Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2018; 24(18): 1962-1977
Published online May 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.1962
Published online May 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.1962
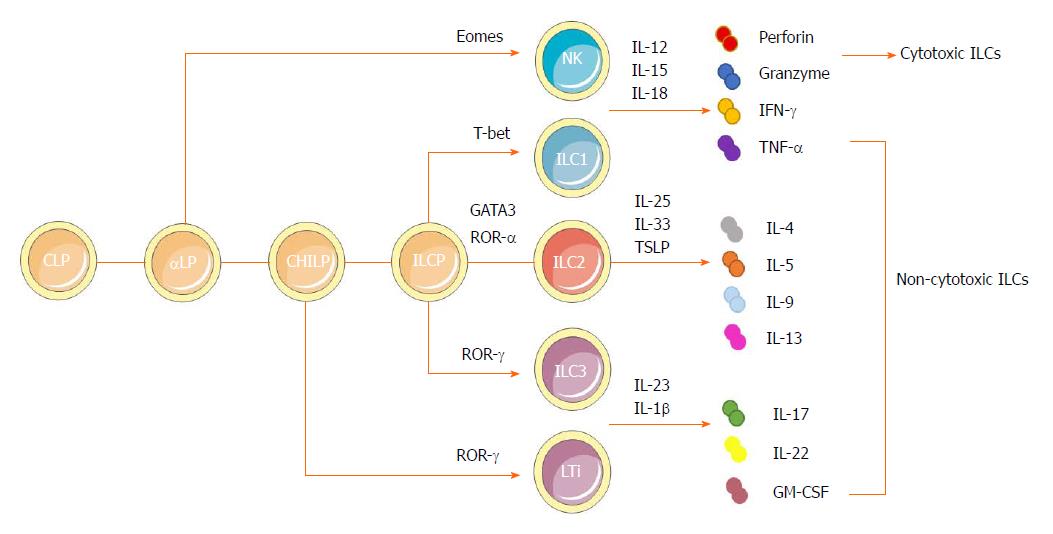
Figure 1 Developmental pathways and classification of innate lymphoid cells.
ILCs are derived from a CLP. With the same phenotype as CLP as well as expressing α4β7 integrin, αLP gives rises to cytotoxic NK cells and differentiates into a CHILP, which gives rise to all noncytotoxic ILCs. The transcription factor PLZF further divides the progeny of CHILPs into a PLZF+ ILCPs that are restricted to ILCs except LTi cells and PLZF-independent LTi cells. Group 1 ILCs comprise both Eomes-dependent NK cells and T-bet-dependent ILC1s. They could produce IFN-γ and TNF-α in response to the stimulation by IL-12, IL-15 and IL-18. NK cells can also secrete granzymes and perforin to exert cytotoxic functions. Dependent on GATA3 and ROR-α as well as respondent to cytokines IL-25, IL-33 and TSLP, group 2 ILCs could produce Th2 effector cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-9 and IL-13 and amphiregulin). Group 3 ILCs encompass both RORγ-dependent LTi cells and ILC3s. They can produce IL-22, IL-17 and GM-CSF, mainly in response to IL-1β and IL-23. αLP: α-lymphoid progenitor; CHILP: Common helper-like innate lymphoid progenitor; CLP: Common lymphoid progenitor; GM-CSF: Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL: Interleukin; ILC: Innate lymphoid cell; ILCP: Innate lymphoid cell precursor; INF: Interferon; LTi: Lymphoid tissue-like; NK: Natural killer; PLZF: Promyeloid leukemia zinc finger; Th: T helper; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TSLP: Thymic stroma lymphopoietin.
- Citation: Shen Y, Li J, Wang SQ, Jiang W. Ambiguous roles of innate lymphoid cells in chronic development of liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(18): 1962-1977
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i18/1962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.1962