Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2018; 24(18): 1962-1977
Published online May 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.1962
Published online May 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.1962
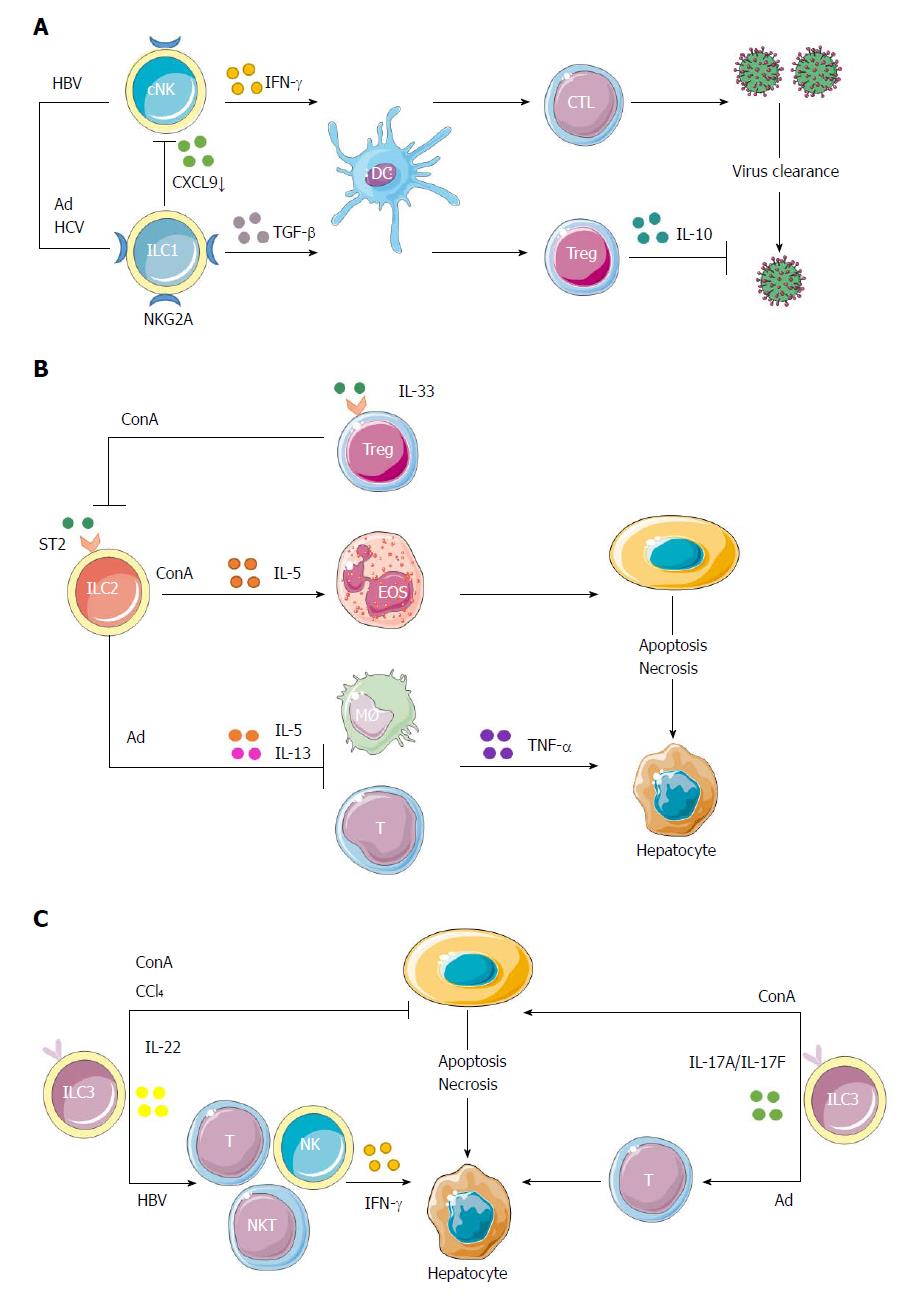
Figure 2 Protective and pathogenic roles of innate lymphoid cells in hepatic inflammation.
A: cNK cells could produce IFN-γ to enhance the priming of CD8+ T cells to clear HBV. The interactions of NK cells with hepatocytes via NKG2A inhibitory receptor could prime DCs to induce CD4+CD25+ Tregs, which would in turn up-regulate the expression of NKG2A on NK cells via IL-10 production, thus impairing the antiviral ability of NK cells. Because of increased expression of NKG2A on ILC1s in hepatic Ad as well as hepatitis C virus infection, ILC1s play a role in maintaining the liver as a tolerogenic site by inhibiting CXCL9 expression, which is required for the accumulation of cNK cells. This would further impair the activation of liver CD103+ DCs, thus interrupting the proliferation of virus-specific CD8+ T cells and the clearance of virus; B: In ConA-induced immune hepatitis, hepatic ILC2s could amplify inflammation through the expression of IL-5 to recruit eosinophils in response to IL-33 released upon liver tissue damage. The inflammatory activity of endogenous ILC2s in immune-mediated hepatitis might be regulated by IL-33-elicited ST2+ Tregs. Besides, in Ad-induced viral hepatitis, a strong expression of ILC2s was induced by IL-33 to exert a protective role through down-regulation of the hepatotoxic cytokine TNF-α in T cells and macrophages. Both the proinflammatory and protective roles of ILC2s in hepatitis are part of IL-33 action; C: In immune hepatitis, ILC3-derived IL-22 has a protective role in ConA- and carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatitis, while IL-17 plays a pathological role in ConA-induced hepatitis. Besides, Notch-mediated IL-22 is an important mediator of the inflammatory response in HBV infection, being responsible for the recruitment of antigen-nonspecific inflammatory cells into the liver and subsequent liver injury. In Ad-induced acute hepatitis, the IL-17A/F signaling is critical for adaptive T response and is responsible for affected lymphocyte infiltration and hepatic inflammation. Ad: Adenovirus; cNK: Conventional natural killer; ConA: Concanavalin A; DC: Dendritic cell; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; IL: Interleukin; ILC: Innate lymphoid cell; NK: Natural killer; Tregs: T regulatory cells.
- Citation: Shen Y, Li J, Wang SQ, Jiang W. Ambiguous roles of innate lymphoid cells in chronic development of liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(18): 1962-1977
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i18/1962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.1962