Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2019; 25(12): 1465-1477
Published online Mar 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i12.1465
Published online Mar 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i12.1465
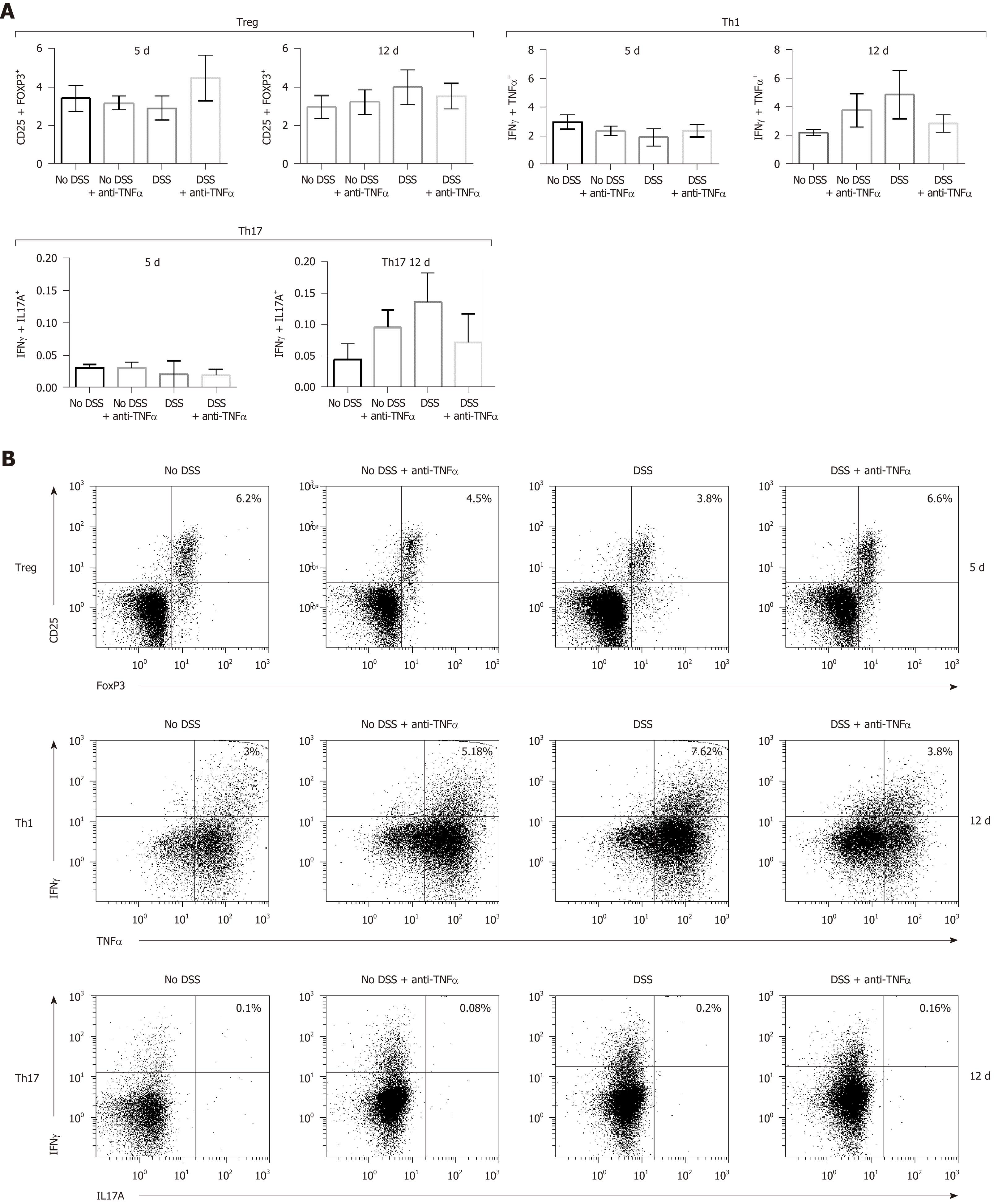
Figure 4 T cells subsets characterization in presence of an anti-tumor necrosis factor α agent.
T cells were isolated from mesenteric lymphnode of mice and CD4+ cells were studied by flow cytometry. In particular, CD4+ regulatory T lymphocytes characterization was possible through the use of anti-CD25 and anti–FoxP3 antibodies (B); type 1 helper T lymphocytes expressed interferon (IFN)γ and tumor necrosis factor α (C); IFNγ+ and interleukin 17+ cells identified the type 17 helper T lymphocytes cluster (D). In each panel (B), (C) and (D) the cells in the upper right quadrant were the double staining cells. Treg: CD4+ regulatory T lymphocytes; Th1: Type 1 helper T lymphocytes; Th17: Type 17 helper T lymphocytes; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; IFNγ: Interferon γ; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Petito V, Graziani C, Lopetuso LR, Fossati M, Battaglia A, Arena V, Scannone D, Quaranta G, Quagliariello A, Del Chierico F, Putignani L, Masucci L, Sanguinetti M, Sgambato A, Gasbarrini A, Scaldaferri F. Anti-tumor necrosis factor α therapy associates to type 17 helper T lymphocytes immunological shift and significant microbial changes in dextran sodium sulphate colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(12): 1465-1477
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i12/1465.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i12.1465