Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2018; 24(14): 1507-1520
Published online Apr 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i14.1507
Published online Apr 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i14.1507
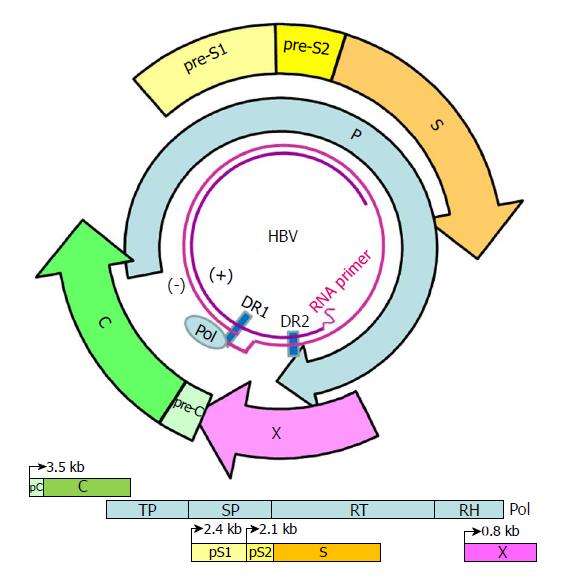
Figure 1 Genome structure and organization of hepatitis B virus.
The relaxed-circular DNA genome of HBV with a complete minus strand and incomplete plus strand is shown (inner circle), along with the four main open reading frames (ORFs): pre-S/S; precore/core (pC/C); Pol, including four domains: TP, SP, reverse transcriptase (RT), and RNase H (RH); and X. The minus (-) and plus (+) DNA strands are marked. The HBV Pol and capped mRNA oligomer at the 5' end of the (-) and (+) strands as well as the DR-1 and DR-2 are illustrated. The space between the DR-1 and DR-2 is the "cohesive overlap region." The (+) strand is typically incomplete.
- Citation: Chen BF. Hepatitis B virus pre-S/S variants in liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(14): 1507-1520
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i14/1507.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i14.1507