Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2019; 25(39): 5961-5972
Published online Oct 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5961
Published online Oct 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5961
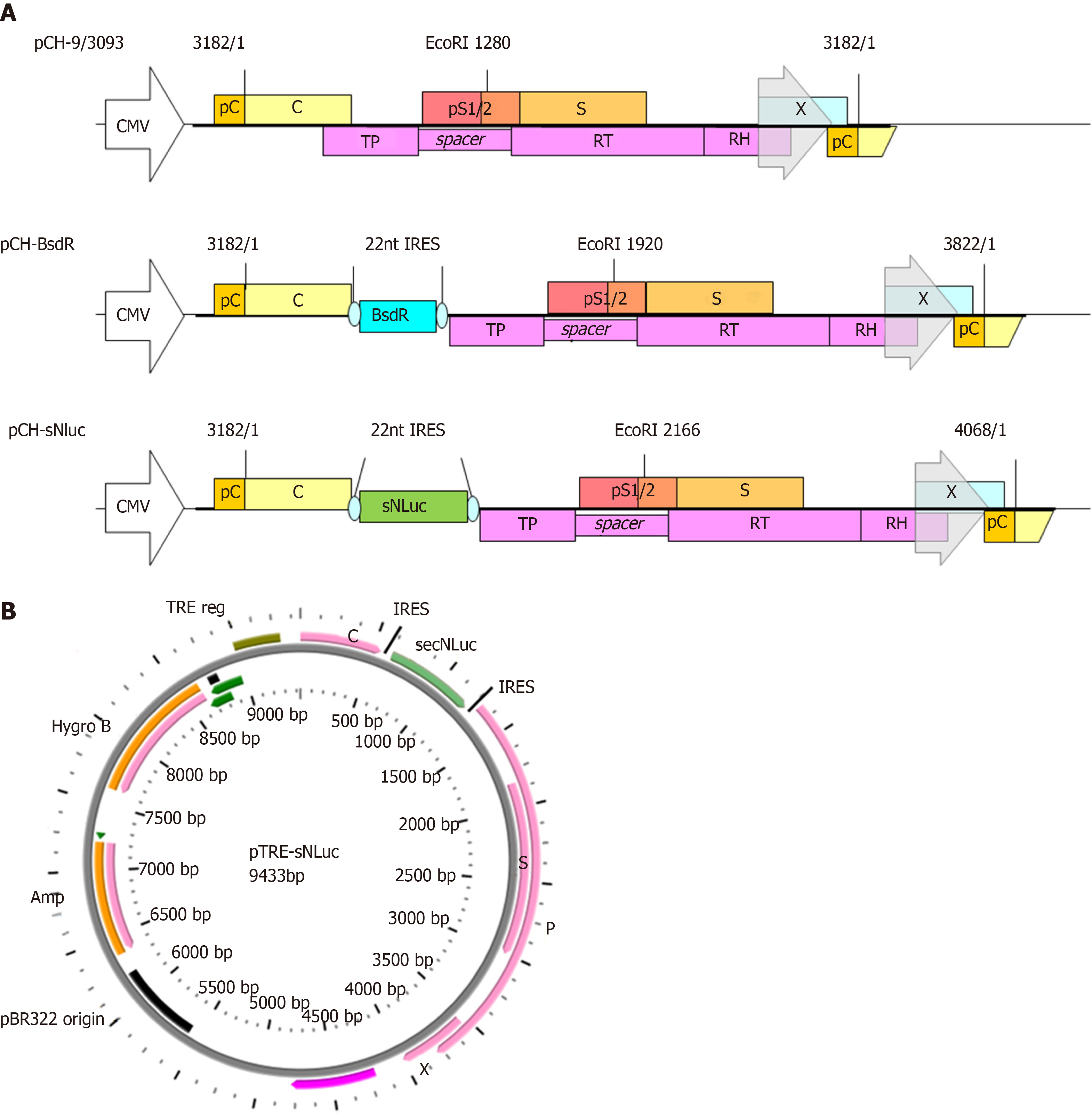
Figure 1 Genomic organization of wild-type hepatitis B virus vector pCH-3093 and replication-competent hepatitis B virus vectors.
A: The parental plasmid pCH-3093 is based on hepatitis B virus (HBV) genotype D, subtype ayw (GenBank accession No. V01460.1), including the 1.056 HBV genome, in which the CMV promoter replaces the primitive HBV core promoter to start pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) transcription. The HBV genome contains four open reading frames (ORFs): PreC/C (encoding precore protein giving rise to the hepatitis B e antigen and core protein), pS1/2 and S (encoding preS1, preS2, and S domains of the envelope proteins, respectively), X (encoding hepatitis B x antigen), and P (encoding viral polymerase, Pol). All regions are widely overlapping, and the P ORF overlaps with all other ORFs. TP, RT, and RH indicate terminal protein, reverse transcriptase, and RNase H domains of Pol (P). Regarding pCH-BsdR, the BsdR gene is inserted among the uncoupled P ORFs from the preC/C ORFs of pCH-3093. Regarding pCH-secNLuc, secNLuc gene was used to replace BsdR gene and inserted into among uncoupled P ORFs from the preC/C ORF of pCH-BsdR; B: Schematic map of pTRE-sNLuc vector. pTRE-sNLuc is based on pTRE-HBV-C7-5 and pTRE-HBVT, in which the Tet responsive promoter replaces the primitive HBV core promoter to control HBV pgRNA transcription. A hygromycin resistance gene serves as a selection marker, and the HBV-sNLuc fragment stems from pCH-secNLuc. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; TRE: Tet responsive promoter; ORFs: Open reading frames; pgRNA: Pregenomic RNA; PreC/C: Encoding precore protein giving rise to the hepatitis B e antigen and core protein; S: Encoding preS1, preS2, and S domains of the envelope proteins, respectively; X: Encoding hepatitis B x antigen; P: Encoding viral polymerase, Pol.
- Citation: Ruan J, Ping CY, Sun S, Cheng X, Han PY, Zhang YG, Sun DX. Construction of a replication-competent hepatitis B virus vector carrying secreted luciferase transgene and establishment of new hepatitis B virus replication and expression cell lines. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(39): 5961-5972
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i39/5961.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5961