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP1), and CC chemokine receptor-2 in the liver evaluated by Western blot; B: Immunohistochemical staining for macrophage-specific F4/80 in the liver. Scale bars = 100 µm; C: Detection of serum MCP1, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-18, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interferon-γ by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; D: The diagram showing the mechanism of hepatocyte pyroptosis for expanding the inflammatory responses; Data are presented as the mean ± square error. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, and eP < 0.001. WT: Wild type; GSDMD-/-: GSDMD genetic knockout; D-Galn/LPS: D-galactose/lipopolysaccharide; PBS: Phosphate buffer saline; GSDMD-N: Cleaved N-terminal fragment of GSDMD; MCP1: Monocyte chemotactic protein 1; CCR2: CC chemokine receptor-2; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IL-18: Interleukin-18; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IFNγ: Interferon-γ.
- Citation: Li H, Zhao XK, Cheng YJ, Zhang Q, Wu J, Lu S, Zhang W, Liu Y, Zhou MY, Wang Y, Yang J, Cheng ML. Gasdermin D-mediated hepatocyte pyroptosis expands inflammatory responses that aggravate acute liver failure by upregulating monocyte chemotactic protein 1/CC chemokine receptor-2 to recruit macrophages. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(44): 6527-6540
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i44/6527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i44.6527