Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
Published online Oct 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077
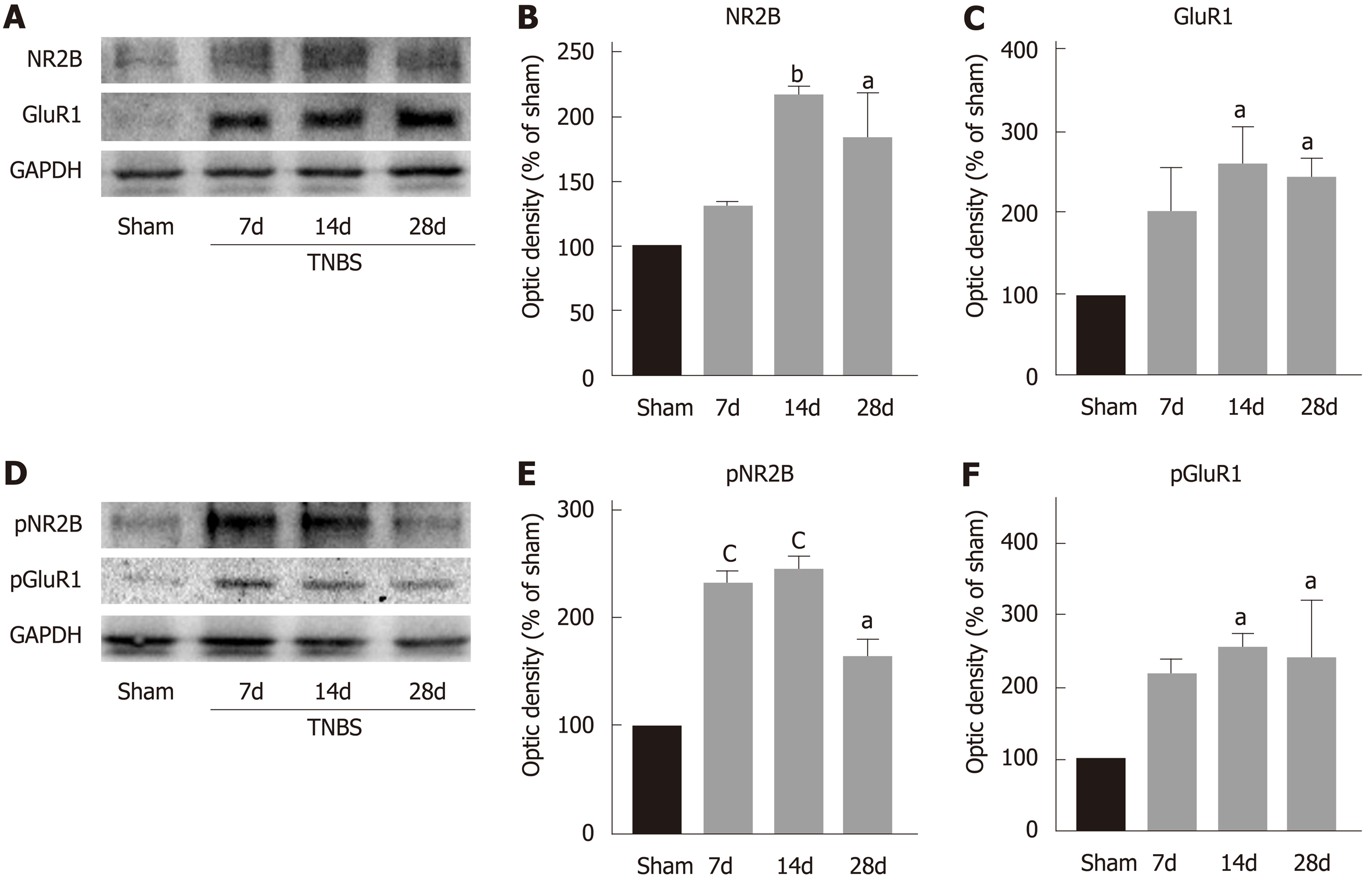
Figure 4 Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid treatment upregulates the expression of N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor subtype 1 within the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius.
A: Representative Western blots for NR2B and GluR1 within the caudal nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) on postoperative days (POD) 7, 14, and 28; B: The amount of NR2B within the caudal NTS was significantly increased on POD 7, 14, and 28 after trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) treatment; C: The amount of GluR1 within the caudal NTS was significantly increased on POD 7, 14, and 28 after TNBS treatment; D: Representative Western blots for pNR2B and pGluR within the caudal NTS after TNBS treatment; E: The amount of pNR2B within the caudal NTS was significantly increased after TNBS treatment; F: The amount of pGluR1 within the caudal NTS was significantly increased after TNBS treatment. n = 3 rats per each group, one-way ANOVA, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, TNBS vs sham. GluR1: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor subtype 1; NR2B: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; TNBS: Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.
- Citation: Bai Y, Chen YB, Qiu XT, Chen YB, Ma LT, Li YQ, Sun HK, Zhang MM, Zhang T, Chen T, Fan BY, Li H, Li YQ. Nucleus tractus solitarius mediates hyperalgesia induced by chronic pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(40): 6077-6093
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i40/6077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6077